Immunoglobulin M (IgM), Waldenstorm’s Macroglobulinemia
Immunoglobulin M (IgM)
Sample for Immunoglobulin M (IgM)
- Fresh serum of the patient is needed.
- Analyze the sample as soon as possible or can store it at 4 °C for a few hours (less than 72 hours).
- The sample is stable at -20 °C for 6 months.
Indications for Immunoglobulin M (IgM)
- Used to detect monoclonal gammopathy.
- It diagnoses Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia.
- It is advised for immune deficiencies.
- It is advised in acquired IgM immunodeficiencies.
- Earliest immunoglobulin (IgM) in the diagnosis of infectious diseases.
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) facts:
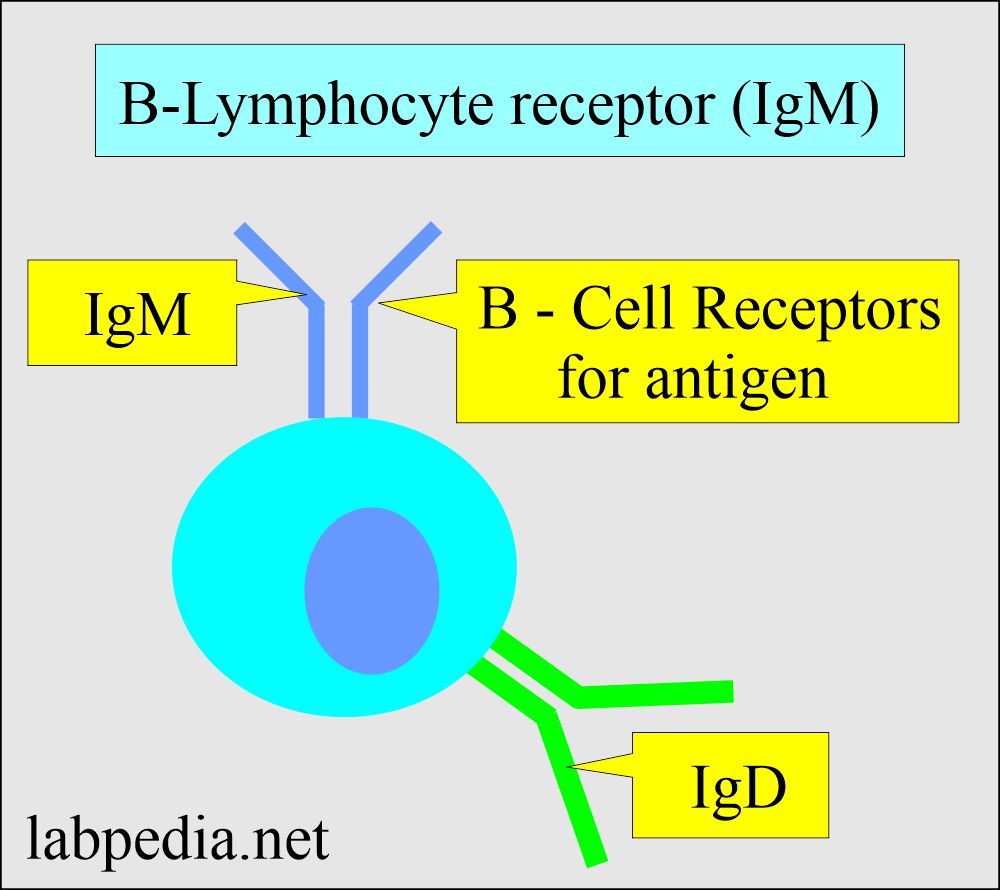
- IgM exists in two forms:
- Monomeric IgM form exists as a B- cell receptor for antigen.
