Hemolytic Disease of Newborn (HDN)
What sample is needed for the Hemolytic disease of Newborn (HDN) workup?
- The sample is serum from the mother.
- Whole blood (RBC) from the fetus or newborn.
What are the indications for Coombs’ test?
- To diagnose hemolytic anemia of newborn (hemolytic disease of newborn = HDN).
- To find out the presence of an anti-D antibody in the mother’s serum.
How will you define hemolytic disease of newborns (HDN)?
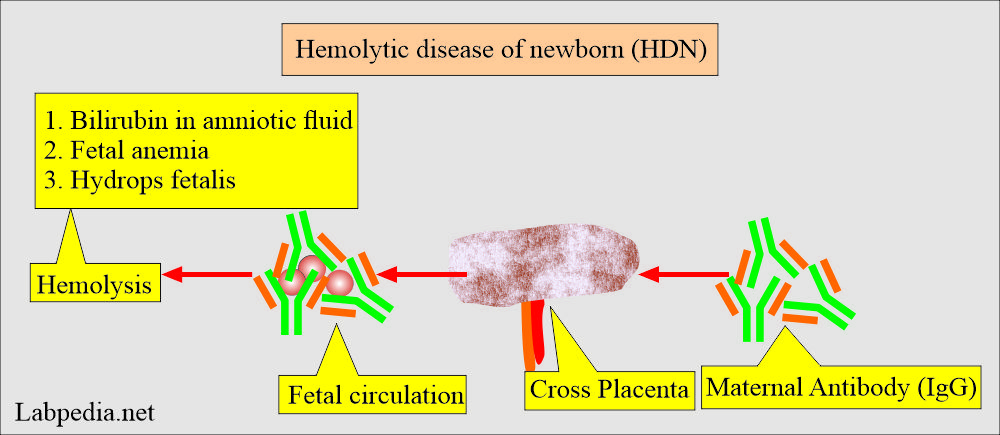
- Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) results from maternal alloantibodies that cross the placenta and enter fetal circulation, causing hemolysis.
- IgG antibodies are passed from the mother’s placenta into the fetus, which reacts with fetal RBCs and destroys them.
- Anti-D antibodies are responsible for most cases of severe HDN.
- This condition is also called erythroblastosis fetalis.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of hemolytic anemia of the newborn (HDN)?
- The red blood cells have various antigens on their surface, forming various blood groups. The Blood group ABO system and Rh-systems (D-antigen) are important.
- Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) results from fetal antigens, while the mother’s RBCs lack these antigens.
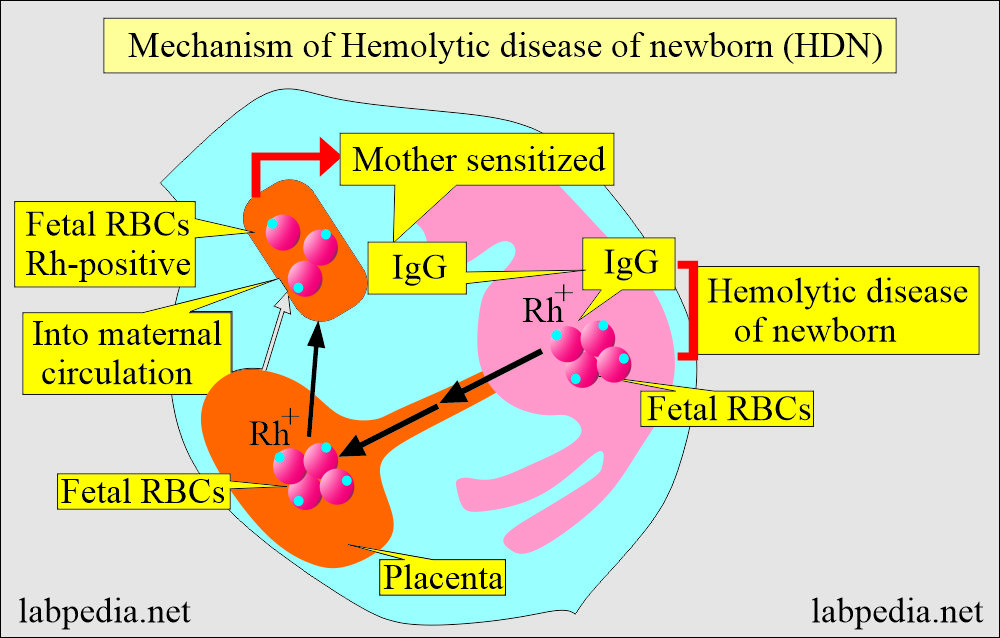
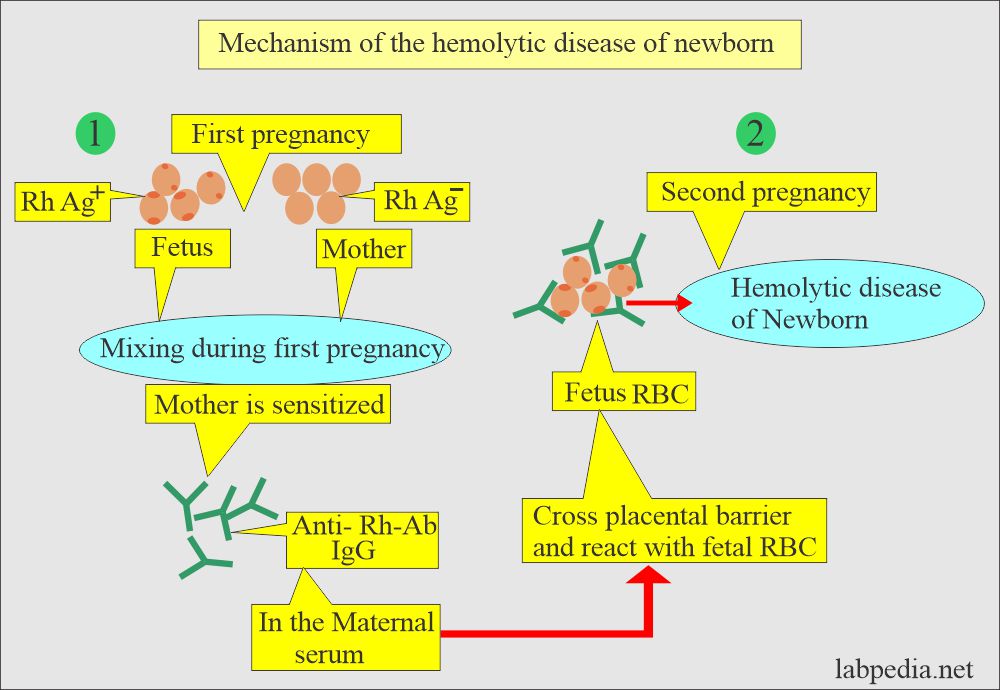
