Lipids Total, Lipids Role in Our Body
Lipids Total
Sample for Lipids Total
- This is done on the serum of the patient.
- Fasting samples for 8 to 12 hours are needed.
Indications for Lipids Total
- Total lipid is advised to assess lipid metabolism.
- It is helpful for the diagnosis of hyperlipidemia.
Definition of Lipids:
- Lipids are carbon- and hydrogen-containing compounds that are hydrophobic: insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents.
- Biologically groups are:
- Neutral fats (consists of fatty acids, primarily oleic acid, linoleic acid, stearic, arachidonic, and palmitic acid).
- Conjugated lipids.
- Sterols (biologically active cholesterol).
- The lipids are a heterogeneous group of compounds related more by their physical characteristics rather than their chemical properties.
- The lipids have the common properties:
- Relatively insoluble in water.
- Soluble in nonpolar solvents like ether, benzene, and alcohol.
- Lipids are essential dietary constituents due to their importance of:
- Fat-soluble vitamins.
- High energy.
- Essential fatty acids are present in natural foods.
- Lipids include fats, oils, steroids, waxes, and related compounds.
- The major lipids are:
- Cholesterol.
- Triglycerides.
- Phospholipid.
Importance of lipids for our body:
- Lipids serve as an efficient source of energy when stored in adipose tissue.
- Lipids serve as thermal insulators in the subcutaneous tissues and organs.
- Nonpolar lipids act as an electrical insulator allowing the rapid progression of depolarization waves along myelinated nerves.
