Fluid Analysis:- part 7 – Pericardial fluid Analysis, Pericardiocentesis
Pericardial fluid Analysis
Sample for Pericardial Fluid Analysis
- Pericardial fluid is aspirated and tested.
What are the indications for pericardial fluid analysis?
- Pericardiocentesis is done to find the unexplained pericardial effusion.
- Pericardiocentesis is advised to relieve intrapericardial pressure.
- To diagnose acute pericarditis and pericardial effusion.
- To diagnose acute rheumatic fever.
- To diagnose bacterial infections.
What are the contraindication of pericardiocentesis?
- Avoid in uncooperative patients because there may be some damage to the coronary artery or epicardium.
- Avoid in patients who have a bleeding disorder.
What are the possible complications of pericardiocentesis?
- There may be a laceration of the coronary artery or myocardium.
- This procedure may lead to acute myocardial infarction.
- This procedure may lead to needle-induced ventricular arrhythmia.
- There may be vasovagal hypotension or cardiac arrest.
- The needle may lead to pleural or pericardial infection.
- The needle may cause pneumothorax by mistake.
- The needle may cause lacerations of the liver.
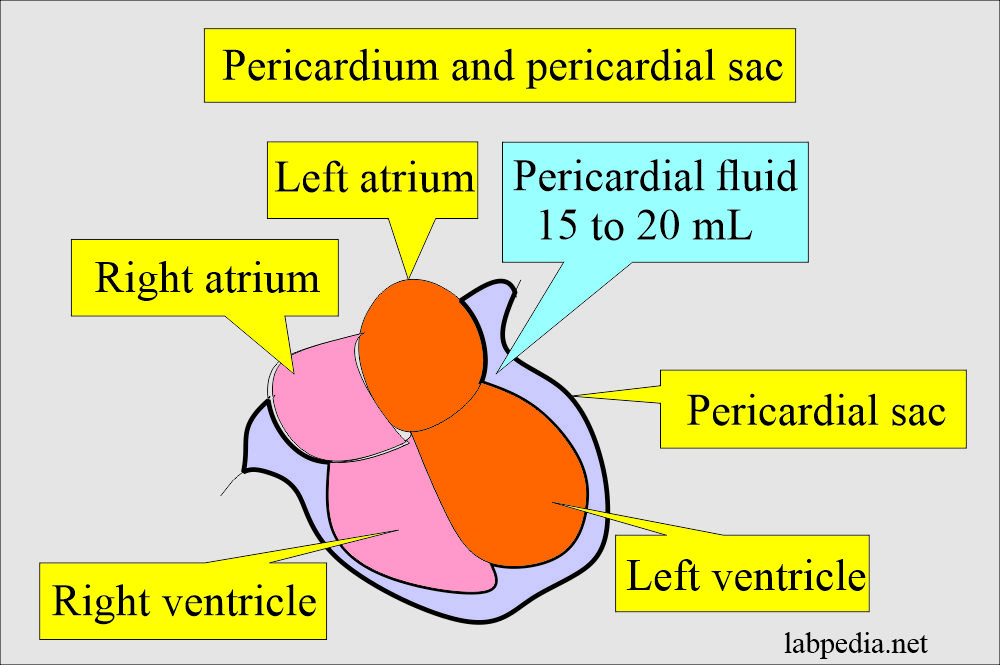
How will you define pericardial fluid?
- The pericardial cavity is formed by two thin membranes that surround the heart.
- These membranes are separated by a fluid-containing space called the pericardial cavity.
- Pericardial fluid is secreted by the mesothelial cells, and it will lubricate the membranes that line the pericardial cavity.
Discuss the pathophysiology of Pericardial fluid?
- Normally, there is 10 to 50 mL of pericardial fluid (another reference: 15 to 20 mL) between the pericardial serous membrane.
- This pericardial fluid formation is due to a change in the membrane’s permeability, possibly due to infection (pericarditis), malignancy, injury, and metabolic disorders like uremia.
What are the functions of the pericardial fluid?
- It will allow the heart to move easily during contraction and relaxation.
- Pericardial fluid lubricate the membranes.
- It enables the membranes to slide over one another with minimal friction as the heart beats.