- Fetal antigens provoke maternal antibody formation, which is IgG type. It happens when the fetal RBCs enter the maternal circulation during delivery (or pregnancy).
- These maternal antibodies (IgG) can cross the placenta and enter fetal circulation, leading to hemolytic anemia by attacking the fetal RBCs.
- If the mother and fetus are ABO-incompatible, then sensitization can not occur due to maternal AB antibodies’ immediate destruction of the fetal RBCs.
- An Rh-positive baby occurs in ∼10% of Rh-negative mothers in white females, 5% in black females, and 1% in Asian females.
What is the mechanism of Rh-incompatibility?
- Hemolytic disease of the newborn due to Rh-incompatibility varies in severity from:
- Subclinical disease.
- Mild jaundice with anemia.
- Erythroblastosis fetalis is a dangerous condition.
- The main findings are jaundice and anemia.
- Reticulocytosis >6% accompanies the anemia.
- In severe cases, there are nucleated RBCs in the peripheral blood smear.
- Jaundice is due to mainly unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin.
- Jaundice is not present at birth; it appears after 24 hours.
- Physiologic jaundice may be confused with pathological jaundice. Physiologic jaundice has no anemia.
- Normal hemoglobin in newborns is 18 g/dL; anemia is established when hemoglobin is <15 g/dL.
- Direct Coombs’ test is positive.
How will you discuss the Rh system?
