Lipoprotein: – Part 1 – High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL), HDL-Cholesterol (HDL-C), Lipoprotein
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
Sample for High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
- This test is done on the serum.
- A fasting sample is preferred. Advised the patient to fast for 12 to 14 hours.
- This test can be done on plasma as well.
- Can store serum or plasma at 4 °C for 4 days (can keep for 5 to 7 days).
Precautions for High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
- Don’t use oxalate, fluoride, citrate, or heparin to collect blood.
- HDL values are age and sex-related.
- HDL value is increased in Hypothyroidism and decreased in Hyperthyroidism.
- Drugs that increase the value are oral contraceptives, aspirin, phenothiazine, steroids, and sulphonamides.
- Smoking and alcohol decrease HDL value.
Purpose of the test (Indications) for High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
- Advised to evaluate coronary artery disease risk.
- This can be advised as part of a lipid profile.
Pathophysiology of Lipoproteins
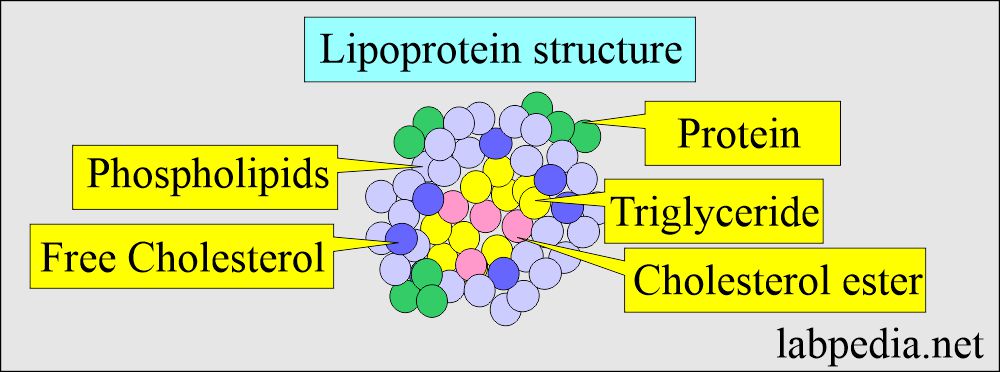
- Lipoproteins are insoluble and are transported in the plasma as a macromolecular complex.
- Lipoproteins are sphericle particles with:
- Nonpolar lipids are triglycerides and free cholesterol.
- Polar lipids are phospholipids and free cholesterol.
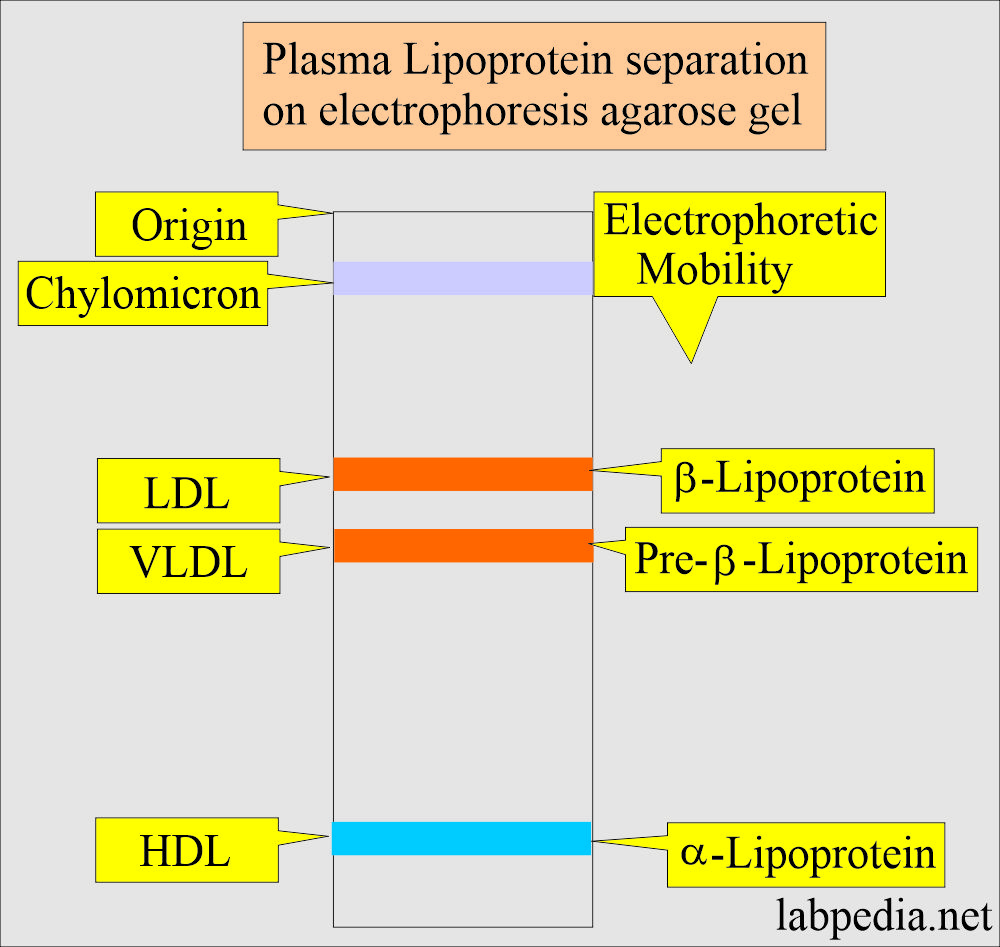
