Urine 24 hours Urea, Urine Urea Nitrogen/24 Hours
Sample
- The test sample is urine.
- Collected urine for 24 hours.
- The urine sample is stable at 4 to 8 °C for 4 days or preserves with thymol to avoid bacterial action.
- Discard the first urine sample and note the time. Add the last sample of urine to the container.
- 10 grams of boric acid can be used as preservative/24 hours.
Indications
- This test is mainly used to:
- Determine protein metabolism.
- It determines the amount of protein needed by severely ill patients.
- It gives information about kidney function.
- It can monitor kidney disease.
- Patients with confirmed or suspected protein digestion and absorption problems.
- Patients on long-term enteral nutrition or parenteral nutrition.
Pathophysiology
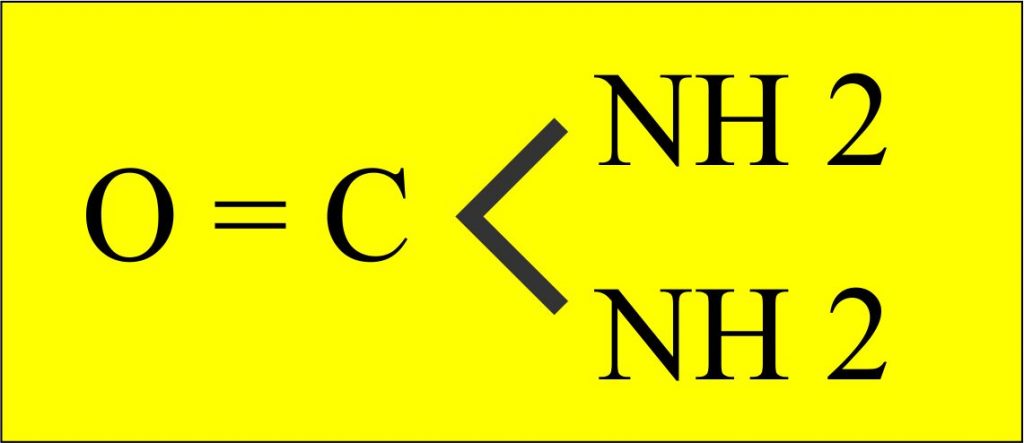
- Urea formula =
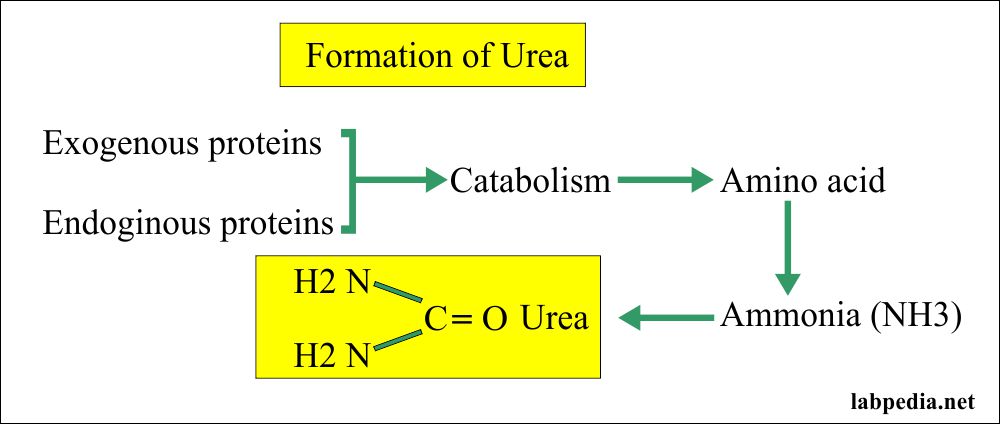
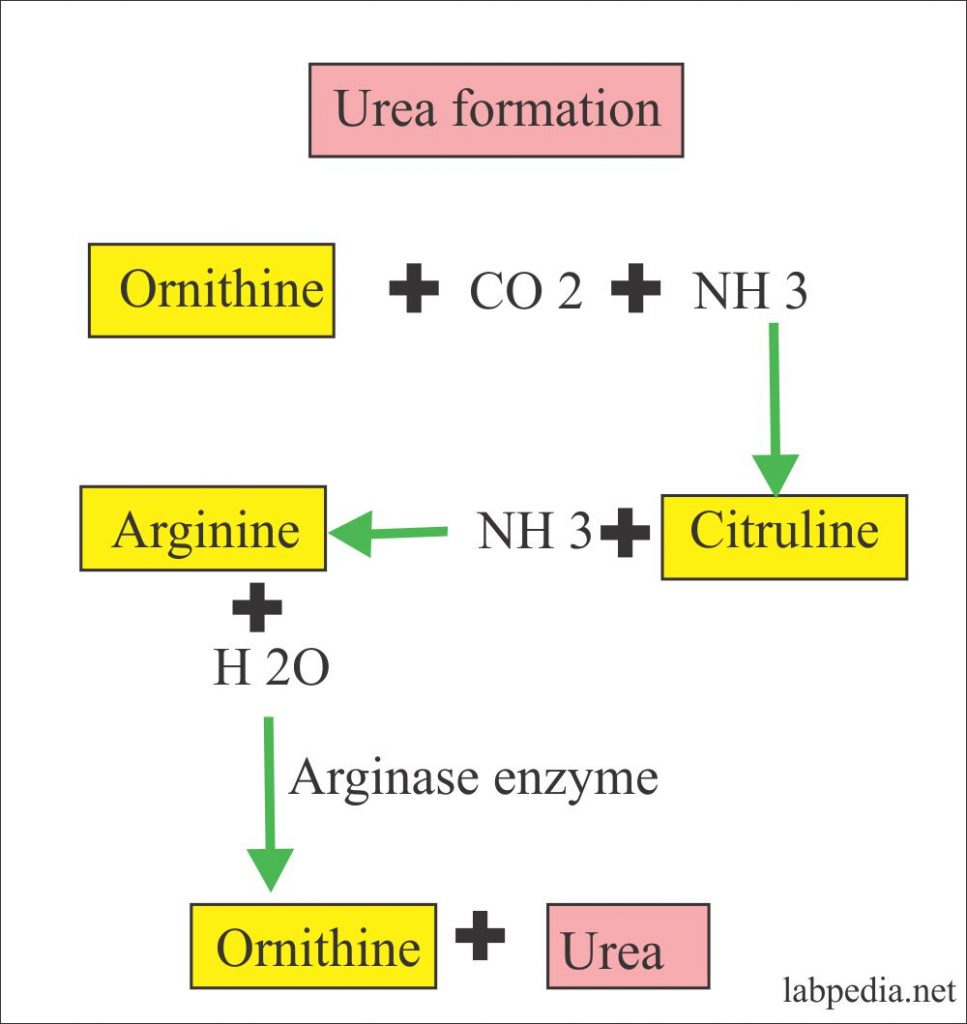
- Urea is the major excretory product of protein metabolism.
- Urea is a low molecular weight substance and is easily excreted by glomeruli and is mostly excreted in the urine.
- The kidneys excrete urea, so the excretion of urea can reflect kidney function.
- It is synthesized in the liver, carried to the kidney, filtered through the glomeruli, mostly into the urine.
- 40% is reabsorbed by passive diffusion.
