Fungal infections, Diagnosis and Treatment
Fungal infections
What samples are needed for fungal infections?
- The pathologist can take the sample from the patient’s lesion site.
- The sample can be taken from the following sites.
- SKIN: Scrape the area with a glass slide or knife and get adequate scrapings on the slide. Clean the slide with 70% alcohol.
- Scraping should be done at the edge of the skin lesion. You can use the scalpel blade’s side or the glass slide’s edge.
- HAIRs: Pluck the hairs with tweezer with roots because the fungus is deep-seated and near the hairs’ roots.
- NAILS: Get from the nail undersurface areas and not the outer surface.
- Ulcer scrapings. Avoid superficial samples, and try to get deep scraping, aspirate, or tissue biopsy as the best samples.
- Place the material in the saline-soaked gauze, and don’t use formaline.
- Pus.
- Cerebrospinal fluid. Collect the CSF by a spinal tap in a sterile container.
- Blood. Clean the site to avoid bacterial contamination. Collect the blood in special fungal media.
- Bone marrow.
- Urine. The early morning sample, collected in a sterile container, is the best.
- Stool.
- Bronchial washings.
- Sputum. This sample may be collected by deep sputum, bronchoscopy, or alveolar lavage.
- Prostatic secretion.
- Tissue biopsy.
- Vaginal swabs are an adequate sample, and keep these in saline or transport media.
- SKIN: Scrape the area with a glass slide or knife and get adequate scrapings on the slide. Clean the slide with 70% alcohol.
- Blood sample for the antibody test.
Fungal diseases, their samples, and method to diagnose:
| Disease | Causative agents | Source of the sample | Diagnostic methods |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the Indications for fungal infections?
- To diagnose fungal infections.
How will you define fungi?
