Lipase Serum
Lipase Serum
Sample for lipase
- The venous blood is needed to prepare the serum.
- EDTA or citrated plasma interferes with the result.
- The serum is stable at room temperature for several days.
- Can refrigerate the sample or freeze it.
- A fasting sample is not important.
- Pleural fluid and ascitic fluid can be used for pancreatic diseases.
Precaution for Lipase Serum
- Hemolysis will inhibit lipase activity.
- Certain drugs that increase the level are, Codeine, Indomethacin, Cholinergic, and Morphine.
- Certain drugs decrease the level is calcium ions.
Purpose of the test (Indications) for Lipase Serum:
- Advised to diagnose acute pancreatitis.
- Advised to monitor the treatment of acute pancreatitis.
- It differentiates pancreatitis from other causes of acute abdomen.
Important facts about Lipase Serum:
- Lipase is specific for pancreatitis and is not like amylase.
- The lipase level parallels a raised amylase level but remains elevated for up to 14 days.
- Lipase is considered superior to amylase for the diagnosis of pancreatitis.
Pathophysiology of Lipase serum
- The glomeruli filter the Lipase enzyme and are completely reabsorbed by the proximal tubules.
- Normally lipase is not detected in the urine.
- Lipase structure:
- Lipase is a glycoprotein (Triacylglycerol acyl hydrolase) and has enzymatic activity.
- Its molecular weight is 54000.
- The lipase gene resides on chromosome 10.
- The concentration gradient between the pancreas and serum is ∼20,000 folds.
- The major source of Lipase is the pancreas (100 times greater than the other tissues), and from there, it enters the duodenum.
- Lipase changes fats (triglycerides) to fatty acids and glycerol in the presence of bile salt and cofactor colipase.
- Colipoase cofactor is secreted by the pancreas.
- Lipase appears in the blood due to damage to the pancreas. At the same time, Amylase also appears.
- Lipase lasts longer than Amylase (7 to 10 days).
- There are other sources of the lipase-like enzyme in the kidney, where there will be an increased lipase level in renal failure.
- Intestinal infarction or obstruction may be associated with the raised level of lipase.
- Pancreatitis:
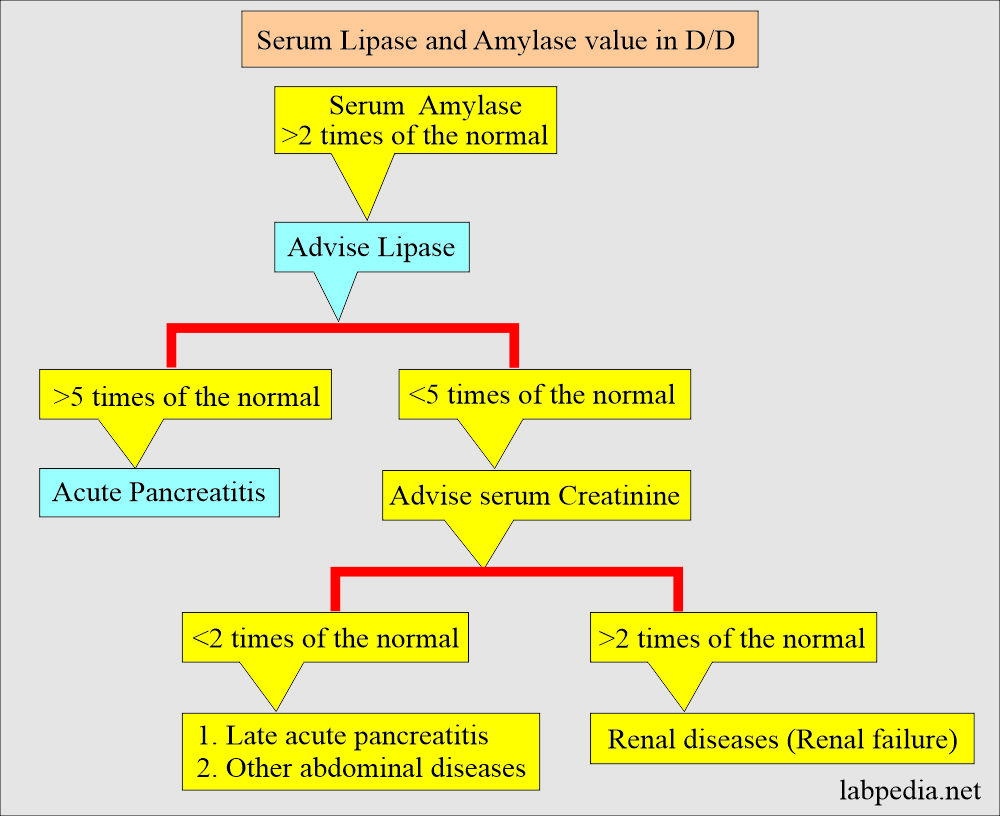
- Lipase is raised in pancreatitis 5 to 10 times the normal value; in non-pancreatic diseases, this value is less.
- In acute pancreatitis, the lipase level is parallel to the amylase level.
- Its raised level is parallel to the amylase level but may remain elevated for up to 14 days (second source).
- The lipase level is better in the late diagnosis of pancreatitis.
- Lipase level is less useful in chronic pancreatic diseases like chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma.