- Lipoprotein is classified by electrophoresis based on its physical and chemical structure as follows:
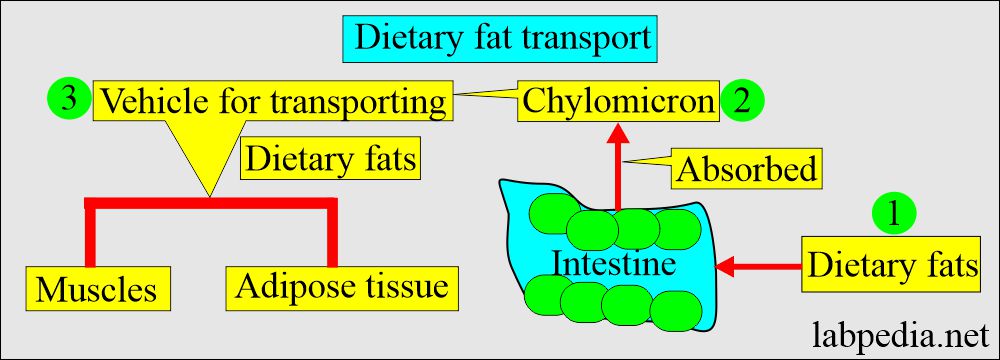
- Chylomicron:
- These are primarily triglycerides.
- These are the vehicles where lipids are absorbed from the intestine and can enter the bloodstream.
- LDL:
- Beta-lipoprotein, are the primary carrier of cholesterol.
- It arises primarily from the degradation of VLDL into LDL1, and it is called intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL).
- LDL-1 is short-lived, and it is converted into LDL-2.
- LDL-2 will remove some of the triglyceride load.
- LDL is a membrane protein.
- There are tissue receptors on the cells, which are engulfed by the cells and degraded by the lysosomal enzymes.
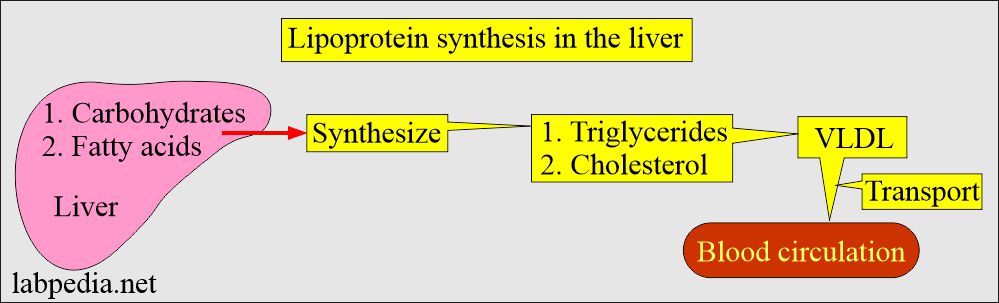
- VLDL:
- It is Pre-beta – lipoproteins, which are mainly triglycerides.
- It originates in the liver and transports triglycerides from the liver to other tissues.
- HDL:
- α–Lipoproteins are mainly proteins with a small amount of cholesterol.
- It arises from the liver and intestine and primarily contains apolipoproteins A-I and A-II.
- It is a cholesterol scavenger and removes cholesterol from the tissues.
- HDL will esterify cholesterol and carries it to the liver for removal.
- HDL converts cholesterol into bile acids and excretion into bile.
- Chylomicron:
- The outer covering lipoproteins are called Apoproteins, and these are classified into:
- Apo-1.
- Apo-II.
- Apo- B.
- Apo-D.
