Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH), Mean Cell Hemoglobin
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
Sample for Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
- This test is done on blood in EDTA (anticoagulant).
Indication for Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
- It is done as part of blood indices.
- It is done to diagnose anemia. It has limited value in diagnosing anemia.
Precaution for Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
- Keep in mind that the abnormal size of the RBC may affect the value.
- The presence of cold agglutinins gives a false raised value.
- Raised WBC count also affects the value.
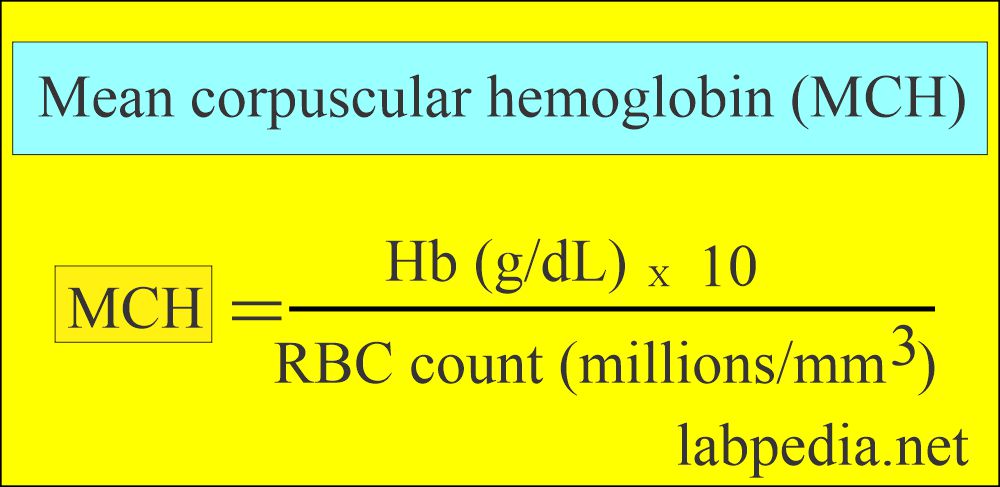
Definition of Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) is obtained by dividing hemoglobin by RBC count.
- It represents the average amount of hemoglobin/RBCs.
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH) Calculation
- This is the mean of the weight of average hemoglobin in one RBC.
- MCH and MCHC values are used to determine the hemoglobin contents in the RBCs.
- MCH adds very little value to other blood indices.
NORMAL
Source 1
| Age | pg/cell | |
| Fetal blood | ||
| 18 to 20 weeks | 43.14 ± 2.7 | |
| 21 to 22 weeks | 41.39 ± 3.32 | |
| 23 to 25 weeks | 40.48 ± 2.88 | |
| 26 to 30 weeks | 37.04 ± 3.67 | |
| Infants and Child | ||
| Cord blood | 31 to 37 | |
| 0.5 month | 30 to 37 | |
| 0ne month | 29 to 36 | |
| 2 month | 27 to 34 | |
| 4 month | 25 to 32 | |
| 6 month | 24 to 30 | |
| 9 month | 25 to 30 | |
| 12 month | 24 to 30 | |
| 1 to 2 year | 22 to 30 | |
| 3 to 5 year | 25 to 31 | |
| 6 to 8 year | 25 to 31 | |
| 9 to 11 year | 26 to 32 | |
| Male | Female | |
| 12 to 14 year | 26 to 32 | 26 to 32 |
| 15 to 17 year | 27 to 32 | 26 to 34 |
| 18 to 44 year | 27 to 37 | 27 to 34 |
| 45 to 64 year | 27 to 35 | 27 to 34 |
| 65 to 74 year | 27to 34 | 27 to 35 |
Source 2
- Adult = 27 to 31 pg (picogram).
- Newborn = 32 to 34 pg (picogram)
Another source
- 26 to 34 pg
Interference for estimation of Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH):
- Lipemia.
- Cold agglutinins.
- Increased white blood cells (Leucocytosis = >50,000/cmm).
- In vivo hemolysis.
- In case of high concentration of heparin.
- Monoclonal proteins in the blood.
