Fibrinogen Degradation Products (FDPs), Fibrin split products (FSP), and d-Dimer, DIC
Fibrinogen degradation products (FDPs) and d-Dimer
What Sample is needed for Fibrinogen Degradation Products (FDPs)?
- It is done in the serum.
- Collect 2 ml blood in a test tube containing Thrombin, soybean, and Trypsin inhibitor.
- Allow to clot at 37 °C for 30 min.
- OR Collect blood with 1:20 dilution (ESR solution 0.2 ml and 1.8 ml blood).
- For d-dimer, citrated plasma is stable for 8 hours at room temperature.
What is the purpose of the test for Fibrinogen Degradation Products (FDPs)?
- This test establishes a DIC diagnosis (Disseminated intravascular coagulopathy).
- Thromboembolic disorders like pulmonary embolism.
- This is a screening test for DVT (Deep vein thrombosis).
- It can be used to determine the duration of anticoagulation treatment of DVT.
What Precautions will you take for Fibrinogen Degradation Products (FDPs)?
- Keep in mind that menstruation may be associated with increased FDP value.
- Remember that drugs like barbiturates, streptokinase, urokinase, and heparin may increase their value.
- Some drugs like warfarin and other oral anticoagulants decrease the value.
- Avoid the excessive agitation of the blood.
- Avoid prolonged use of a tourniquet.
- Some of the drugs may affect and increase the level of FDPs like:
- When heparin was given to treat the blood clots.
- When streptokinase is given in patients with coronary thrombosis.
- Barbiturates may increase the FDP level.
- Treatment by the urokinase to dissolve the clot.
- Drugs affecting the FDP level:
How will you define fibrinogen degradation products (FDPs)?
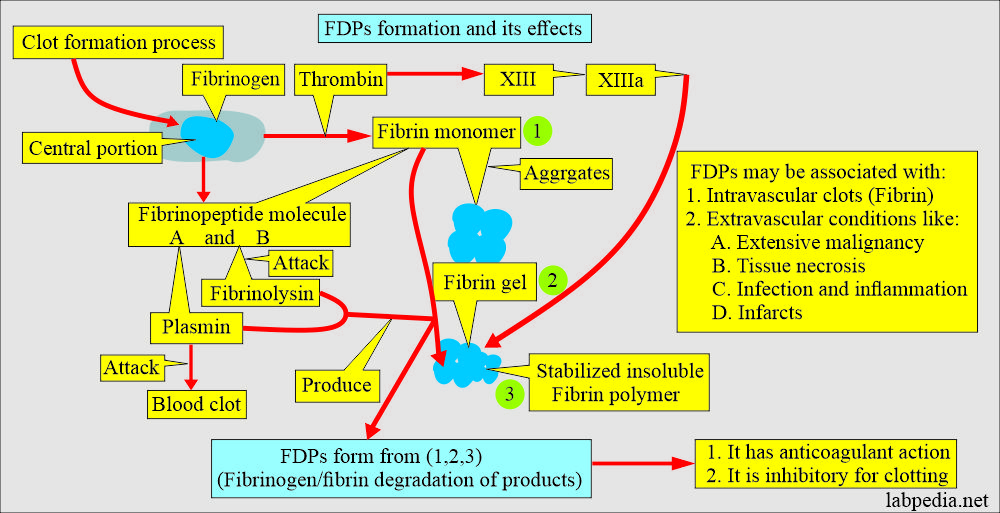
- Fibrinogen Degradation Products (FDPs) are the substances left behind when a clot dissolves in the blood.
- Fibrinogen Degradation Products (FDPs) are the fragments released following plasmin-mediated degradation of fibrinogen or fibrin.
- d-dimer is a specific fragment formed after the degradation of the cross-linked fibrin.
- FDPs are raised mostly >40 µg/mL in 85% to 100% of the patients with DIC.
- FDPs are also raised in thromboembolism, acute myocardial infarction, transplant rejection, and surgery.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Fibrinogen/Fibrin degradation products (FDPs and d-dimer)?
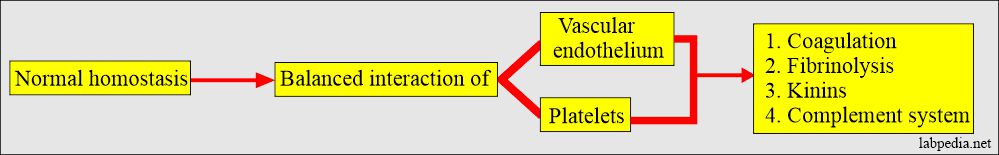
- Normal homeostasis is a balanced interaction of the vascular endothelium, platelets, and biochemical systems.
- Measurement of FDPs provides a direct indication of the activity of the fibrinolytic system.
- The Fibrinolytic system is important in balancing clot formation and clot dissolution.