- Fungi are a group of eukaryotic microorganisms.
- These fungi may cause superficial, cutaneous, subcutaneous, or systemic diseases.
How will you discuss the Pathology of the Fungi?
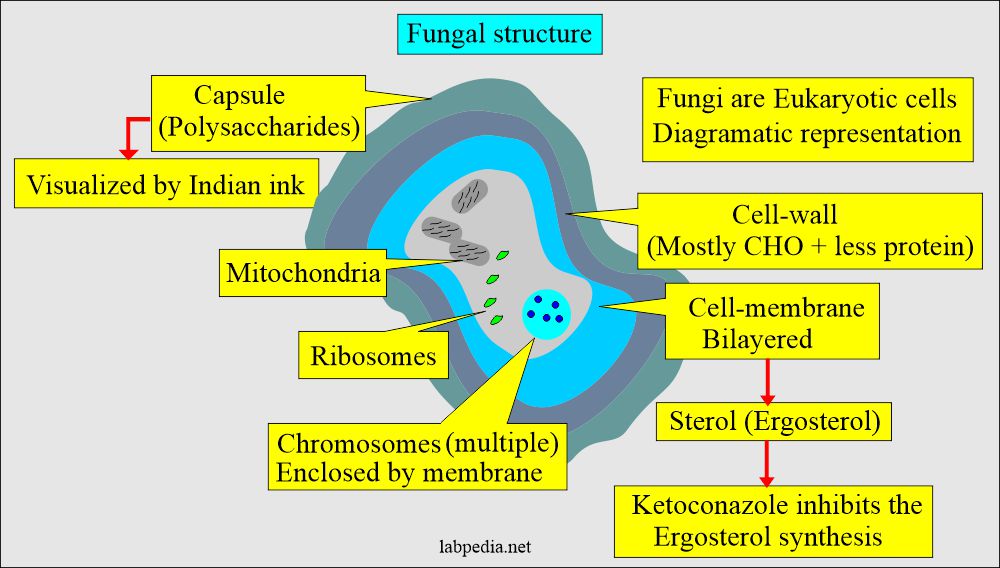
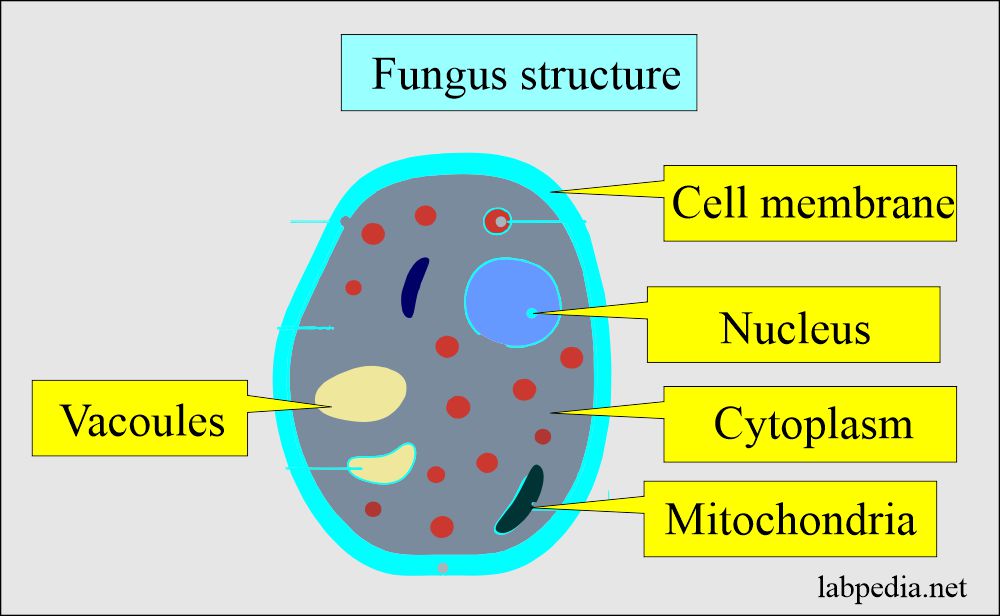
Fungi are eukaryotic cells:
- Fungi are eukaryotic cells lacking chlorophyll, so they can not generate energy through photosynthesis.
- The fungus nucleus contains multiple chromosomes, and the cytoplasm has mitochondria and ribosomes.
- Membranes surround chromosomes.
- It needs an aerobic environment.
- Most fungi are eukaryotic and divided into two main groups:
- Yeast.
- Molds.
How will you discuss the growth pattern of fungi?
- Many fungi grow sexually (meiosis).
- Some fungi grow in filaments (hyphae) and form a mesh called Mycelium.
- Some fungi produce buds; yeast is an exception.
- Few of these are pathogenic.