- The rate of absorption depends upon:
- Urine flow rate.
- The degree of hydration.
- 10 % of urea is excreted through:
- GI tract.
- Skin.
- Blood urea level depends upon:
- Renal function and perfusion.
- The protein content of the diet.
- Amount of protein catabolism.
Normal
Source 1
Urine urea nitrogen
- 12 to 20 g/day (428.4 to 714 mmol/day).
Another source
- 6 to 7 G /24 hours ( 60 to 90 mg/dL )
- Another reference says:
- 7 to 20 g /total volume
- 12 to 24 g /24 hours.
- This also depends upon the protein intake.
The decreased urine urea level is seen in:
- Malnutrition.
- Too little amount of protein in the diet.
- Kidney dysfunction.
- Increased reabsorption.
The increased level is seen in:
- Excessive protein intake.
- Increased protein catabolism.
Normal urine picture:
Physical features Chemical features Microscopic findings - Color = Pale yellow or amber
- Appearance = Clear to slightly hazy
- pH = 4.5 to 8.0
- Specific gravity = 1.015 to 1.025
- Blood = Negative
- Glucose = Negative
- Ketones= Negative
- Protein = Negative
- Bilirubin = Negative
- Urobilinogen = Negative (±)
- Leucocyte esterase = Negative
- Nitrite for bacteria = Negative
- RBCs = Rare or Negative
- WBC = Rare or Negative
- Epithelial cells = Few
- Cast = Negative (Occasional hyaline)
- Crystal = Negative (Depends upon the pH of the urine)
- Bacteria = Negative