- FDPs are generated when inappropriate clotting is seen in disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC).
What is a summary of fibrinogen degradation products (FDPs)?
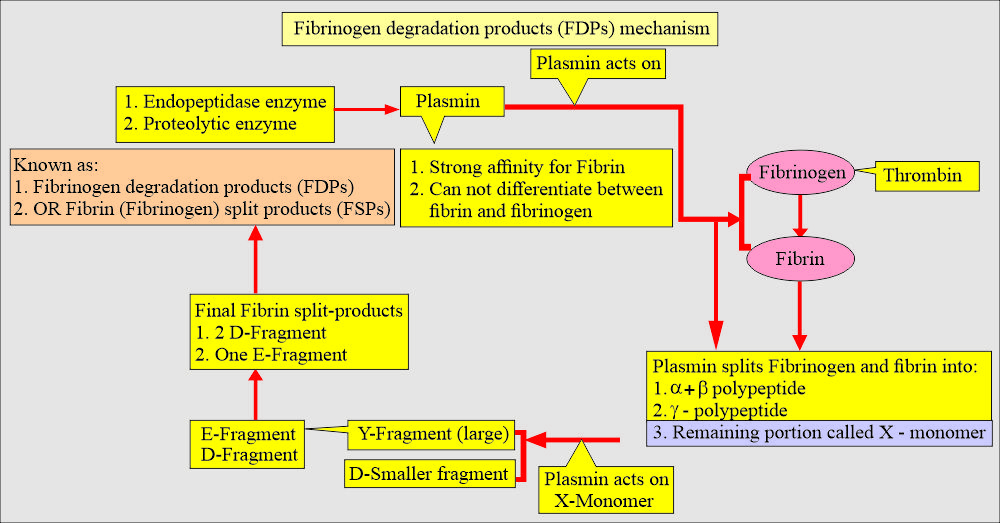
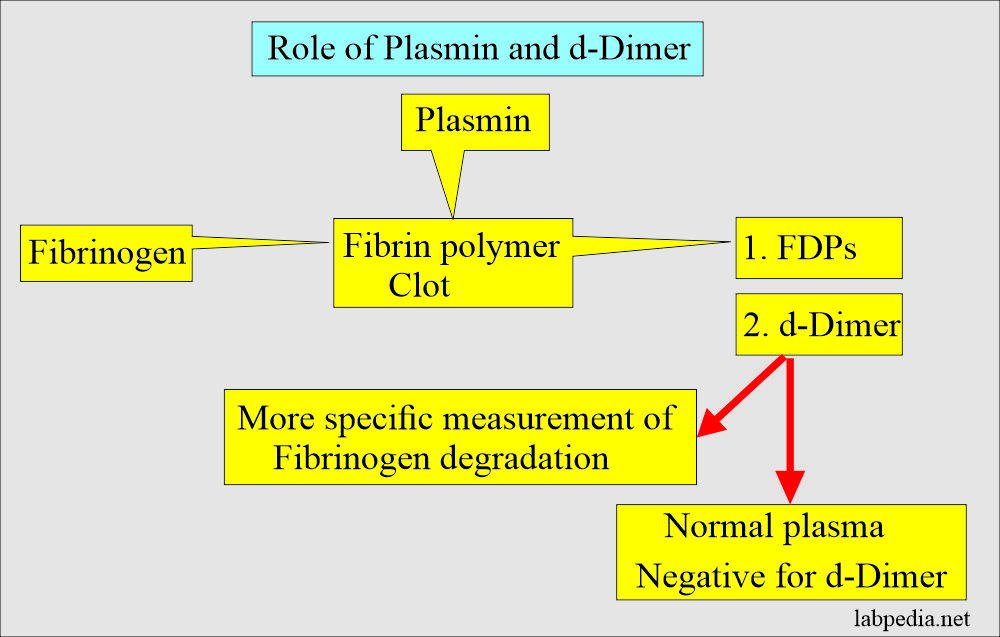
- Plasmin actually leads to fibrinogen/fibrin degradation products (FDPs).
- Plasmin has a strong affinity for fibrin but can not differentiate between fibrinogen and fibrin.