- If the Rh antigen is present in some of the RBCs, those are called Rh-positive blood groups, while the RBCs lack Rh – antigens and are called Rh-negative blood groups.
- The other common causes are Rh-c antigen and blood group Kell antigens.
- There are a group of Rh antigens like Rh-C, Rh-D, Rh-E, and more.
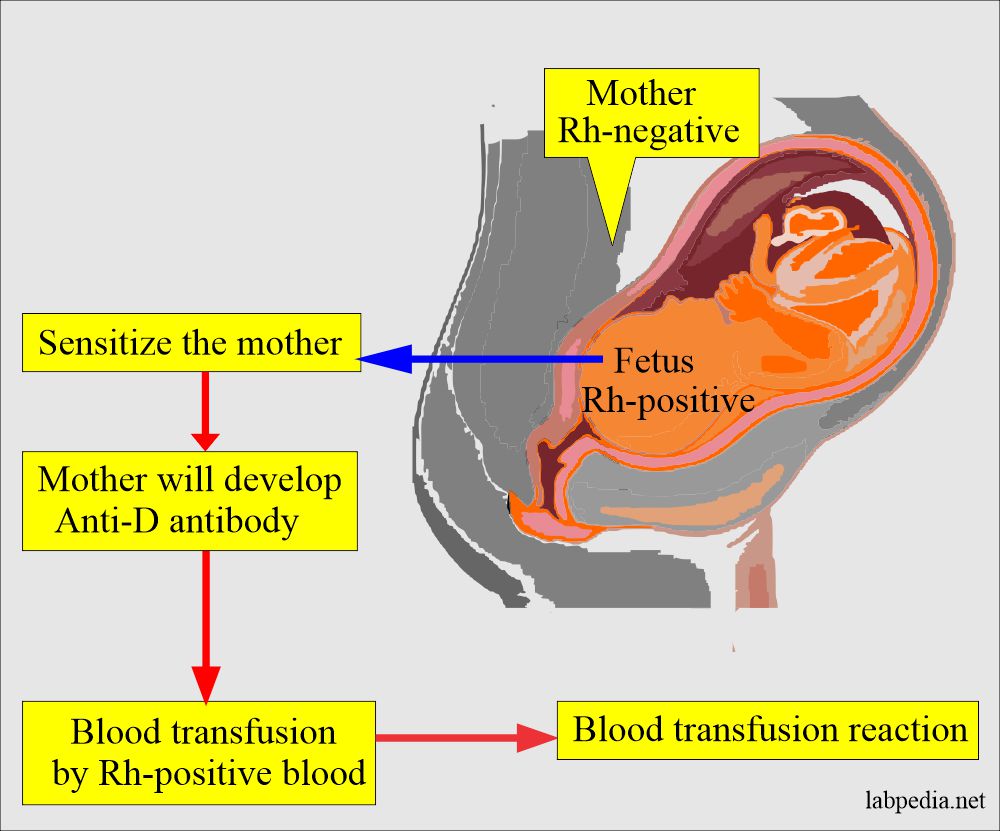
- Suppose the mother is Rh antigen (D-negative) and the baby is Rh antigen (D-positive) because of the feto-maternal hemorrhage. In that case, the mother may be sensitized to Rh antigen and develop Rh antibodies, mostly IgG-type (anti-D) antibodies.
- This sensitization occurs due to pregnancy, abortion, ectopic pregnancy, placental trauma, amniocentesis, blood transfusion with Rh-positive RBCs, or contaminated blood products like platelet concentrates.
- The most common is the fetomaternal mixing of fetal RBC Rh-positive cells.
- This mixing occurs after 16 weeks of the pregnancy or a single large dose of fetal RBCs mixing at the delivery time.
- 10% to 13% of mothers risk sensitization by the Rh-positive fetal RBCs.
- Usually, the first child is not affected.
- First-born infants are affected by 5% to 10% with HDN, either due to a previous pregnancy or abortion or the high sensitivity of the mother to Rh-antigens.
- Usually, the mother and fetus are ABO compatible.