- Fungi are aerobic and can grow on simple media.
How will you classify Fungi?
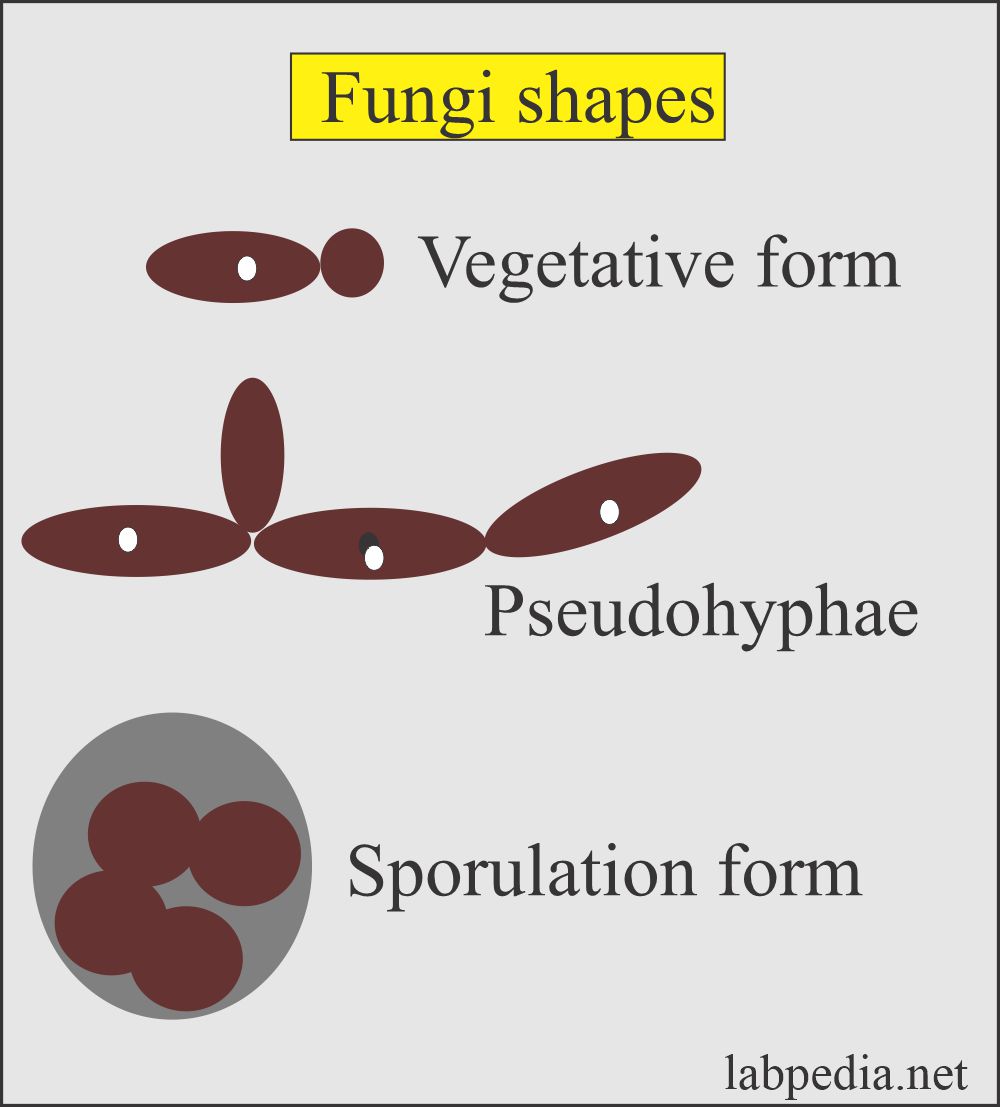
Yeast:
- These are round to oval unicellular fungi which can reproduce by budding.
- These reproduce asexually.
- When budding can not separate, then it may produce pseudohyphae.
- Very few can form true hyphae.
- Yeast reproduces at a slower rate than bacteria.
- Examples are Candida, Cryptococcus, and Candida glabrata.
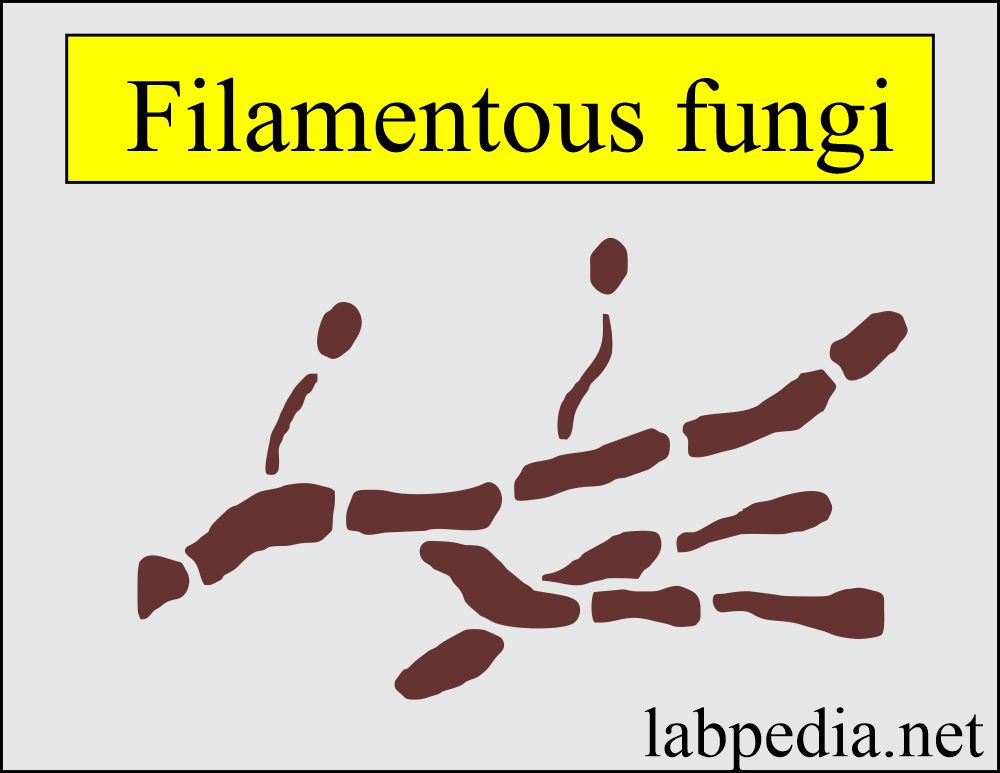
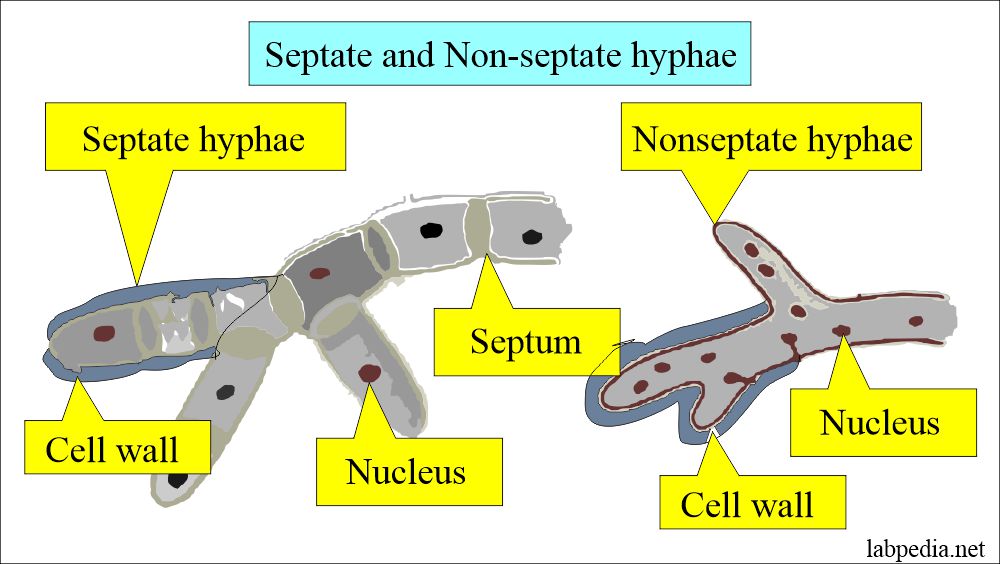
Filamentous fungi:
- These are a group of fungi that cause the infection of skin, nails, and hair.
- These fungi do not involve living tissue.
- These are Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermphyton.
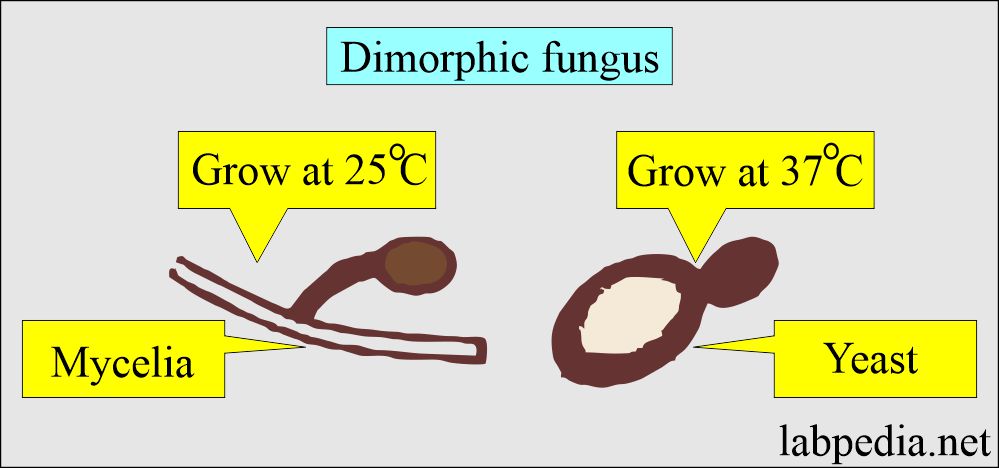
Dimorphic fungi:
- This exists in two forms: molds (mycelial form) and yeast. It depends upon environmental conditions and temperature.
