Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
What sample is needed for the Hepatitis A Virus?
- Venous blood is needed to prepare the serum.
- Random sampling can be used.
- The serum can be stored at 4 °C for 5 days.
- Feces can be taken for immuno-electron microscopy.
What are the Indications for Hepatitis A Virus?
- To diagnose viral hepatitis A (HAV) infection.
How will you define Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)?
- Hepatitis A viral infection is also called Infectious hepatitis or short incubation hepatitis.
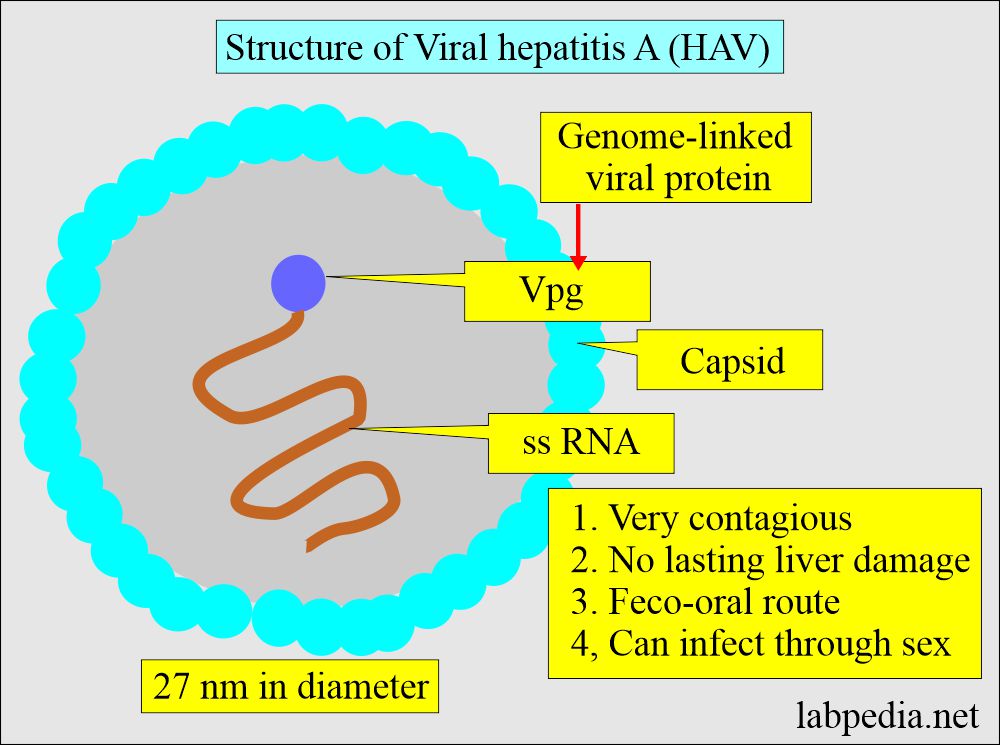
- Hepatitis A is a non-enveloped virus belonging to the hepatotropic virus family and is 27 nm in diameter.
- HAV belongs to the Picornaviridae family.
- It is a picornavirus.
- The genus is a hapatovirus.
- There is no cross-reactivity with HBV or other hepatotropic viruses.
How will you describe the structure of the Hepatitis A Virus?
- It comprises a linear single-stranded RNA virus (ssRNA) genome with 7.5 kb.
- It measures 27 to 32 nm spherical particles with cubic symmetry.
- VPg is a Viral protein genome-linked. It is a protein attached to the positive strand of viral RNA.
- VPg acts as a primer during RNA synthesis.
- HAV is a self-limiting acute liver disease.
What is the incubation period for Hepatitis A virus infection?
- The incubation period is short, 3 to 4 weeks (range is 2 to 6 weeks).