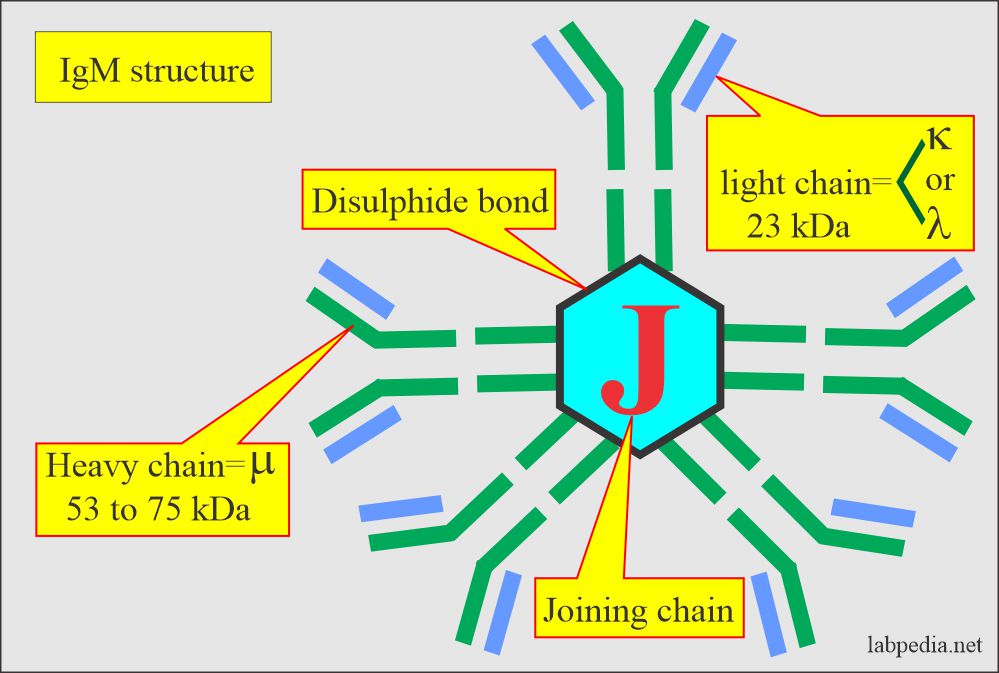
- Pentameric IgM form is present in the blood. It consists of five basic units and is joined by the J-chain.
- It is 10% of the total immunoglobulin with a molecular weight of 900,000 and is 19 S.
- Its concentration is 120 mg/dl.
- Its molecular weight is 900,000 and 19S.
- There are 10 potential sites for antigen binding.
- IgM is the first antibody production in response to antigenic stimulation, called Primary immune response.
- In primary response, there is the stimulation of B-Lymphocytes which form the plasma cells and produce IgM.
- IgM, as a pentamer form, is the most effective stimulator of the complement system for a lytic reaction.
- In fetal life, this is the first immunoglobulin that appears first, and its raised level in neonates indicates intrauterine infection.
- IgM has a half-life of 10 days.
- It is predominantly present in the intravascular spaces.
- It is a poor toxin-neutralizing antibody.
- It can not cross the placental barrier.
- Cold agglutinins are IgM antibodies.
- These are usually directed against the antigen on the RBC membrane.
- These may be 15% to 30% of the Coomb’s positive antibodies.
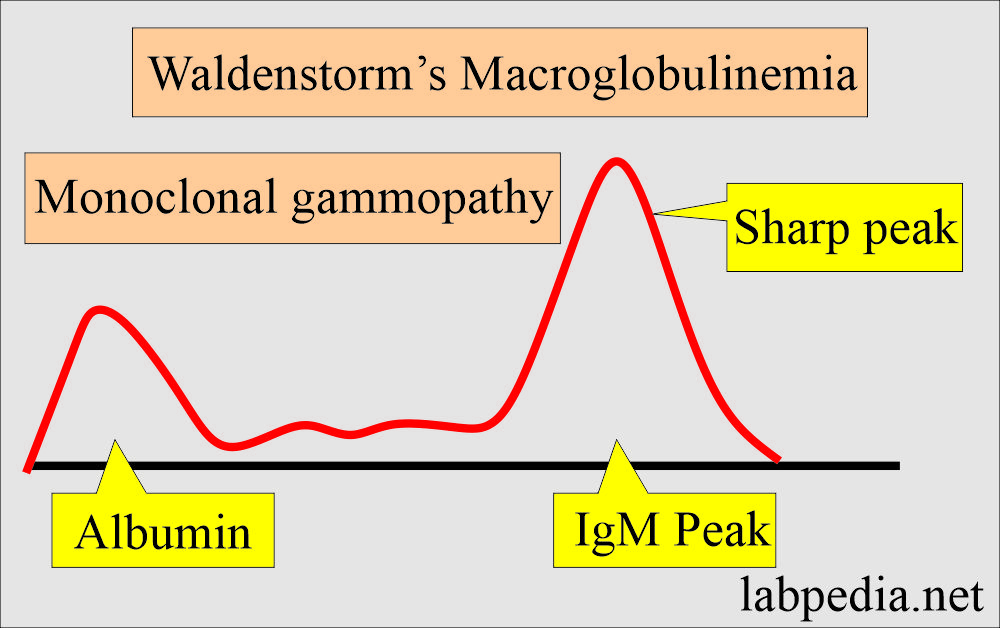
Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia:
Definition of Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia:
- Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia is a hyperviscosity syndrome caused by low-grade small-cell lymphoma and produces abundant monoclonal IgM immunoglobulin.