- The yeast form is found in the infected tissue and on artificial media at 37 °C.
- Filamentous fungi are present in the soil and grow on artificial media at 22 to 25 °C.
- These are Blastomycosis, Coccidodioides, Histoplasmosis, and Sporothrix.
Spores:
- It reproduces bodies of molds.
- Spores are rarely seen in skin scrapings.
Molds:
- These are also called mycelia.
- There are multicellular colonies composed of clumps of intertwined branching hyphae.
- Molds grow by longitudinal extension and produce spores.
Saprophytes:
- These fungi utilize organic matter like rotten soil vegetation as an energy source.
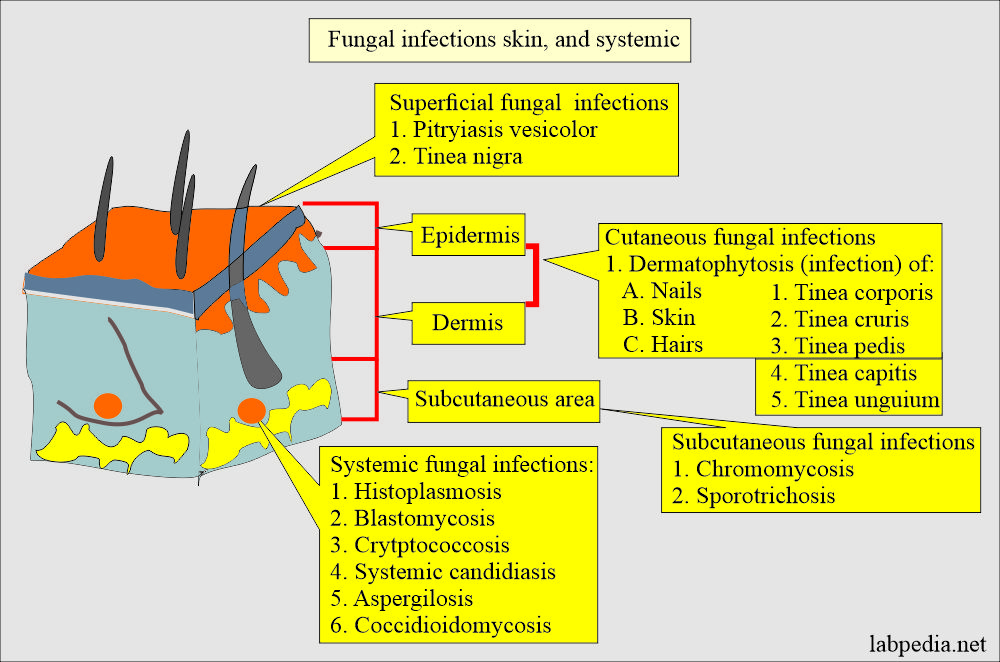
How will you classify fungal infections?
- Superficial infection:
- The mucosa leads to Thrush in the mouth by yeast.
- Filamentous fungi, e.g., ringworm, cause nail, skin, and hair infections.
- Deep or systemic fungi:
- The involvement of visceral organs or penetrating type of infection characterizes deep or systemic fungal infections.
- Subcutaneous infection is caused by trauma and gives rise to the sinus.
- Systemic infections (mycosis) are serious and fatal for the patient.
- Mycotoxicosis is caused by eating the food infected by these fungi due to their toxic metabolites, e.g., aflatoxin.
- An allergic reaction like type I and III is mostly due to fungal spores.
What are the types of Fungal diseases?
- Dermatophytosis:
- Where there is the involvement of superficial skin, e.g., Athlete’s foot and Ringworm.
- Other examples are:
- Tinea versicolor.
- Tinea nigra.
- Piedra (white piedra).
- Black Piedra.
