Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT), Partial thromboplastin time (PTT), Prothrombin time (PT)
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT)
Sample for Activated Partial Thromboplastin
- The blood is collected in an anticoagulant with a fixed ratio carefully.
- Take 0.2 ml anticoagulant (ESR solution may be used) and 1.8 ml whole blood.
- Can draw the blood from a 3.2% buffered citrated tube with a 9:1 = blood: citrate ratio.
- Citrate binds calcium and prevents coagulation.
- The APTT sample may be taken 30 to 60 min before the next dose of Heparin.
Precautions for Activated Partial Thromboplastin
- Plasma is stable for one hour at 4 °C and 28 days if frozen.
- Sample handling is very critical. If the ratio of blood and anticoagulant is not correct, then the results are false and raised.
Principle of Activated Partial Thromboplastin (APTT)
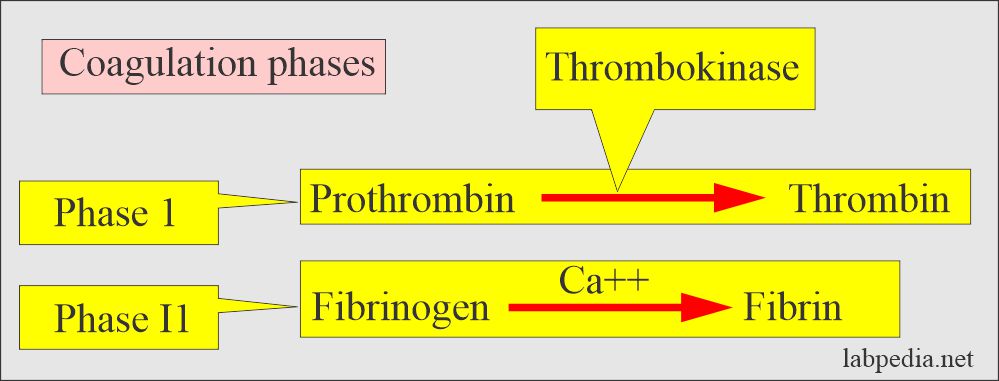
- The PTT is a one-stage test.
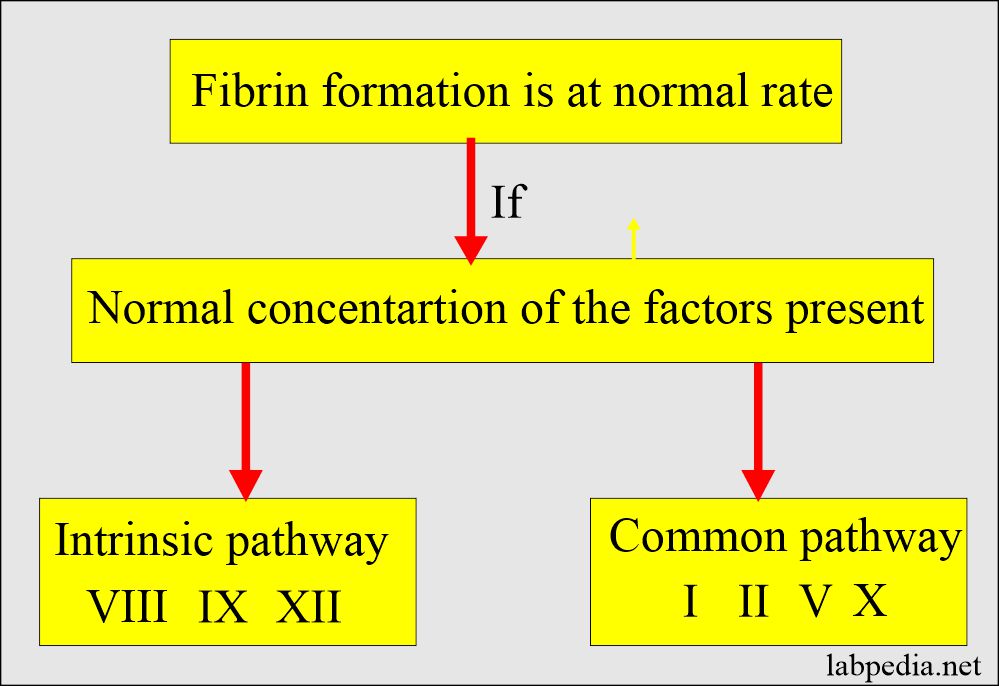
- PTT evaluates Factor I (Fibrinogen), Factor II (prothrombin), Factor V, VIII, XI, X, XI, and XII (5, 8, 9, 10, 12) http://Blood Coagulation Factors.