- The fat contents of the nerve tissue are high.
- The combination of lipids and protein as lipoproteins are important cellular constituents.
- It is part of the cell membranes and mitochondria within the cytoplasm.
- It is means of transporting lipids in the blood.
- Lipids are important to understanding atherosclerosis, obesity, and polyunsaturated fatty acids in nutrients and health.
Properties of lipids:
- Lipid is defined as soluble in the organic solvent (ether, hexane, or chloroform) and insoluble in water.
- These are carbon and hydrogen-containing compounds and are mostly hydrophobic.
- Lipids are insoluble in liquid media like plasma. Therefore these must be packaged into lipoproteins particles.
- Lipids have a hydrophilic exterior with the help of a phospholipids coat.
- The phospholipid layers have various types of apolipoproteins.
- In the central part of lipoproteins are cholesterol and triglycerides.
- Every lipoprotein contains:
- Cholesterol.
- Triglycerides.
- Phospholipids.
- Apolipoproteins
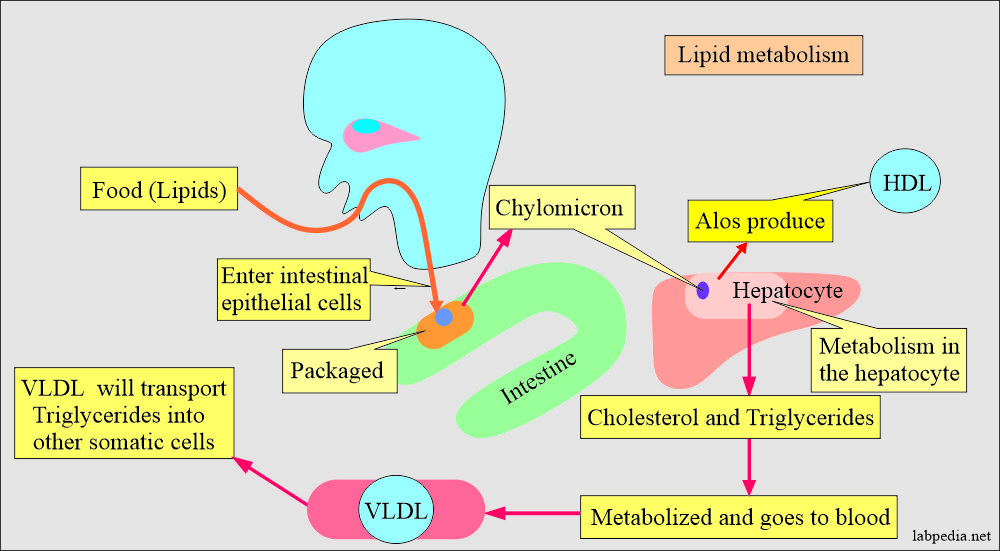
Metabolism of lipids:
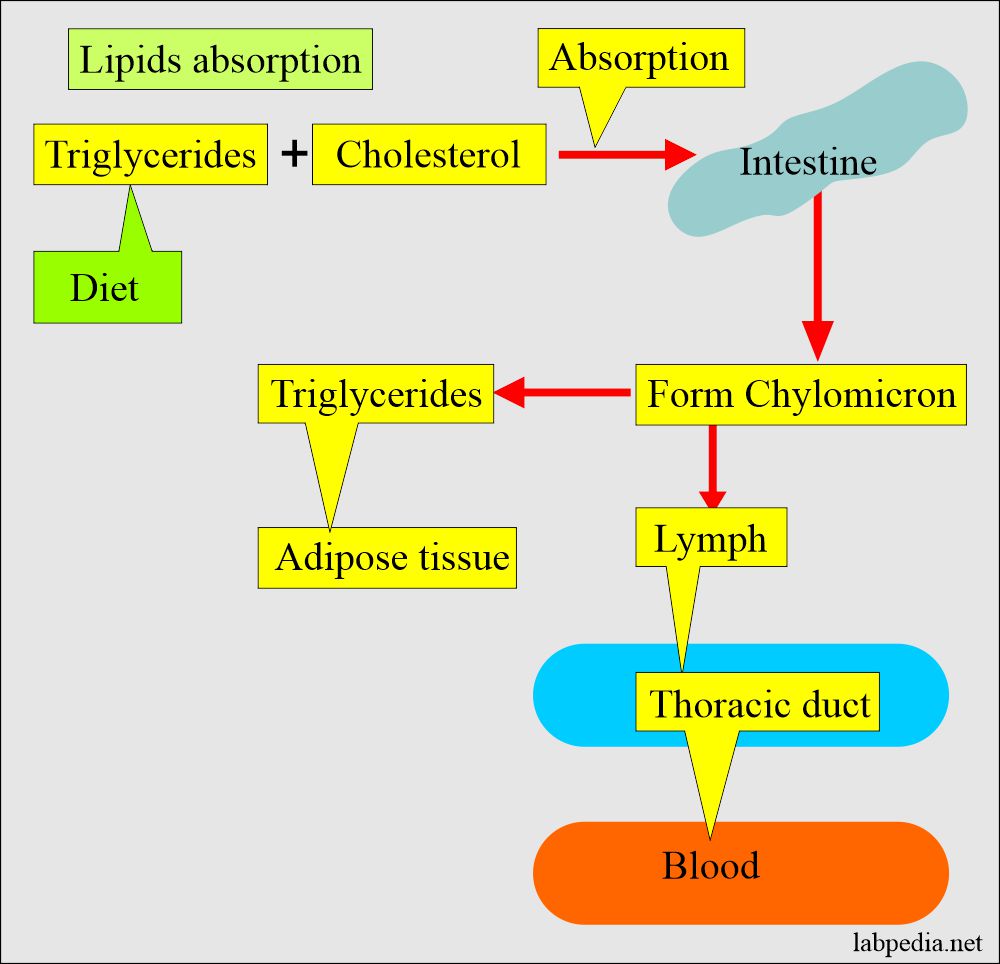
- Lipids are synthesized from dietary fat.
- Ingested lipids are taken up by the intestinal epithelial cells and packaged into lipoproteins called a chylomicron.
- Chylomicron is the lipoprotein that transports lipids from the intestinal epithelium to other somatic cells, particularly liver cells, where these are endocytosed via apolipoprotein E.