- Subcutaneous mycosis:
- It is where there is the involvement of deeper tissue and muscles.
- These will give rise to chronic granulomatous inflammation.
- Sporotrichosis.
- Chromomycosis.
- Mycetoma.
- Systemic mycosis:
- It is where there is the involvement of deeper tissues and organs.
- Examples are:
- Blastomycosis (Blastomyces dermatitidis).
- Histoplasmosis (Histoplasma capsulatum).
- Coccidioidomycosis (Coccidioides immitis).
- Cryptococcosis (Cryptococcus neoformans).
- Paracoccidioidomycosis.
How will you diagnose fungi?
- Wood’s light (Ultraviolet rays) sees fungus directly over the hairs.
- Then, it is examined in the darkroom where infected hair gives fluorescence of bright yellow-green light.
- Phase-contrast microscopy:
- This is quick, and no need for any special stains.
- There is a very good identification of fungi.
- Direct microscopic examination:
- Clean the skin with 70% ethyl alcohol.
- The different sites are:
- Make scrapings from the edge of the lesion.
- Pluck the hairs.
- Take a sample from underneath the nails, not the outer surface.
- Procedure :
- Add Potassium hydroxide (KOH) 10% to 20% solution.
- Leave this scraping for 10 to 20 minutes for the keratin to be digested.
- Cover with coverglass and press it to make a thin smear.
- Then, under the microscope, you can see fungal elements like spores or mycelia.
- Stained smears:
- The clinical sample is stained with gram stain or Papanicolaou stain.
- Wright or Giemsa stain is used for Histoplasmosis.
- The advantage is that you can get results immediately.
- Fungal infections:
- Blood culture: Blood is collected in the special fungal culture media.
- Urine culture: Collect the morning sample, which has a good yield.
- Cerebrospinal fluid can be collected for the culture.
- Sputum culture: The sample can be obtained by bronchoscopy or alveolar lavage.
- Culture:
- It can be done to identify the fungus in Sabouraud’s media. This is good for the cutaneous or vaginal sample.
- Add antibiotics like chloramphenicol to suppress the growth of bacteria (selective media).
- Brain-heart infusion media with antibiotics and antifungals will prevent bacterial growth and rapidly growing fungi.
- Fungi are slow-growing organisms.
- Examine daily for up to 21 days and check daily for growth.
- Identify the colony’s appearance and pigmentation.
- Transfer the colony to slide, stained with lactophenol cotton blue, and covered with the cover glass.
- Examine under the microscope.
- Serological test:
- These are not highly reliable.
- Antibodies are present in 70 to 80% of the patients.
- There may be a cross-reaction of the antibodies.
- These serological tests cannot tell about recent or old infections.
- A titer greater than 1: 32 indicates a fungal infection.
- A complement test can be done for the diagnosis of Histoplasmosis and coccidioidomycosis.
- The immunodiffusion test is helpful for the diagnosis of Blastomycosis.
- These are not highly reliable.
- Biopsy:
- Biopsy of the tissue can be stained with the following:
- Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) reaction.
- Silver stain (Gamori’s methenamine silver).
How will you treat Fungal infections?
- Clotrimazole or Miconazole can treat superficial infections.
- A local application like Benzoic acid was also used.
- For severe infection, oral Griseofulvin was used for 4 to 6 weeks.
- In the case of hairs used for 3 to 6 months.
- In the case of nails, it is for one year.
- Oral Terbinafine and Itraconazole are also effective.
- For systemic fungal infection, the drugs used are:
- Amphotericin B.
- Itraconazole.
- Ketoconazole.
- For cutaneous fungal infections, the drugs used are:
- Griseofulvin.
- Locally used are nystatin, clotrimazole, and miconazole.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is dimorphic fungi?
Question 2: What is the value of serological tests for the diagnosis of fungal infections?

The information on this web-sit is perfect, and i will pass it on.
Do you know where or who will do these type of blood test in California?
You can try these techniques if facilities are available in California.
Where can I go to be tested for Mycoses (spores) (fungus), and Echovirus 7, Coxsackievirus B3 & B4 in California.
I am sure you need a referral from your primary physician.