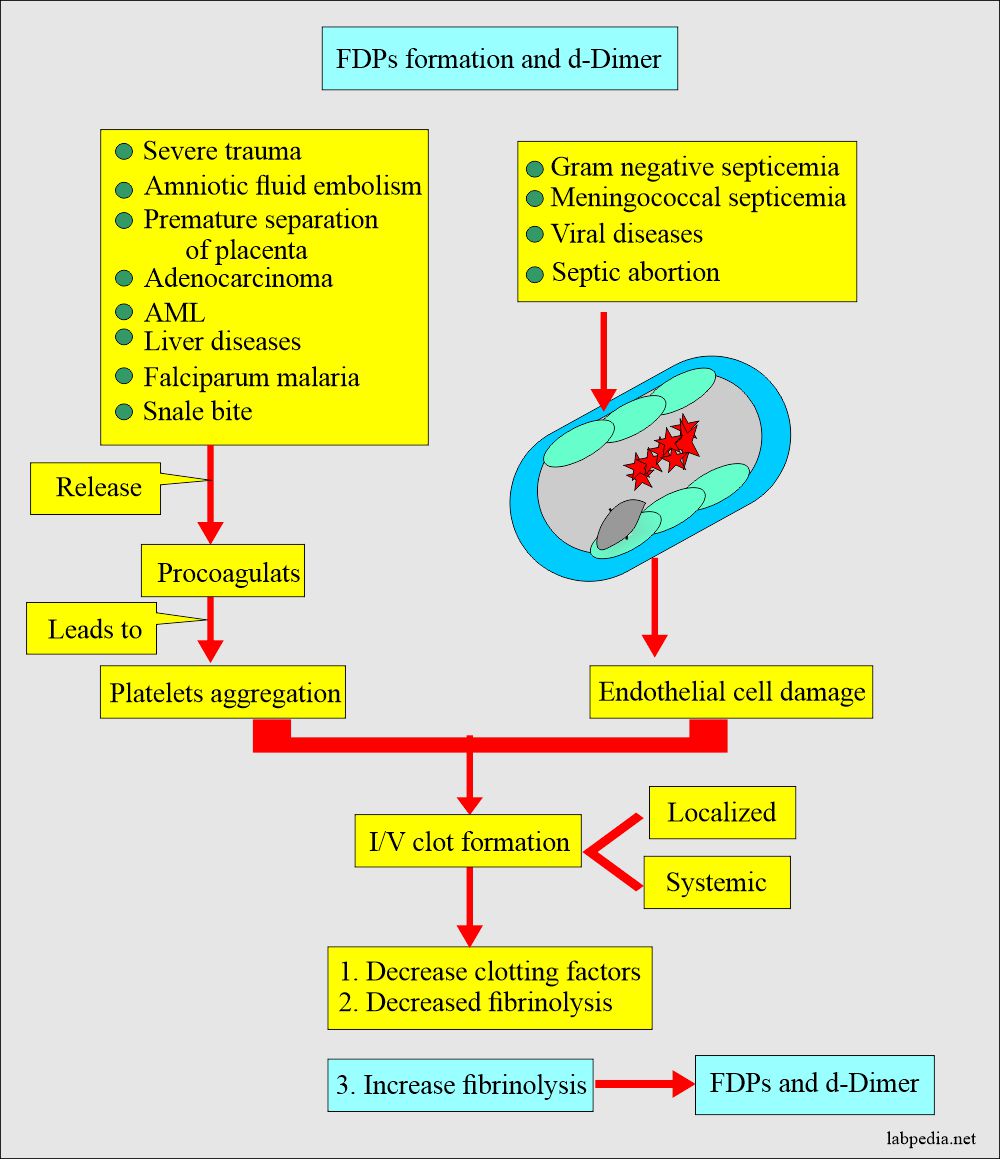
What is the trigger for this excessive intravascular coagulopathy?
- Severe trauma.
- Amniotic fluid embolism.
- Premature separation of the placenta.
- Mucinous Adenocarcinoma.
- Liver diseases.
- Acute myelocytic leukemia.
- Falciparum malaria.
- Snake Bites.
- All the above factors lead to the release of procoagulants and give rise to platelet aggregation.
- Gram-negative and meningococcal septicemia, septic abortion, and viral diseases lead to endothelial injury and cause intravascular clot formation.
Fibrinogen degradation products (FDP) and d-Dimer facts:
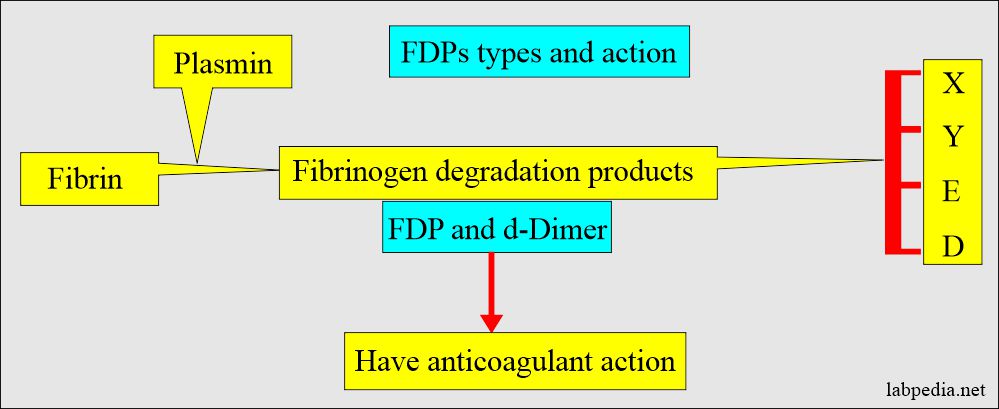
- When the body tries to dissolve blood clots, these are polypeptide fragments generated by the enzymes (plasmin).