- These maternal anti-D antibodies can cross the placental barrier, enter fetal circulation, and lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
How will you diagnose Hemolytic anemia in a newborn (HDN)?
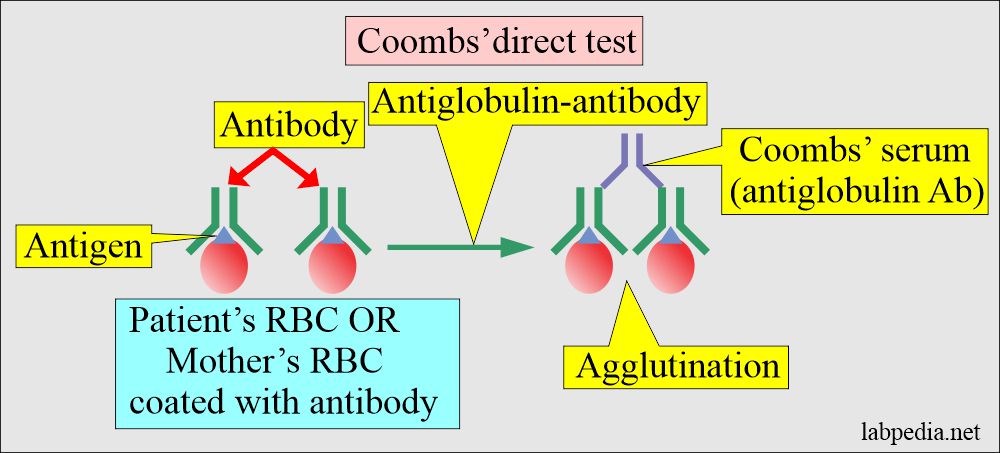
- In the case of Rh-induced hemolytic anemia of newborn (HDN), direct Coomb’s test on cord blood is positive.
- The Coombs test is frequently but not always positive in the case of ABO-induced HDN on cord blood.
- The direct Coombs test on infant blood is usually positive in Rh-induced HDN but negative in ABO-induced HDN when done more than 24 hours after delivery.
- Cord blood bilirubin usually increases, and cord blood hemoglobin is decreased in severe HDN.
What is the significance of Coombs’ test for hemolytic disease of newborns (HDN)?
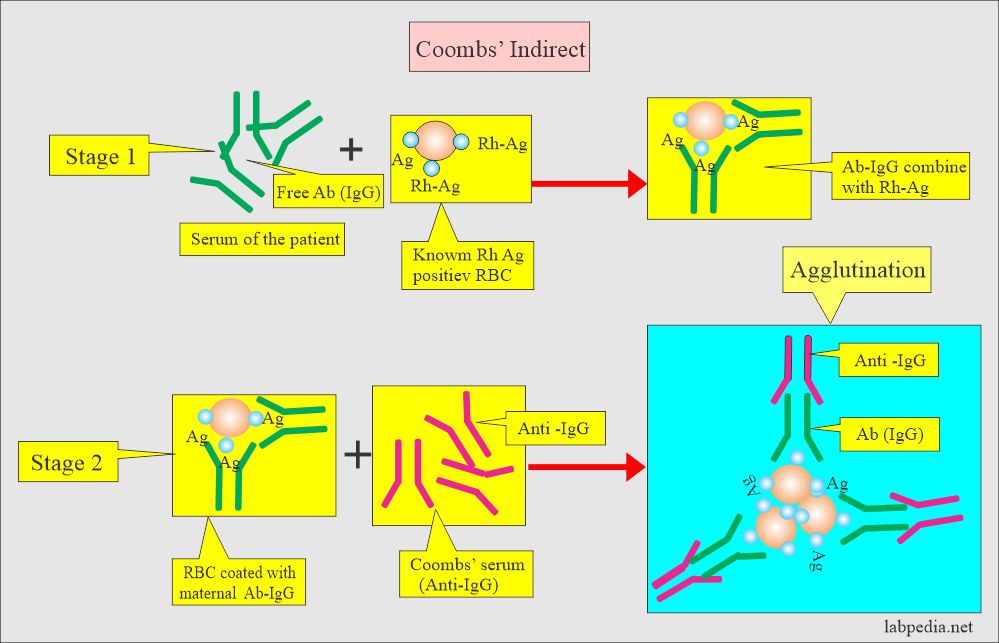
- Coombs’ test is used to detect antibodies in Rh-negative mothers or newborns.