- These are lymphoproliferative disorders characterized by monoclonal IgM production.
- This IgM molecular weight is 1,000,000 daltons or 19S.
S/S of Waldenstorm’s macroglobulinemia:
- This condition has typical clinical S/S:
- There is hyperglobulinemia with rouleaux formation.
- There is hyperviscosity syndrome. This may lead to the following:
- Neurological abnormalities.
- Shortness of breath.
- There are visual abnormalities and changes in the retina.
- In some patients, it is interpreted as malignant lymphoma.
- Lymphadenopathy.
- Hepatosplenomegaly.
Diagnosis of Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia:
- 10% to 30% of the patients secrete Bence Jones proteins in the urine.
- IgM protein is >3 g/dL.
- Total proteins and globulins are markedly increased.
- There is severe anemia. It is usually normochromic and normocytic.
- There is prominent rouleaux fiormation.
- Differential count:
- White cells show leucopenia with lymphocytosis. But there is no evidence of leukemia.
- There is an increased number of eosinophils and monocytes.
- There is a positive Coomb reaction, so the difficulty in blood cross-matching.
- ESR is markedly raised.
- Lymph node biopsy shows a mixture of mature lymphocytes and plasmacytoid lymphocytes.
- In some cases, the picture is a diffuse type of lymphocytic lymphoma.
- Bone marrow aspirate shows:
- Normal changes or hypercellular marrow.
- In some cases, this aspirate may be hypocellular.
- Nonspecific lymphoid infiltrates, and there are atypical lymphocytes.
- Lymphoma-like infiltrate.
- Radiological studies do not show punched-out osteolytic areas like myeloma.
Normal Level of Immunoglobulin M (IgM)
Source 1
| Age | mg/dL |
| Cord blood | <25 |
| one month | 20 to 80 |
| 2 to 5 month | 25 to 100 |
| 6 to 9 month | 35 to 125 |
| 10 to 12 month | 40 to 150 |
| 1 to 8 year | 45 to 200 |
| 9 to 12 year | 50 to 250 |
| >12 year | 50 to 300 |
- To convert into SI unit x 10 = mg/L
Source 2
- Adult = 55 to 375 mg/dL
- Children = 20 to 200 mg/dL
Another source
- 0 to <5 months = 26 to 122 mg/d
- 15 to <24 months = 46 to 152 mg/dL
- 2 to <4 years = 37 to 184 mg/d
- 10 to <13 years = 41 to 255 mg/dL
- 16 to <18 years = 49 to 201 mg/dL
- More than 18 years = 37 to 286 mg/dL
- Values vary from different methodologies.
Decreased level of Immunoglobulin M (IgM) seen in:
- Decreased levels are seen in congenital deficiency diseases.
- In protein-losing syndrome.
- Non-IgM myeloma.
- Infancy and early childhood.
Increased level of Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is seen in :
- Elevations of IgM may be due to polyclonal immunoglobulin production, which was seen in various infections.
- An isolated increase in IgM level may be seen in viral infections, e.g., Viral hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, and early response to bacterial or parasitic infection.
- Increased levels of IgM may be seen in Rheumatoid arthritis, biliary cirrhosis, and some other chronic disorders.
- Raised levels are also seen in Hyper IgM dysgammaglobulinemia, active sarcoidosis, collagen vascular diseases, and nephrotic syndrome.
- Monoclonal raised levels are seen in :
- Waldenstrom’s globulinemia.
- Lymphomas.
- Chronic infections.
- Liver diseases.
Question 1: What is the diagnosis of Waldenstorm' s macroglobulinemia?
Question 2: What is the role of IgM?