Estrogen Receptor Assay (ER, Estradiol Receptor)
Estrogen Receptor Assay
What sample is needed for Estrogen Receptor Assay?
- Breast cancer tissue blocks are needed.
- Fresh tumor cells to get slices of cytoplasm (Cytosol).
What are the Indications for Estrogen Receptor Assay?
- ER is done on the breast cancer tissue to evaluate the hormone response.
- ER also gives an idea about the prognosis.
What are the precautions for Estrogen Receptor Assay?
- What are the reasons for False-negative ER receptors?
- Incorrect handling and storage of tissue samples leading to thermolabile receptor protein degradation.
- If there is a low protein concentration in the assayed sample.
- If a biopsy is taken from the surrounding normal tissue.
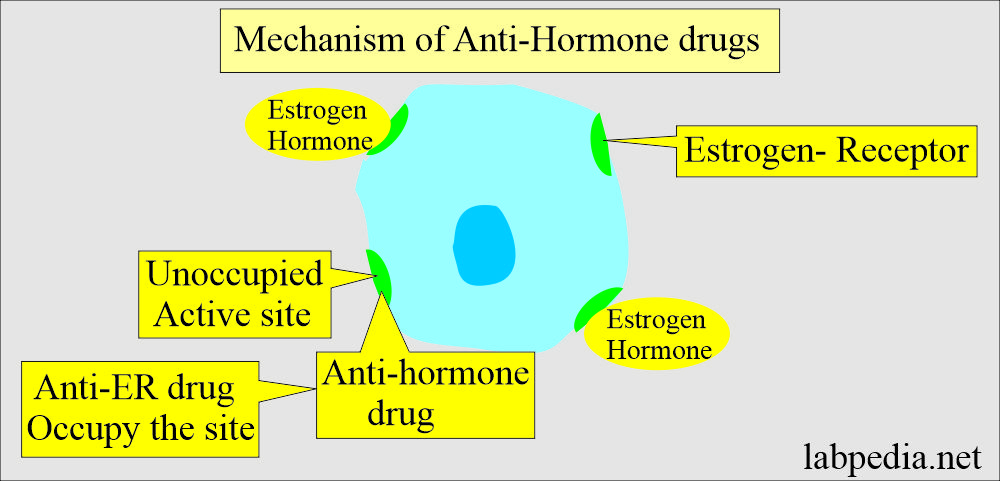
How will you describe the Pathophysiology of Estrogen Receptor Assay?
- The estrogen receptor is a specific cellular protein with high affinity and specificity for the Estrogen hormone.
- The estrogen receptor protein is found in the target tissue like the breast, uterus, pituitary gland, and hypothalamus.
- Estrogen stimulates the cells through the Estrogen receptor.
- A reduction in the blood estrogen level reduces the biochemical activity of these cells.
- This is the basis for the treatment of breast cancer by anti-hormone therapy,
- ER-positive breast cancer is twice more responsive than ER-negative cases.
- Postmenopausal women’s breast cancers are more ER-positive than young women.
- ER-positive tumors have a better prognosis than ER-negative cases.
- More than 50% of ER-positive cases respond to anti-hormone therapy (Tamoxifen).
- In metastatic carcinoma of the breast, 1/3 of the women have various types of endocrine therapy directed at lowering their estrogen level, e.g.
- Oophorectomy.
- Hypophysectomy.
- Adrenalectomy (ablation therapy).
- Anti-estrogen and androgen (additive therapy).
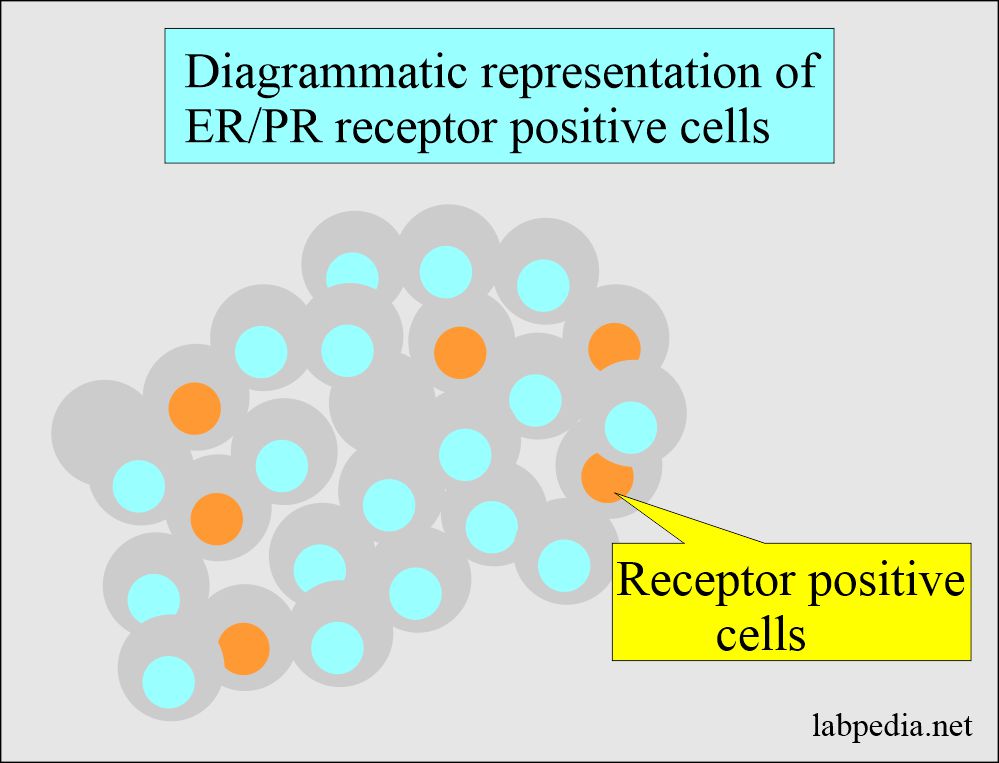
What is the significance of ER/PR?