- Apo-E.
| Apolipoproteins | Type of lipoprotein | Molecular mass in Da |
| Apo A-1 |
|
28,000 |
| Apo A-II |
|
17,000 |
| Apo A-IV | It is secreted with chylomicron and transferred to HDL | 46,000 |
| Apo B-100 |
|
550,000 |
| Apo B-48 |
|
260,000 |
| Apo C-I |
|
76,000 |
| Apo C-II |
|
8,916 |
| Apo C-III |
|
8,750 |
| Apo D |
|
19,300 |
| Apo E |
|
34,000 |
- Apolipoproteins are a hydrophilic component of lipoproteins.
- While lipids like cholesterol and triglycerides are hydrophobic and need to be placed in water-soluble micellar structures (Apolipoproteins) to be transported in the plasma.
- In the case of endogenous pathways, the lipoproteins are synthesized in the liver from carbohydrates and fats.
Summary of the lipoproteins:
| Type of lipoprotein | Apoprotein contents | Electrophoresis pattern | The main type of lipids | % of Apoprotein | Origin tissue | Functions |
| Chylomicron |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| LDL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| VLDL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| HDL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
High-density lipoprotein (HDL):
- HDL cholesterol is synthesized and secreted into the liver and intestine.
- This can be separated by electrophoresis and ultracentrifugation.
- HDL is composed of phospholipids and apolipoprotein (Apo A-1 and Apo – A-II), almost 90% of the total protein.
- The ratio of Apo – A-1 to Apo – A-11 is ∼ 3:1 by weight.
- HDL from the intestine does not contain Apo-C or Apo-E and only contains Apo-A.
- The dominant Apoprotein is Apo-A I (67%), and it is followed by A-II, C, and E.
- This may be responsible for the transport of dietary cholesterol.
- HDL plays a role in transporting cholesterol to the liver from the tissue where it is excreted in the bile.
- HDL transports cholesterol to the liver, where cholesterol serves as the precursor of the bile acids or part of the VLDL component.
- While lipoproteins transport cholesterol, triglycerides, and other insoluble fats.
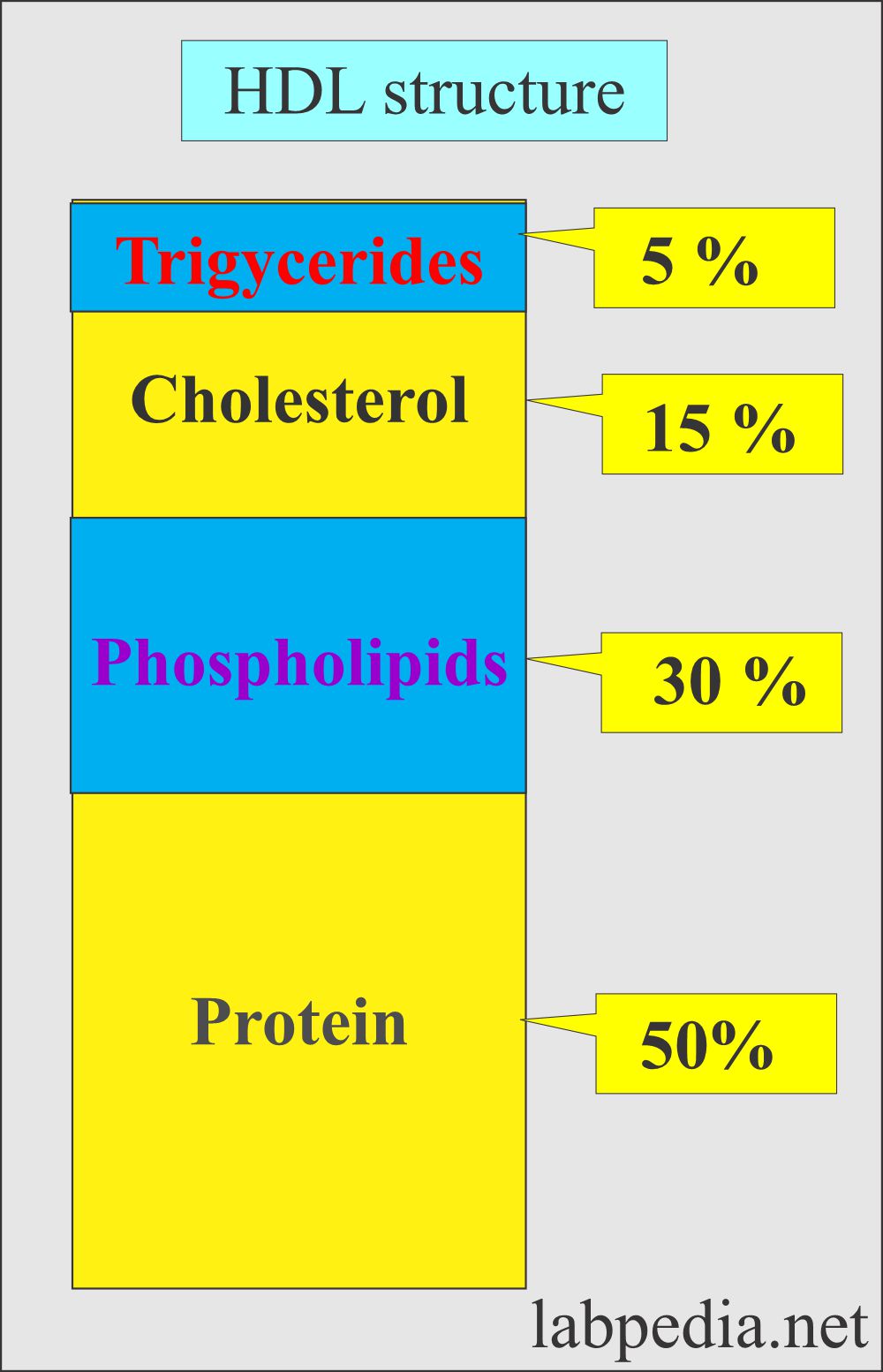
- HDL (Composition) consists of the following:
- Cholesterol = 6%.