- In the liver, cholesterol and triglycerides are packed into another type of lipoprotein called Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), which is secreted into the blood.
- VLDL has increased the amount of Triglycerides (TG). VLDL is the mean for the transport of TG to the other somatic cells.
- Hepatocytes also produce high-density lipoproteins (HDL).
Lipids play an important role in life :
- These are precursors of the hormone
- Help indigestion.
- Provide a store of energy.
- They provide metabolic fuels.
- They are part of the cell membranes.
- Make certain hormones.
- Lipids yield fatty acids on hydrolysis.
- Lipids can form esters.
- Cholesterol and triglycerides are the main lipids measured in routine blood chemistry tests.
Classification of the lipids:
Lipids are a group of substances that consists of :
- Glycerol ester includes:
- Triglycerides.
- Diglycerides.
- Monoglycerides.
- Phosphoglycerides.
- Free fatty acids.
- Phospholipids.
- Sterols include:
- Cholesterol
- Steroid hormone.
- Bile acids.
- Vit.D.
- Carotenoids.
- Vitamins A, E, and K.
Another classification of Lipids is as follows :
- Neutral fat consists of fatty acids (oleic, linoleic, Stearic, Arachidonic, and Palmitic acids) in triglycerides.
- Waxes.
- Phospholipids :
- Lecithin.
- Cephalins.
- Sphingomyelin.
- Glycolipids :
- Cerebrosides.
- Gangliosides.
- Lipoproteins.
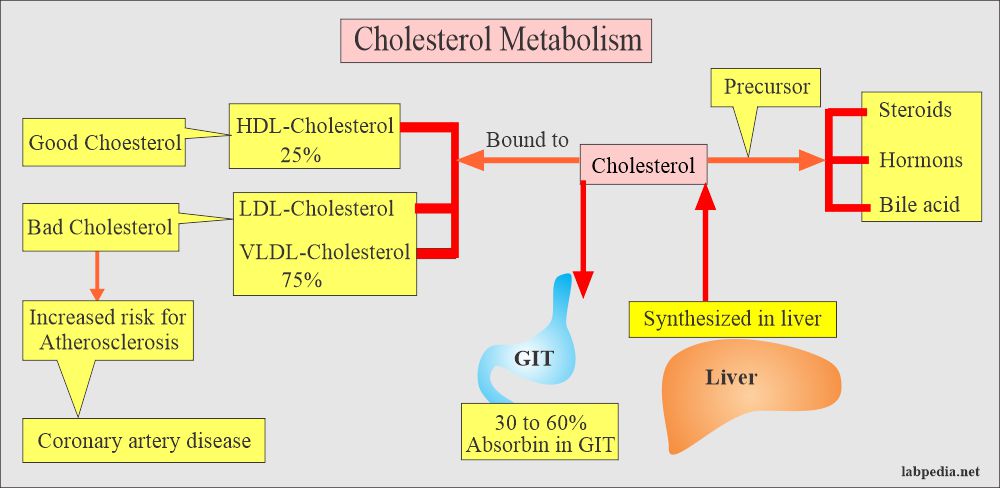
- HDL
- HDL-Cholesterol
- LDL
- LDL-Cholesterol.
- VLDL
- Sterols:
- Cholesterol and esters (major biologic significance).
- Steroids.
- Bile acids.
- Substances associated with lipids:
- Carotenoids.
- Vit. K.
- Vit. E.
- Lipids may be classified as:
- Simple lipids.
- Neutral fats.
- Waxes.
- Complex Lipids.
- Phospholipids.
- Glycolipids:
- Cerebrosides.
- Gangliosides.
- Lipoproteins.
- Simple lipids.
- Lipid-associated substances are :
- Triacylglycerols are the major component of most foods, typically making up more than 95 to 99% of the total lipids.
- Cholesterol and triglycerides are the main lipids measured in routine blood chemistry.