- PR- receptor is useful to help assay the ER receptors.
- Metastatic cancer with ER and PR receptor-positive tumors has a response rate of 75% to endocrine therapy.
- If the ER-positive and PR-negative tumors have a 40% response rate.
- If ER-negative and PR-positive patients’ only response rate is 25% for endocrine therapy.
- In the case of ER and PR negative, the response rate is only 5%.
- The percentage of positive cases in postmenopausal women is more significant than in premenopausal women.
| Hormone receptor | ER | PR | Response to the treatment |
| Hormone receptors | Positive | Positive | 75% response to anti-hormone therapy |
| Hormone receptors | Positive | Negative | 40% response to anti-hormone therapy |
| Hormone receptors | Negative | Positive | 25% response to anti-hormone therapy |
| Hormone receptors | Negative | Negative | 5% response to anti-hormone therapy |
What are the procedures for Estrogen Receptor Assay Detection?
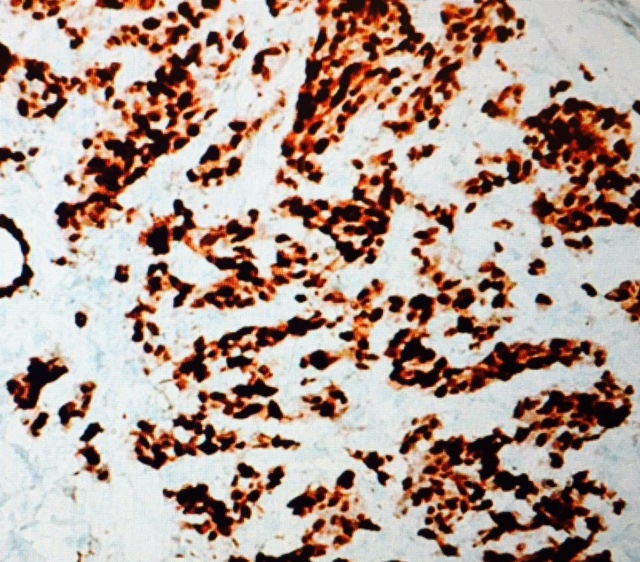
- Mostly, ER is done on the cancer tissue (paraffin blocks) as immunohistochemistry.
- Another method can be enzyme immunoassay.
- Chromatography techniques.
- EIA.
How will you interpret immunocytochemistry slides for ER/PR?
- Negative = <5 % of the nuclei of the cells for the receptors.
- Positive = >5 % of the nuclei of the cells stain for the receptors.
What is ER/PR positivity?
- Carcinoma of the breast, 60%, shows positivity.
- Approximately 2/3 of the cases show a response to hormone therapy.
- In ER-negative cases, 90% do not respond to hormone therapy.
- The hormone receptor positivity varies in different patients:
- ER+ = 80% of the cases.
- ER+ PR+ = 65% of the cases.
- ER+ PR- = 13% of the cases.
- ER- PR+ = 2% of the cases.
- ER- PR- = 25% of the cases.
How will you interpret ER positivity?
- Favorable response >20% cell stain.
- The borderline response is 11% to 20% of the cell stain.
- The unfavorable response is <10% cell stain.
- ASCO guidelines are:
- Positive for ER/PR if ≥ 1% of the tumor cell nuclei are immunoreactive.
- Negative ER/PR if <1% of tumor cell nuclei are immunoreactive.
- Allred scoring: This replaced the early scoring system.
- ER-positive tumor cells have >10% positive cells.
- ER-negative tumor cells are 1 to 9% positive cells.
- ER-positive tumor cells have >10% positive cells.
| Score | Positive cells % | Intensity | Intensity score |
| 0 Score | o | None | 0 |
| 1 | None | Week | 1 |
| 2 | 1 to 10 | Intermediate | 2 |
| 3 | 11 to 33 | Strong | 3 |
| 4 | 34 to 66 | ||
| 5 | 66 to 100 |
- Progesterone receptors (PR) should be done along with the ER. Because PR depends upon estrogen activity.
- PR positivity confirms that all the steps for the ER are done correctly.
- When ER/PR is positive, then the response of the tumor is 75 % to the treatment.
Response to anti-hormone therapy
| ER | PR | Response to hormones |
|---|---|---|
| positive | positive | 75 % |
| negative | positive | 60 % |
| positive | negative | 35 % |
| negative | negative | 25 % |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the criteria of ASCO guidelines?
Question 2: What is the response of anti-hormone therapy, in case of ER/PR positive cases?