- Cholesterol ester = 13%.
- Triglycerides = 3%.
- Phospholipids = 28%.
- Protein = 50%.
- HDL has very few triglycerides.
- There is a high percentage of proteins, phospholipids, and cholesterol.
- Another source says:
- Triglycerides = 5%
- Cholesterol = 15%
- Phospholipids = 30%
- Proteins = 50%
- The ratio of esterified and free cholesterol is 3:1.
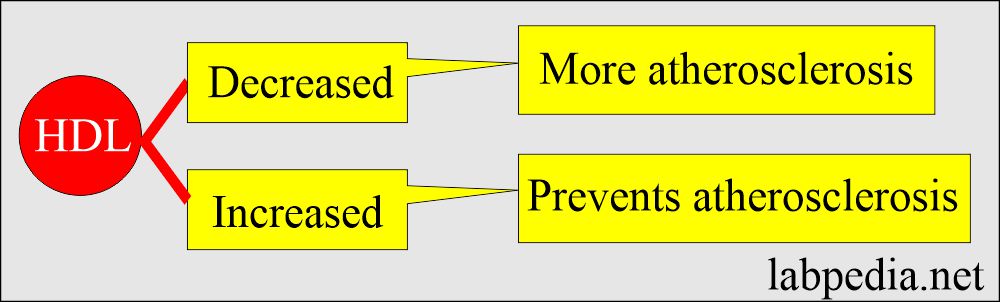
- The decreased level of HDL is atherogenic.
- HDL Raised level protects against atherosclerosis by removing the cholesterol from the arteries and taking it to the liver.
- HDL and LDL may combine to maintain cellular Cholesterol balance through the mechanism of LDL moving cholesterol into the arteries and HDL removing it from the arteries.
- HDL-C is good cholesterol and is proportional to coronary artery disease (CAD) risk.
- The treatment is not indicated when there is a high HDL with a high cholesterol level.
Functions of High-density lipoprotein (HDL) function:
- HDL is the carrier of cholesterol from the peripheral tissue.
- From peripheral tissue, HDL carries cholesterol to the liver for excretion in the bile, known as reverse cholesterol transport.
- HDL has a protective role by preventing cellular uptake of cholesterol and lipids.
- HDL protects against cardiovascular diseases.
Table showing HDL and its relationship with coronary heart disease
| Risk of heart disease | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| Low | 60 mg/dL HDL | 70 mg/dL HDL |
| Moderate | 45 mg/dL HDL | 55 mg/dL HDL |
| High | 25 mg/dL HDL | 35 mg/dL HDL |
The total cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol ratio:
- The ratio is very important to know the risk of coronary heart disease.
- A high ratio is associated with increased risk.
- The normal ratio should be at least 5:1, and the best is 3:1.
Total cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol Ratio Risk for Coronary disease
| Risk | Women | Men |
| Below average | 3.3 | 3.4 |
| Average | 4.4 | 5.0 |
| Above-average x 2 times | 7.0 | 9.6 |
| Above-average x 3 times | 11.0 | 23.4 |
- HDL-cholesterol level of 70 mg/dl or greater is associated with longevity of life.