- These fibrinogen degradation products are named X, Y, D, and E and are collectively called fibrinogen degradation products (FDP) and d-dimer.
d-dimer
- It is more specific for the measurement of fibrinogen degradation. At the same time, normal plasma is negative for d-dimer.
- These FDPs have anticoagulant action and inhibit clotting.
- FDP is the substance that remains in the blood after the blood clot is dissolved.
- The FDPs have an anticoagulant action and inhibit clotting when in excess.
- FDPs and d-Dimer correlate with each other and are evidence for DIC or another intravascular thrombosis.
- FDPs and d-Dimer assess both thrombin and plasmin activity.
- The d-Dimer assay provides a highly specific measurement of fibrin degradation that occurs.
Disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC):
Definition of DIC:
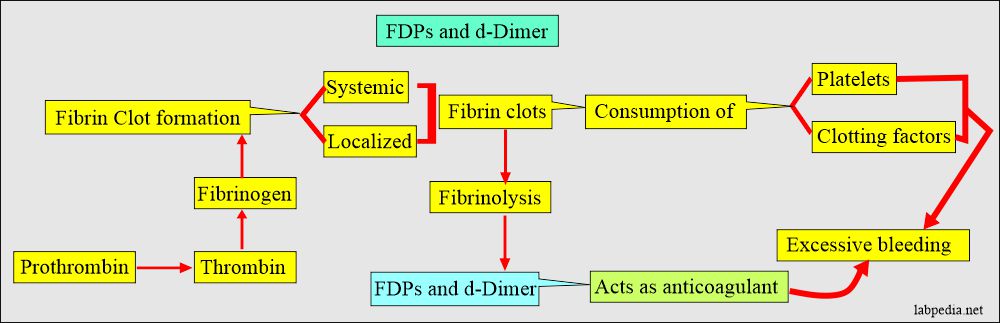
- DIC is an acquired coagulation disorder.
- Excess systemic activation of the coagulation system leads to widespread microthrombi in circulation.
- End result is depletion of the platelets and coagulation factors, leading to bleeding.
- Activation of the thrombin leads to thrombosis of small and medium size blood vessels.
Signs and symptoms of DIC:
- There may be Nausea and vomiting.
- The patient may have bleeding from the gums.
- There is severe muscular pain.
- There may be abdominal pain.
- The patient will have reduced urinary output (oliguria) and hematuria.
- There is dyspnea.
- Ultimately, shock and confusion.
Diagnosis of DIC:
- Platelet count is decreased.
- Fibrinogen level is decreased.
- The protamine sulfate test is positive.
- Factor V and XIII are decreased.
- d-Dimer is positive (FDPs are positive).
- Prothrombin time is increased.
- APTT is increased.
Normal FDPs and d-Dimer
Source 1
- FDP = <10 µg/mL
- To convert to SI unit x 1.0 = <10 mg/L
Source 4
- FDP = Negative at 1:4 Dil.
- The quantitative value is <10 µg /ml or <10 mg/L.
- d-Dimer is more specific than FDP.
- Negative = No d-Dimer fragments are found in plasma.
- <0.25 mg/L (or <0.4 µg/mL).
Source 2
- Negative, no d-dimer fragments are found.
- <250 ng/mL (<250 µg/L)
- When both test d-Dimer and FDPs are done, they are more specific for the diagnosis of DIC.
Increased FDPs or d-Dimer level is seen in:
- Pregnancy ( abruptio placentae, Eclampsia, retained dead fetus, and sepsis ).
- Myocardial infarction.
- Heart or vascular surgery.
- Thrombosis.
- Pulmonary embolism.
- Thrombolytic or defibrination therapy.
- Primary and secondary fibrinolysis.
- In the case of DIC.
- Venous thrombosis (Deep vein thrombosis, DVT).
- Carcinomas.
- Liver disease.
- Surgery.
- Allograft rejection.
- Hematoma.
- Sickle cell anemia.
- Massive trauma.
What are the conditions where FDPs are increased in urine?
- It is seen in kidney diseases.
- Urinary tract infection.
- Proliferative glomerulonephritis.
- Rejection of renal transplant.
Decreased FDP value seen in:
- Anticoagulant therapy.
The critical value of FDP is above >40 µg/mL or 40 mg/L.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the role of plasmin?
Question 2: What is the role of FDPs and d-Dimer?