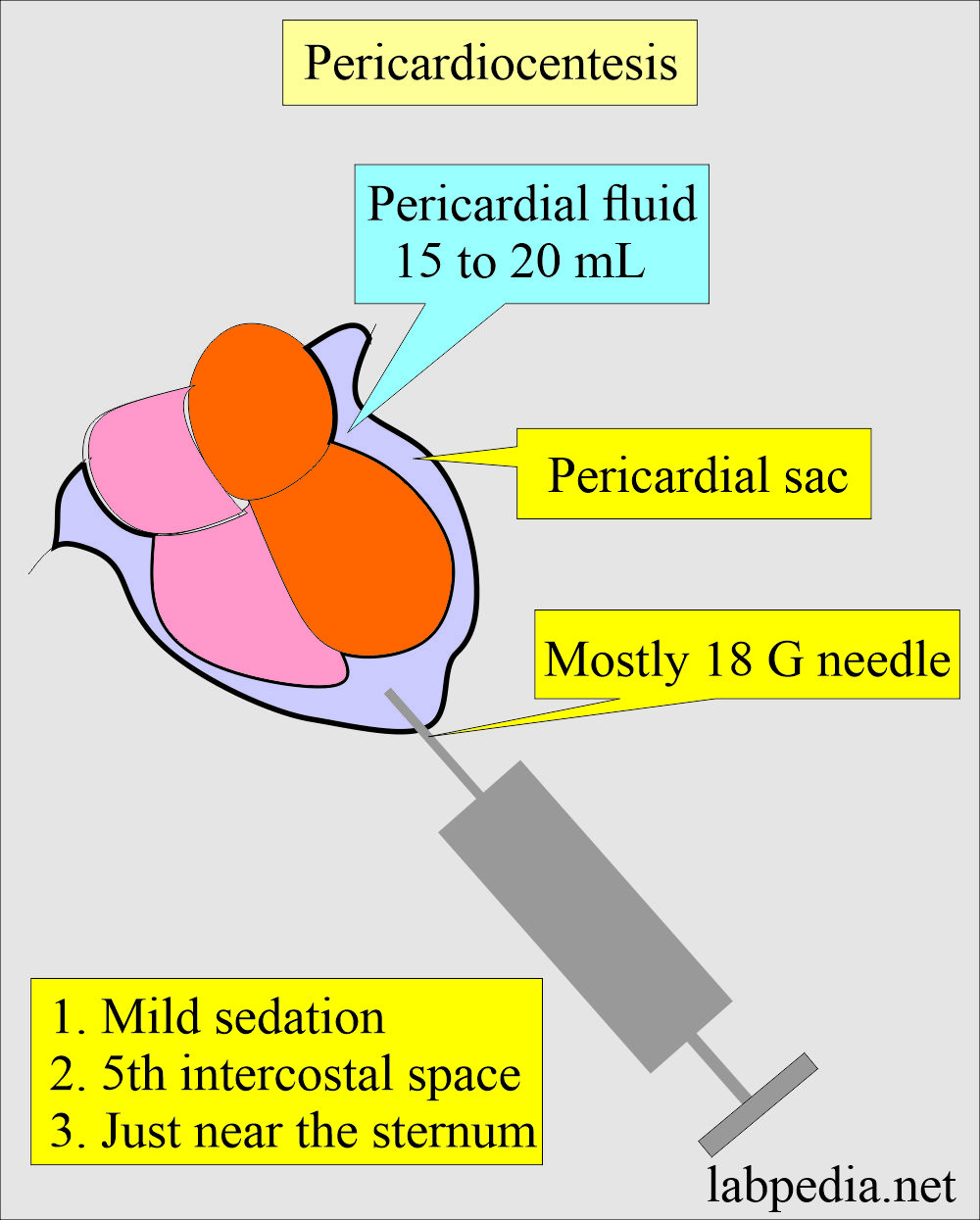
How will you do Pericardiocentesis?
- It removes fluid from the pericardial sac, which may be therapeutic or diagnostic.
- Mild sedation is needed.
- Insert the needle in the 5th intercostal space near the sternum.
- Pericardiocentesis procedure improves diastolic filling.
- It is advised as a therapeutic emergency procedure in the case of cardiac tamponade to diagnose the cause of fluid accumulation.
- Purpose of the pericardiocentesis:
- It will remove the fluid from the pericardial cavity to relieve the tamponade.
- Through this procedure, can administer drugs.
- The fluid was removed for diagnostic purposes.
How will you classify and discuss the etiology of pericardial fluid?
- Inflammation causes pericardial fluid accumulation, and there are other causes as well.
- The pericardial effusion may be classified as:
- Serous type of fluid seen in congestive heart failure and hypoalbuminemia.
- The chylous type is seen in mediastinal lymphatic obstruction
- Serosangineous type is seen due to trauma and malignant tumors.
What are the causes of Pericardial effusion?
- Active rheumatic fever in 40% of the patients.
- In 20% of cases, a bacterial infection is due to tuberculosis, streptococcus pneumonia, staphylococci, and gram-negative bacteria.
- Other infections include Coxsackievirus rickettsia, parasites, and fungi.
- Uremia may be the cause in 11% of the cases.
- Benign nonspecific pericarditis.
- Collagen diseases like SLE (2% of the cases).
- Trauma.
- Myxedema.
- Malignant diseases (3.5% of the patient).
- Rarely caused by severe anemia, scleroderma, polyarteritis nodosa, Wegner granulomatosis, rheumatoid arthritis, radiation, and mycotic infections.
What are the signs and symptoms of pericardial effusion?
- These patients are usually symptomatic.
- Sometimes, the large volume of the fluid is accommodated without any symptoms when it accumulates slowly.
- When there is a massive accumulation of fluid, that may lead to cardiac tamponade.
What is the normal pericardial fluid?
- Appearance = Clear or straw-colored
- Bacteria = Negative
- WBCs = No WBCs are seen.
- Glucose = Equal to serum level
| The pericardial fluid | Clinical significance |
| Appearance | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Microscopic examination | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemicals test | |
|
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the amount of pericardial fluid?
Question 2: Define pericardiocentesis?