Normal High-density lipoprotein (HDL):
Source 1
HDL-Cholesterol
| Age | Male mg/dL | Female mg/dL |
| Cord blood | 6 to 53 | 13 to 56 |
| 5 to 9 year | 38 to 75 | 36 to 73 |
| 10 to 14 year | 37 to 74 | 37 to 70 |
| 15 to 19 year | 30 to 63 | 35 to 74 |
| 20 to 24 year | 30 to 63 | 33 to 79 |
| 25 to 29 year | 31 to 63 | 37 to 83 |
| 30 to 34 year | 28 to 63 | 36 to 77 |
| 35 to 39 year | 29 to 62 | 34 to 82 |
| 40 to 44 year | 27 to 67 | 34 to 88 |
| 45 to 49 year | 30 to 64 | 34 to 87 |
| 50 to 54 year | 28 to 63 | 37 to 92 |
| 55 to 59 year | 28 to 71 | 37 to 91 |
| 60 to 64 year | 30 to 74 | 38 to 92 |
| 65 to 69 year | 30 to 75 | 35 to 96 |
| >70 year | 31 to 75 | 33 to 92 |
- To convert into SI unit x 0.0259 = mmol/L
Source 2
HDL
- Male = >50 mg/dL
- Female = >55 mg/dL
Another source
HDL
- Men= 36 to 65 mg/dl or > 45 mg/dl (>0.75 mmol/L).
- Women= 35 to 80 mg/dl or > 55 mg/dl (>0.91 mmol/L).
Abnormal values of HDL:
| HDL value | Risk for coronary disease (CAD) |
| <25 mg/dL | CAD risk is 2 times and is a dangerous level |
| 26 to 35 mg/dL | CAD risk is 1.5 times. This is a high-risk group |
| 36 to 454 mg/dL | CAD risk is 1.2 times. This moderate-risk group |
| 45 to 59 mg/dL | This is an average-risk group |
| >60 mg/dL | Below-average risk group |
| Critical values | |
| Male | <35 mg/dL |
| Female | <40 mg/dL |
Increased High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)-C value is seen in:
- When it is >60 mg/dL.
- Chronic liver diseases like cirrhosis, hepatitis, and alcoholism.
- Long-term vigorous exercises.
- Familial hyper-alpha-lipoproteinemia.
- The increased level may be due to some drugs.
- Estrogen therapy.
- Moderate intake of alcohol.
- Insulin therapy.
- Hypobetalipoproteinemia.
Decreased High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)-C values are seen in:
- When it is <40 mg/dL.
- Poorly controlled diabetes
- Cholestasis.
- Chronic renal failure, uremia, and nephrotic syndrome.
- Hypertriglyceridemia.
- Familial hypo-alpha-lipoproteinemia.
- Alpha and beta – lipoproteinemia.
- The decreased level may also be seen in some of the drugs.
- Steroids.
- Antihypertensive drugs.
- Diuretics.
- Beta-blockers.
- Thiazide.
- The secondary causes are:
- Stress and recent illnesses like AMI, stroke, and surgery.
- Starvation and a nonfasting sample are 5% to 10% lower.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Liver diseases.
- Uremia and nephrosis.
Table showing the summary of characteristics of the lipoproteins:
| Characteristics | Chylomicron | HDL | LDL | VLDL |
| Plasma appearance | Creamy layer, slightly turbid | Clear | Clear or yellow-orange tint | Turbid to opaque |
| Size (diameter nm) | >70.0 | 4 to 10 | 19.6 to 22.7 | 25 to 70 |
| Electrophoretic mobility | Origin | α – region | β – region | Pre – β region |
| Molecular weight | 0.4 to 30 x 109 | 3.6 x 109 | 2.75 x 109 | 5 to 10 x 109 |
| Synthesized in (Tissue of origin) | Intestine | Intestine and liver | Intravascular | Liver and intestine |
| Composition by weight in % | ||||
| Cholesterol esterified | 5 | 38 | 49 | 11 to 14 |
| Cholesterol unesterified | 2 | 10 | 13 | 5 to 8 |
| Triglycerides | 84 | 9 | 11 | 44 to 60 |
| Phospholipids | 7 | 22 | 27 | 20 to 23 |
| Proteins | 2 | 21 | 23 | 4 to 11 |
| Triglycerides | Markedly raised | Normal | Normal/ Raised | Moderately to Markedly raised |
| Clinical significance of | Pancreatitis and acute abdomen | Decreased risk of CAD | Increased risk of CAD | Increased risk of CAD |
| Functions | Transport dietary lipids to tissue | Carry cholesterol from tissue to liver | Carries cholesterol to tissue | Transport endogenous TG from the liver to adipose tissue |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the role of HDL.
Question 2: What is the role of LDL.