- Conjugated lipids are the combination of phosphate or sugar to lipid molecules.
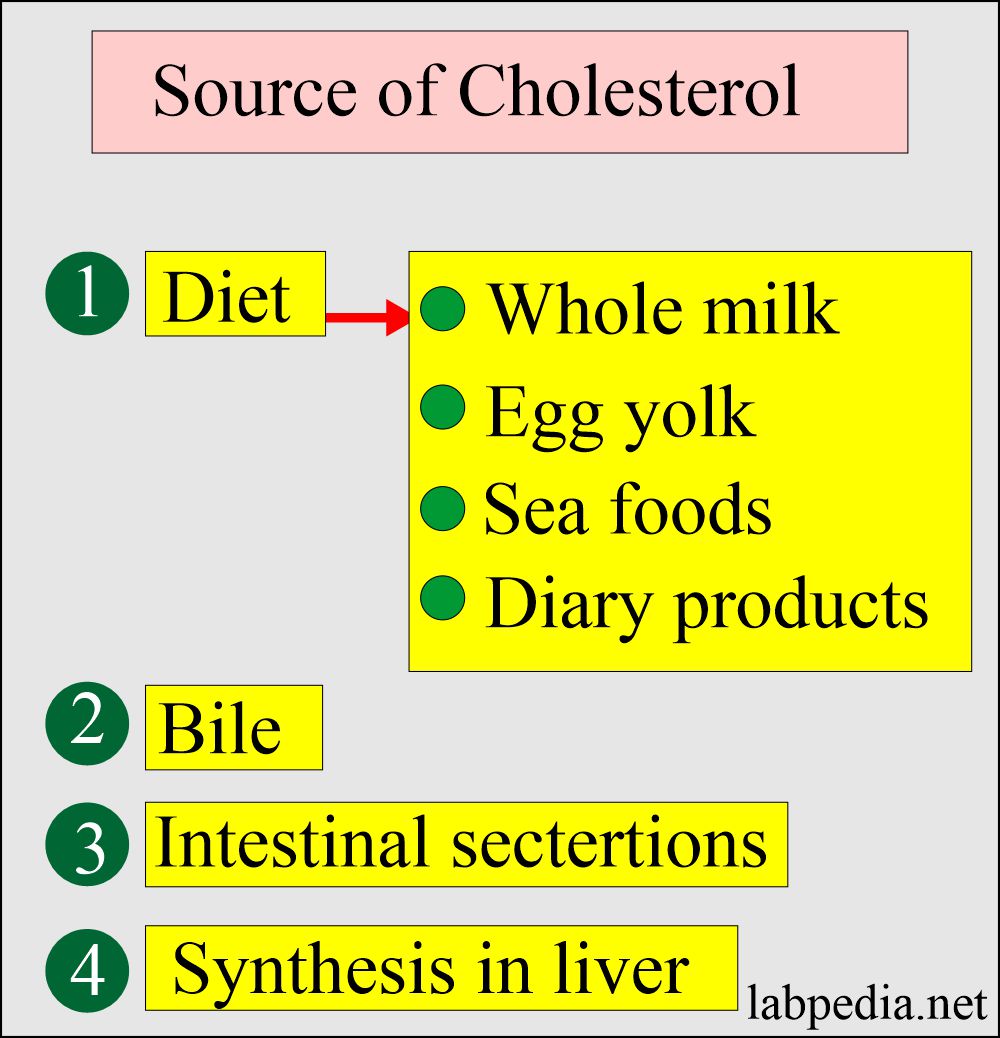
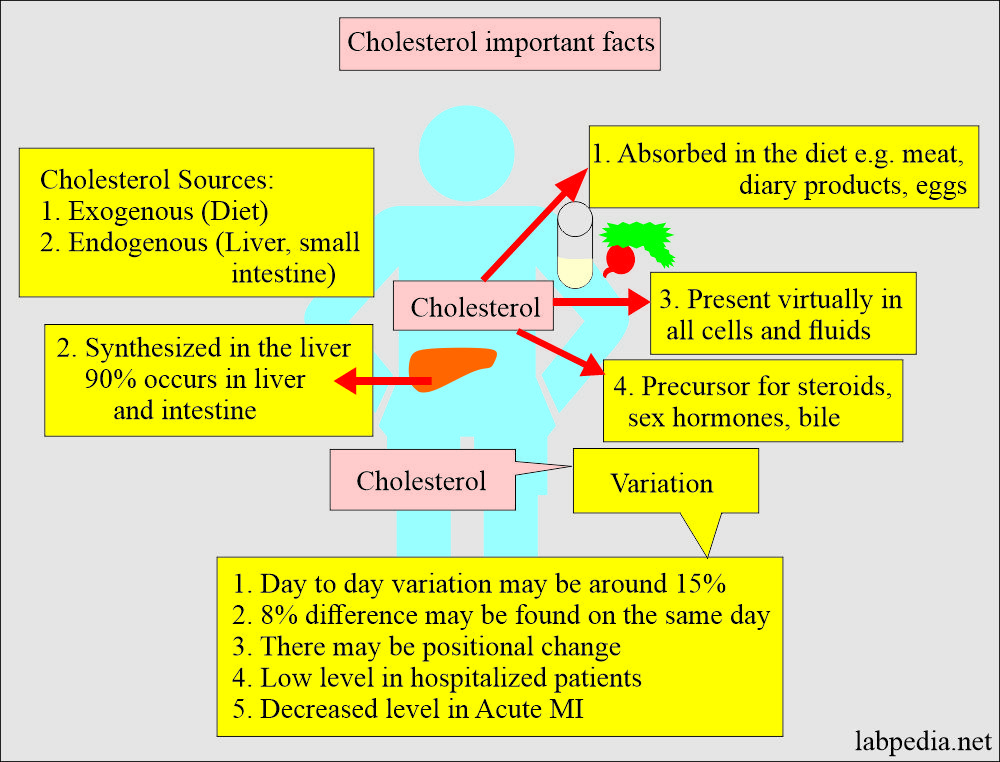
- Cholesterol is the best-known steroid and its an association with atherosclerosis.
- Cholesterol is the precursor of other important steroids like bile acids, adrenocortical hormones, sex hormones, vitamin D, cardiac glycosides, sitosterol of plants, and some alkaloids.
- Cholesterol is distributed in almost all of the body cells. It is abundant in the nervous tissue.
- It is the main component of lipoproteins.