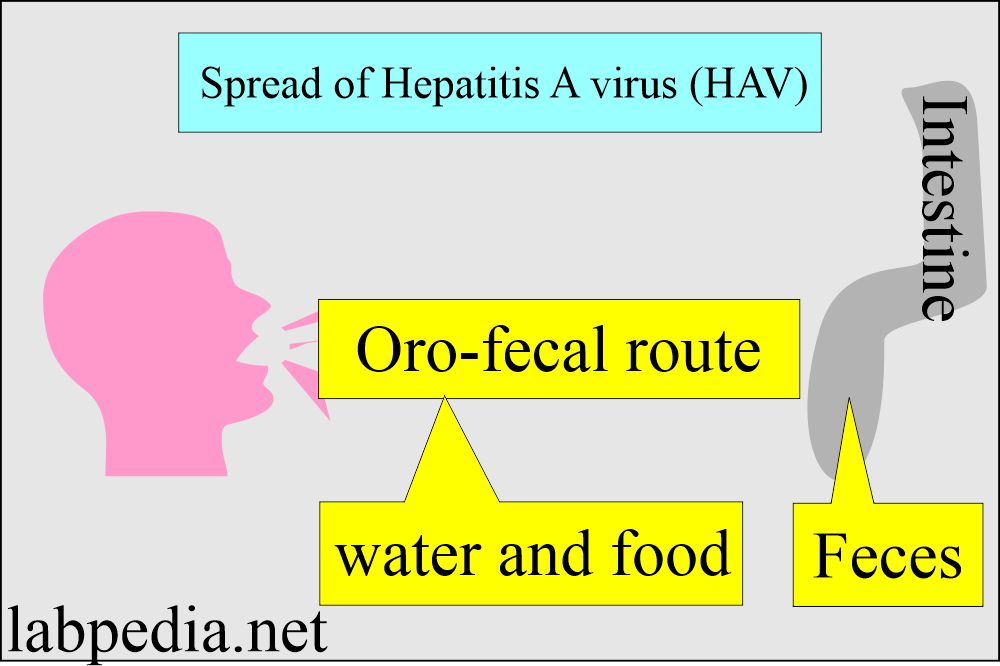
- It is highly infectious during active infection and is excreted in the stool.
- It will spread through contaminated water or food.
- Urine and live viruses are less infective than stool.
- A great number of the virus appears in the stool before the symptoms appear.
- The number of viruses decreases as the symptoms appear.
- Complete recovery in 1 to 3 weeks and no carrier state.
- An occasional patient may have the longer disease for almost one year.
What is the mode of the spread of HAV infection?
- Initially, E/M found it in the stool and liver.
- Saliva and urine are less infective than stool.
- It is a highly contagious viral infection and is most common in children.
- It is common in daycares and orphanages.
- It is also common in mentally retarded children.
- Most children recover from the disease and develop lifelong immunity.
- In the active stage, this virus is excreted in the stool and is very infective. It is in greater amounts in the stool before the patient gets symptoms.
- So, there is an oro-fecal spread because of food and drink contamination.
- Sexual transmission between male homosexuals has been reported.
- Transmission via blood transfusion and I/V drug use is rare.
- It is most common in the third world, almost 90% to 100%.
How will you describe the clinical course of Hepatitis A virus (HAV)?
- Mostly asymptomatic.
- In adults, only 10% are asymptomatic.
- >50% of cases are subclinical, anicteric hepatitis, including almost all infants. 75% of the children are <2 years of age, and 60% are 4 to 6 years.
- The most common age group is children.
- There may be a prodromal period of fever, chills, fatigue, malaise, and headache.
- The above symptoms will be followed by nausea and vomiting.
- There is anorexia.
- Sometimes, there may be abdominal pain, which is usually in the upper quadrant.
- Sometimes, there may be gastroenteritis.
- When jaundice appears, then there is rapid improvement in the clinical symptoms.
- Jaundice may last for a few days to 12 weeks.
- Usually, it is not infective after the appearance of jaundice.
- One report says that 8% to 10% of the cases have a fluctuating course with variations in laboratory tests, which may last as long as 12 to 15 months.
- Like hepatitis C and B viruses, it does not cause chronicity (chronic liver disease).
What is the outcome of Hepatitis A Virus infection?
- There is mild to severe disease.
- Mostly recovered from the HAV infection and gets life-long immunity.
- Very few die of HAV infection with fulminant hepatitis.
How will you Summarize HAV infection?
| Parameters | Characteristic features |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the high-risk groups for the Hepatitis A Virus infection?
- Child-care centers.
- The family members who are in close contact with the patient.
- In the summer camps.
- People are working in correctional centers.
- Homosexual peoples.
How will you describe the immunology of the Hepatitis A Virus?