- Mother has free antibodies in the serum.
- Fetal/newborn has coated RBCs with antibodies.
- One can monitor the presence of the antibody during pregnancy.
- A mother titer of more than 1:16 at the 8th month indicates the presence of anti-D antibodies in the mother. These can cross the placental barrier and enter fetal circulation.
- The fetus can develop hemolytic disease.
- A mother titer of more than 1:16 at the 8th month indicates the presence of anti-D antibodies in the mother. These can cross the placental barrier and enter fetal circulation.
How will you discuss an indirect Coombs test?
- It is done to find a free anti-D antibody in the maternal blood serum.
How will you discuss A direct Coomb’s test?
- Coombs test is done to find RBC-coated antibodies in the fetus or newborn.
How will you do Prenatal screening?
- Must do blood group ABO and Rh at the first prenatal visit during the pregnancy.
- Advise indirect Coombs’ test for mother for ABO or different antigens.
- Rh-negative mothers should be given anti-D immunoglobulin (Rhogam) at the end of the second trimester and again within 72 hours of the delivery in the case of Rh-positive babies. This treatment will decrease the prevalence of HDN.
- Monitor anti-D titer on mother serum to find the sensitization when the titer is >1:8.
- If the titer is ≥1:32, advise serial estimation of the amniotic fluid bilirubin (indirect) level every 2 to 3 weeks to prevent the risk to the fetus.
- Lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio estimation gives an idea of lung maturity.
- Amniocentesis is more reliable than the anti-D titer in determining the severity of the HDN.
- DNA analysis of amniotic fluid by PCR can determine the D-antigen status of the fetus.
- At birth, determine the cord blood (baby blood):
- Hemoglobin.
- Bilirubin level.
- Direct Coombs’ test.
How will you do postnatal workup and follow-up?
- Check the indirect serum bilirubin of the infant because it rises rapidly. There may be an increase of 0.3 to 1.0 mg/dl/hours. It may reach 30 mg/dL in untreated babies in 3 to 5 days; at this level, the baby may die.
- Urobilinogen is increased in urine and feces. This increase will be parallel to blood serum bilirubin.
- Direct Coombs’ test is positive on cord blood RBCs in the case of Rh, Kell, Kidd, and Duffy antibodies.
- It is weakly positive in anti-A antibodies.
- Anemia is not evident at birth but becomes maximum by the 3rd or 4th day.
- Blood examination of the baby:
- MCHC is normal, and MCV and MCH are increased.
- Peripheral blood smears show increased nucleated RBCs in the first 2 days. Their number will decrease, and they may be absent on the 3rd or 4th day.
- It shows anisocytosis, polychromatophilia, and increased macrocytes.
- There is reticulocytosis >6% and sometimes may reach 30% to 40%.
- WBC count is increased.
- The platelet count is mostly normal.
- When these babies are treated, this episode will be over in 3 to 6 weeks, and there will be no more maternal antibodies.
What is the prognosis of Hemolytic Disease of Newborn (HDN)?
- Its (HDN) prevalence is markedly decreased due to in-time administration of Rh-globulin (Rhogam) after abortion or delivery.
How will you treat hemolytic disease in a newborn (HDN)?
- The exchange of blood transfusion can save infants with HDN.
- Indications/criteria for blood exchange transfusion:
- Infants’ serum bilirubin level >20 mg/dL or in premature or severely ill infants with a bilirubin level of 15 mg/dL.
- Cord blood indirect bilirubin level >3 mg/dL.
- Cord blood hemoglobin <13 g/dL and there are references in favor of 8 to 14 g/dL.
- Maternal Rh-antibody titer of 1:64 or greater. If bilirubin does not rise, then this is not the indication.
What are the criteria for the blood exchange transfusion?
| Lab parameters | No treatment is needed; only follow-up | Exchange transfusion needed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Does the first baby will have HDN?
Question 2: When will bilirubin be raised in HDN?