- Lipase and colipase enzymes may be completely absent congenitally and result in steatorrhea.
- Acute pancreatitis produces ascitic fluid and pleural fluid (more on the left side but maybe both pleural cavities).
- There is lipase activity in these fluids.
- 50% develop pseudocyst. This should be suspected when there is no improvement after the treatment within a week of the attack.
- Differential diagnosis of acute pancreatitis from:
- Perforated gastric ulcer.
- Perforated duodenal ulcer.
- Mesenteric vascular obstruction.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Lipase activity is more helpful than amylase in these conditions.
The normal level of Lipase serum
Source 1
- <200 U/L (with triolein)
- <160 U/L (with olive oil)
Another source
- Adult = 10 to 140 U/L.
- Elderly >60 years = 18 to 180 U/L.
- (Values vary from lab to lab. And depends upon the method).
Increased Lipase level is seen in:
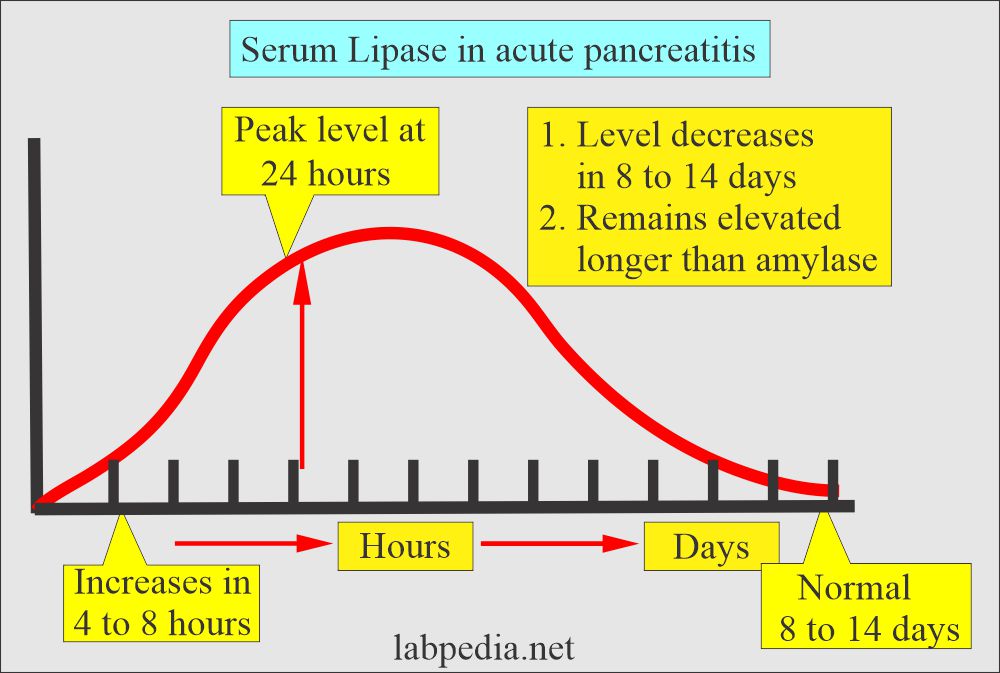
- Markedly increased level seen in Acute pancreatitis after 3 to 6 hours of onset.
- Chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic trauma, pancreatic carcinoma, and pancreatic duct obstruction.
- Intestinal obstruction and infarction.
- Acute cholecystitis due to stones.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis.
- Acute cholangitis.
- Salivary gland inflammation or obstruction.
- Chronic renal failure.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Peritonitis.
- Hemodialysis.
Decreased lipase level is seen in:
Due to the interference in the test by the presence of:
- Hb.
- Quinine.
- Calcium ions.
- Heavy metals.
Normal lipase level is seen in:
- Mumps.
- Values are lower in the neonates.
- Macroamylasemia.
Acute pancreatitis Diagnosis:
- Serum lipase level is more specific for pancreatic tissue injury than amylase.
- Lipase remains elevated for longer than Amylase, so there is greater sensitivity even in the patient who comes late for the consultation.
- The lipase level rises shortly after the Amylase.
- But both enzymes are parallel to each other in values. Lipase increase is greater than amylase.
- Raised level of amylase does not parallel the severity of pancreatitis.
- Lipase rises 4 to 8 hours after the onset of pancreatitis.
- The peak level is at 48 hours.
- Lipase may remain elevated for up to 14 days, while Amylase not.
- Lipase decreases between 8 to 14 days.
- This may increase from 2 to 5o times the normal value.
- Amylase may be elevated in other abdominal pathology and renal insufficiency.
- Hypertriglyceridemia does not interfere with the estimation of Lipase.
- Normal lipase level is seen in 20% of the cases of acute pancreatitis.
- The clinical specificity of lipase level for the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis is 80% to 100%.
- The clinical sensitivity is 80% to 100%.
- D/D of acute pancreatitis from other causes:
- Perforated gastric or duodenal ulcer.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Mesenteric vascular obstruction.
- Biliary tract diseases.
- Obstruction of the pancreatic duct by stone or cancer.
- Patients with renal failure.
- For D/D of acute pancreatitis, the lipase level is >5 times normal.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Why Lipase is better than Amylase?
Question 2: What is the significance of Lipase and Amylase in the renal diseases?