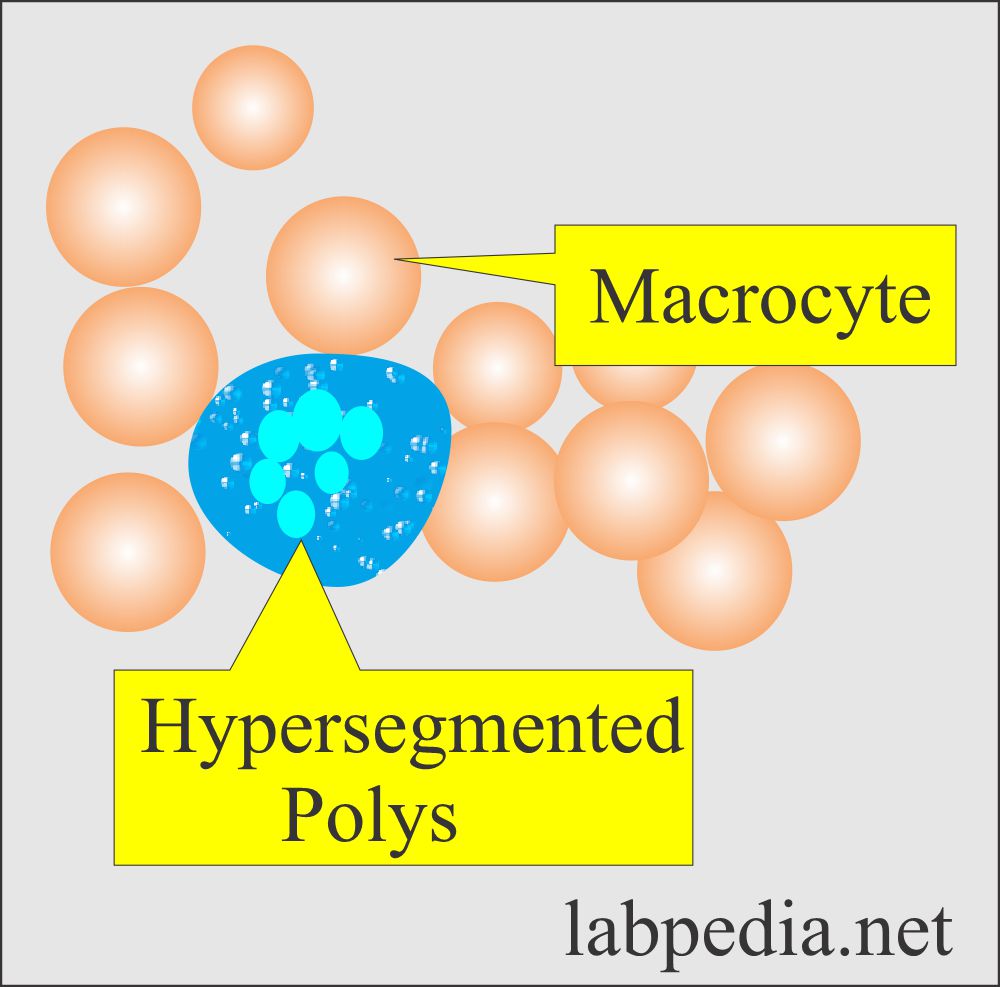
Increased Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) is seen in the following:
- Macrocytic anemia and in newborns.
- Infants and newborns.
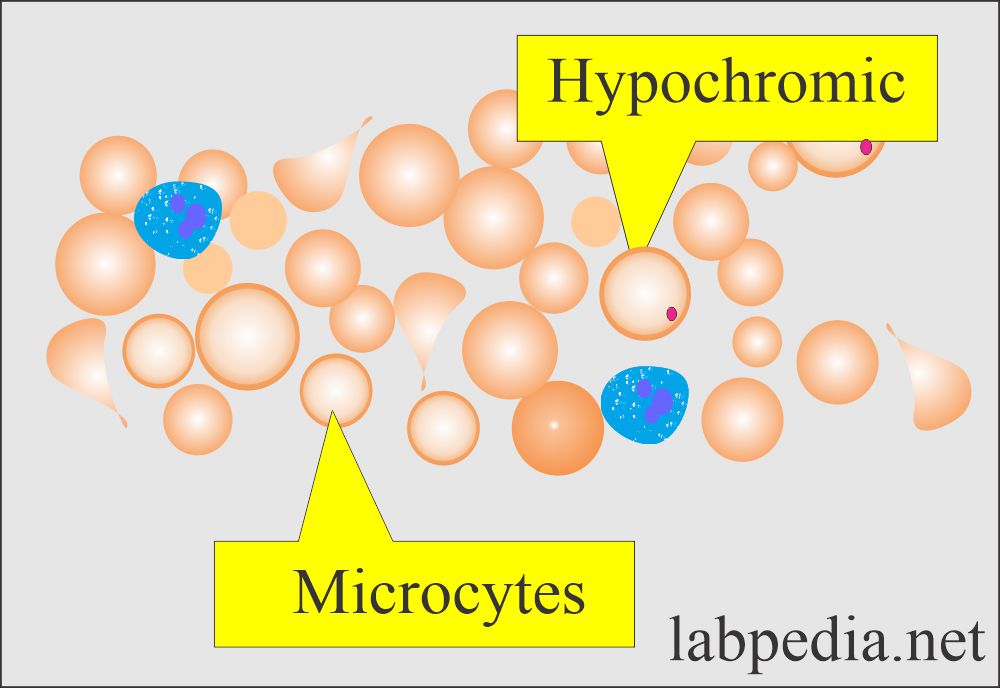
Decreased Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH) is seen in:
- Microcytic anemia.
- Hypochromic anemia.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the value of MHC for the diagnosis of anemia?
Question 2: What is an effect of hemolysis on MCH?