- It is a major part of the cell membranes.
- It is found in animal fats but not plant fats.
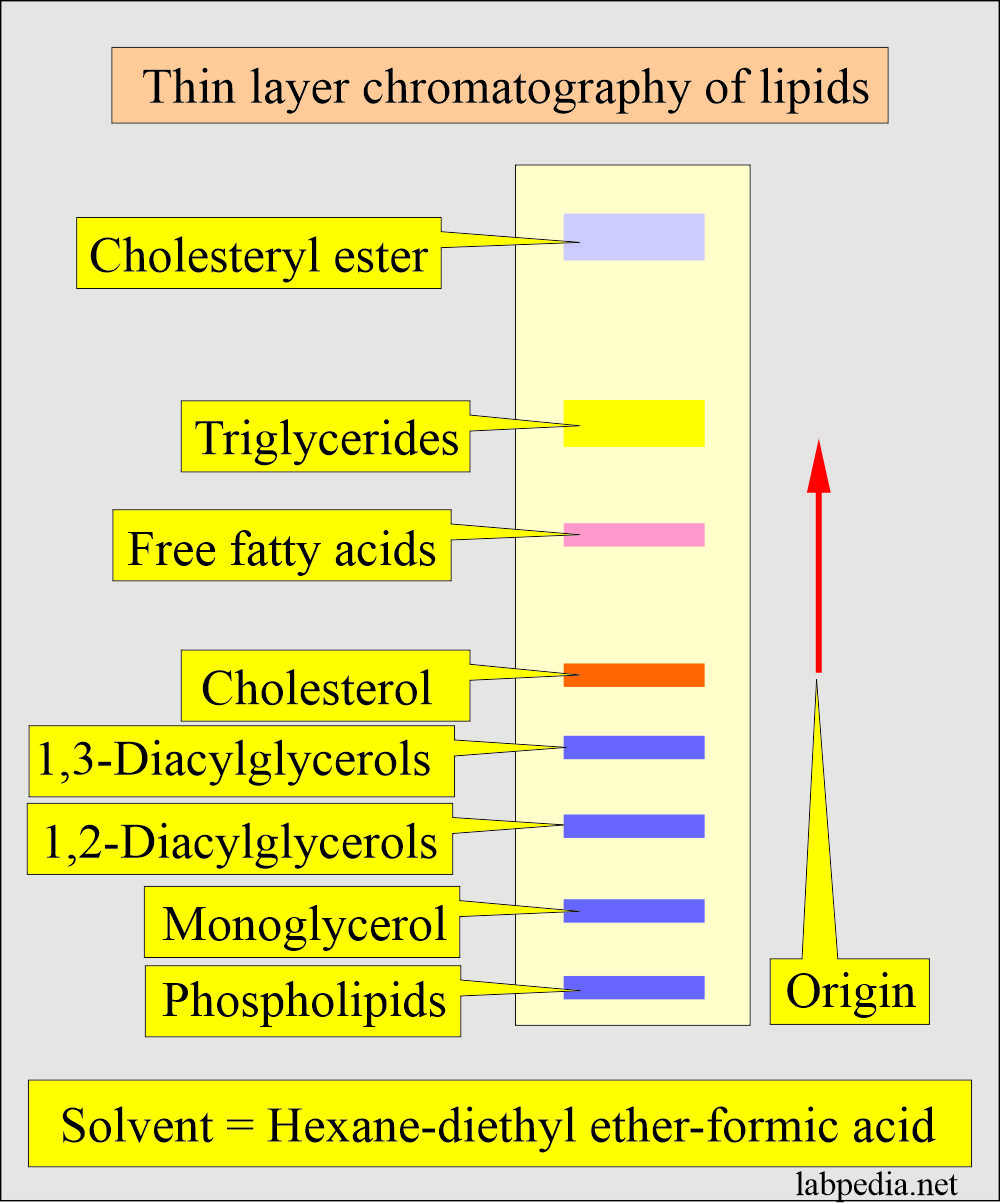
- Lipids on thin-layer chromatography show the following pattern.
Lipids as lipoproteins with their properties:
| Type of lipid | Composition of the lipid | Electrophoretic mobility | Functions | Special features |
| Chylomicron |
|
|
|
|
| Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) |
|
|
|
|
| High-density lipoprotein (HDL) |
|
|
|
|
| Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) |
|
|
|
|
Facts about lipids:
- Lipids are carried in the blood by special proteins made in the liver. The two main forms of protein-bound cholesterol are called LDL and HDL cholesterol.
- As these are water-insoluble, so they are carried by the proteins.
- Free fatty acids are a very small amount of the blood, and these are bound to a loose complex with albumin.
- Major lipid components in the plasma found are triglycerides, Cholesterol, and phospholipids.
- These are transported in the blood as lipoproteins with large molecules of proteins as apolipoproteins.