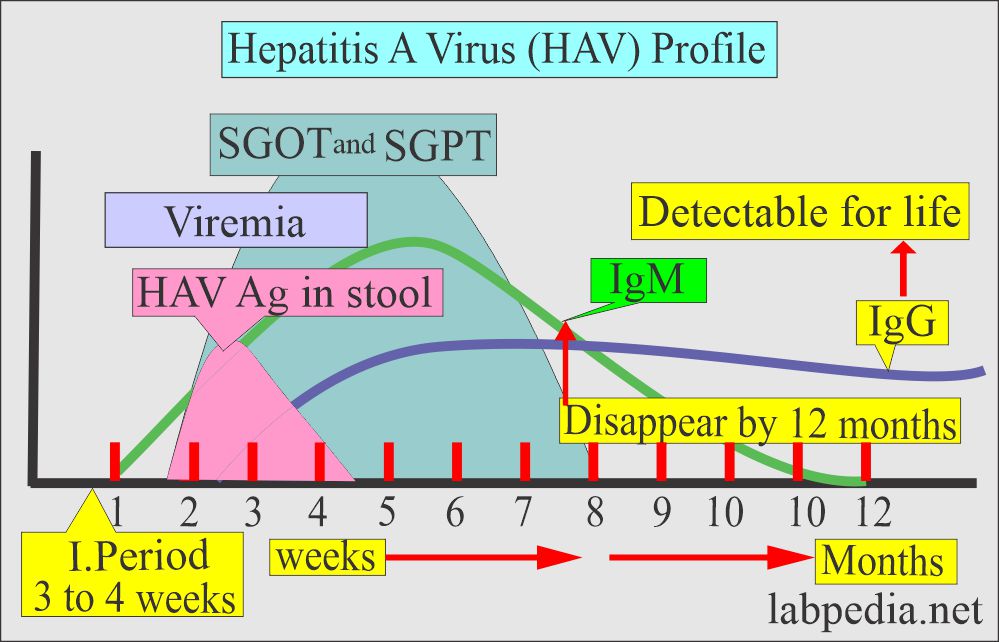
- The first antibody in acute infection is IgM type (HAV-IgM)
- IgM appears 3 to 4 weeks after exposure to the virus or before the liver function tests are raised.
- IgM returns to normal in roughly 8 weeks or disappears in 3 to 4 months. It is not detectable after 12 months.
- HAV-IgG appears after 2 weeks when IgM is increasing.
- IgM is slowly normal, and IgG will appear in the blood.
- HAV-IgG will be detectable in the blood even after 10 years.
- Sometimes, epidemics are confined to adults and are associated with eating contaminated food or shellfish from contaminated water supply.
- In the USA, 40% to 50% of adults tested positive for HAV antibodies.
- This antibody positivity may reach 90% to 100% in the third world.
What are the outcomes of HAV infection?
| Disease stage | IgM | IgG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the outcome of the Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)?
- Chronic disease = Not reported.
- Carrier state = Not reported.
- Infectivity = HAV-RNA
- Recovery = Mostly complete.
How will you diagnose the Hepatitis A Virus?
- SGPT and SGOT have raised the range to hundreds of the normal, which may remain for 1 to 3 weeks.
- Blood shows relative lymphocytosis.
- HAV-IgM
- IgM is macroglobulin, and it indicates acute infection.
- It appears in the blood 3 to 4 weeks after exposure to the HAV virus.
- Or it appears just before the rise in SGPT.
- The peak level reaches one week after the rise begins.
- It appears simultaneously when symptoms appear.
- It becomes normal in about 2 months after the clinical symptoms become normal,
- It is non-detectable for 12 months. In a few cases, it may be detected in 12 to 14 months.
| Clinical presentation | HAV IgM | HAV IgG | Total Hav-antibody | HAV-Antigen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- HAV-IgG
- It appears after 2 weeks of the beginning of IgM increase.
- It is seen in the middle stage of the symptoms.
- It peaks in about 1 to 2 months after it begins to rise.
- Its titer will fall and remain low titer for at least 10 years.
- The rising titer is needed in only IgG-positive cases.
- HAV-IgG positive and HAV-IgM negative:
- It indicate convalescent or chronic stage.
- Anti-HAV- IgG is present throughout life. It is positive in 50% of the USA population, indicating past infection and immune status.
- HAV total antibody indicates present or past infection.
- HAV total antibody also indicates vaccination.
- PCR:
- In the early stage, antibodies are not detectable. Only PCR for RNA can be found in the stool and blood.
- PCR for RNA may be found in the saliva as well.
- PCR is rarely needed.
- HAV antigen:
- The fecal HAV virus is positive 2 weeks before the symptoms appear.
- The HAV virus can be detected in the stool as early as 1 to 2 weeks after exposure.
- This period ends about 1 to 4 days after the appearance of the symptoms.
- At admission in 40% to 64% of the patients, the HAV virus in stool is negative.
- Summary of HAV virus diagnosis:
- For acute infection (current or recent HAV infection) = HAV-IgM.
- Past HAV infection/immunity = HAV-antibody total.
How will you Prevent the Hepatitis A Virus?
- The best way is to give the vaccine to children in epidemic areas.
- Improve:
- Safe water supply.
- A safe food supply is the best hygiene.
- Have good sanitation.
- Washing of hands before taking the food.
How will you treat the Hepatitis A Virus?
- These patients recover without any treatment.
- Mainly, there is a need for supportive treatment.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: How will you diagnose HAV in the acute stage?
Question 2: What is the use of total HAV-antibody?