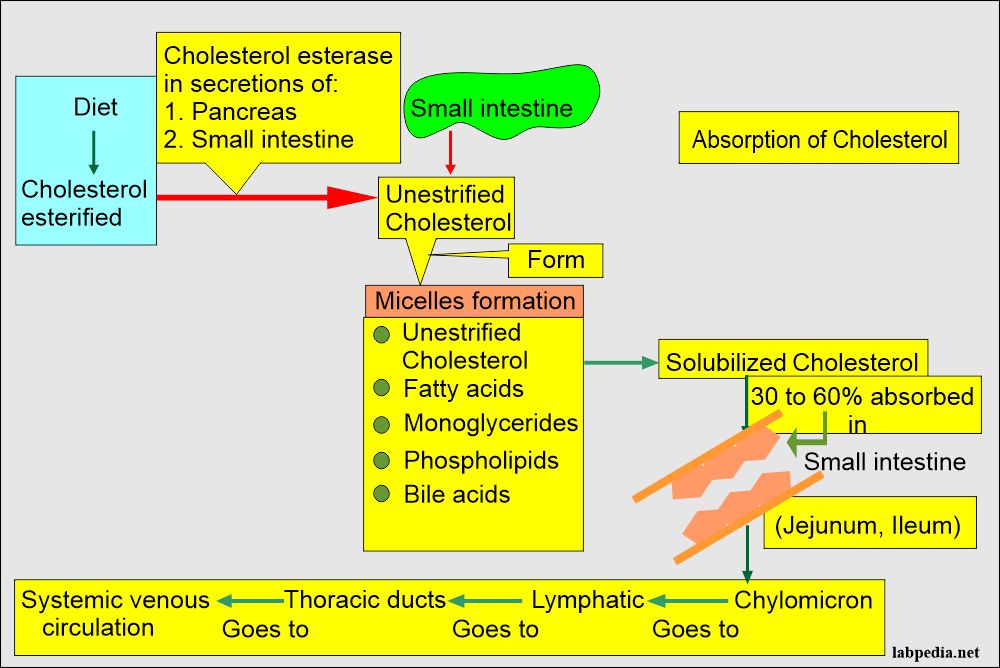
- The largest and least dense molecule of lipoprotein is Chylomicron, and this is followed by:
- Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL).
- Low-density lipoproteins (LDL).
- Intermediate density lipoproteins (IDL).
- High-density lipoproteins (HDL).
- Most of the triglycerides of non-fasting plasma reside in the chylomicrons.
- While fasting plasma sample triglycerides are mostly VLDL.
- Most of the cholesterol is present in LDL.
- A small fraction of the cholesterol, 15 to 25%, is in HDL.
- Triacylglycerols are esters of three fatty acids and a glycerol molecule.
- The terms fat, oil, and lipid are often used interchangeably.
Hyperlipidemia:
- It is the presence of elevated or abnormal levels of lipids and lipoproteins in the blood.
-
- The peak level of raised lipids (Hyperlipemia) occurs 3 to 6 hours after the meal.
- Plasma cholesterol level increases with age.
- In the latter half of the pregnancy, plasma cholesterol is raised by about 30% of the women’s normal level.
- Men’s cholesterol level is higher than women’s.
- Lipids and lipoproteins are highly modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
- One of the most clinically relevant lipid substances is cholesterol, especially in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.
- Hyperlipoproteinemia is elevated levels of lipoproteins.
Functions of lipids
- The main biological function of lipids is to store energy.
- Lipids form structural components of the cell membrane.
- Lipids form messenger and signaling molecules.
- Lipids can easily be stored in the body and work as a source of energy.
Raised level of Lipids is seen in:
- In hypothyroidism, both free and ester-cholesterol are increased.
- In nephrotic syndrome, β-lipoprotein is significantly raised. Total plasma lipids exceed 2 g/dL. The plasma is milky.
- In lipoid nephrosis, the total cholesterol level is 300 to 1000 mg/dL.
- These are raised in Ketosis, generally in untreated Diabetes mellitus. The plasma lipid level ranges from 0.7 to 2.0 g/dL.
- In diabetes mellitus, the level reported reached 22 g/dL.
Now assess the total lipids, mostly Cholesterol, Triglycerides, LDL, and HDL is advised.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is bad cholesterol.
Question 2: What is good cholesterol.