- The partial thromboplastin time (PTT) and Activated Partial thromboplastin time(APTT) are for the same function, but APTT is a more sensitive version of PTT.
Purpose of the test (Indications)
- This is used for the diagnosis of bleeding disorders.
- APTT may be used in the patient to check treatment for those who are taking Heparin or other blood-thinning medicines.
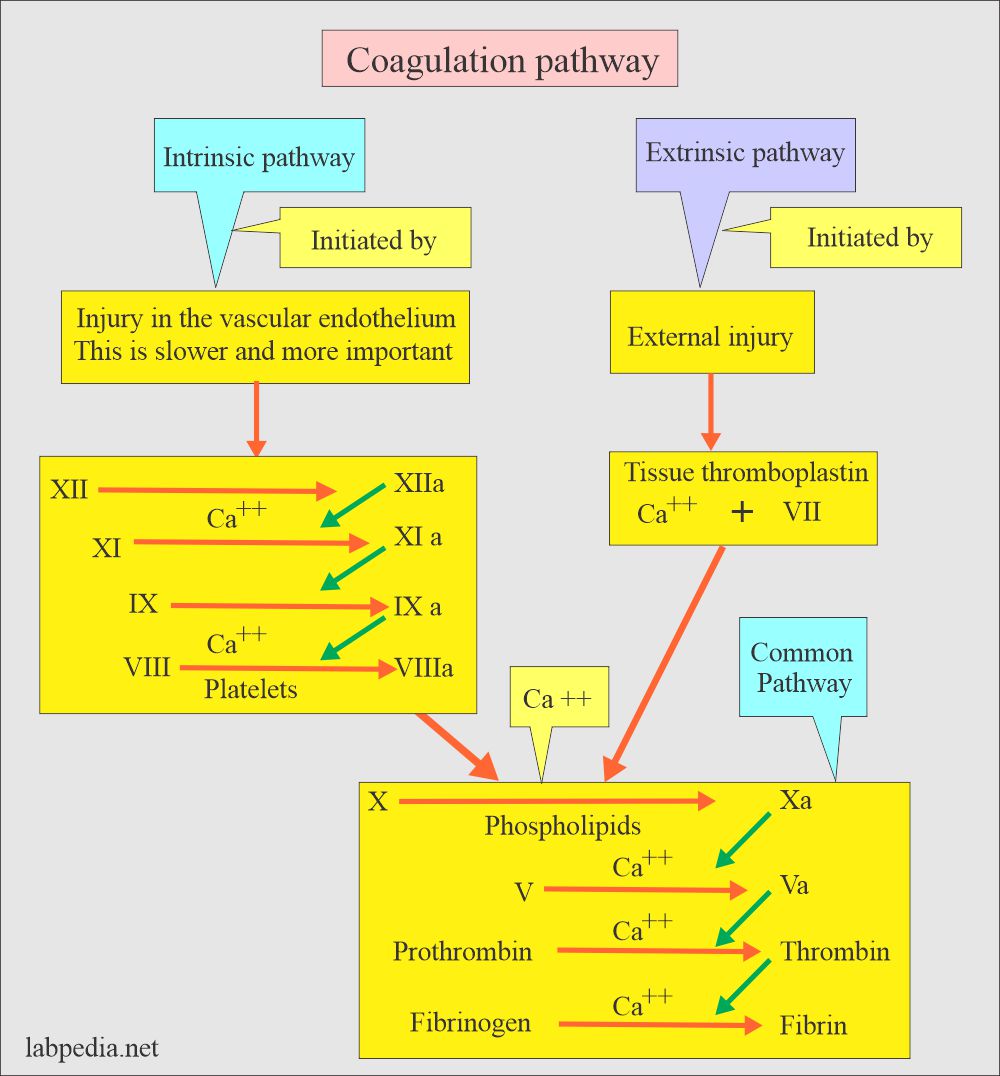
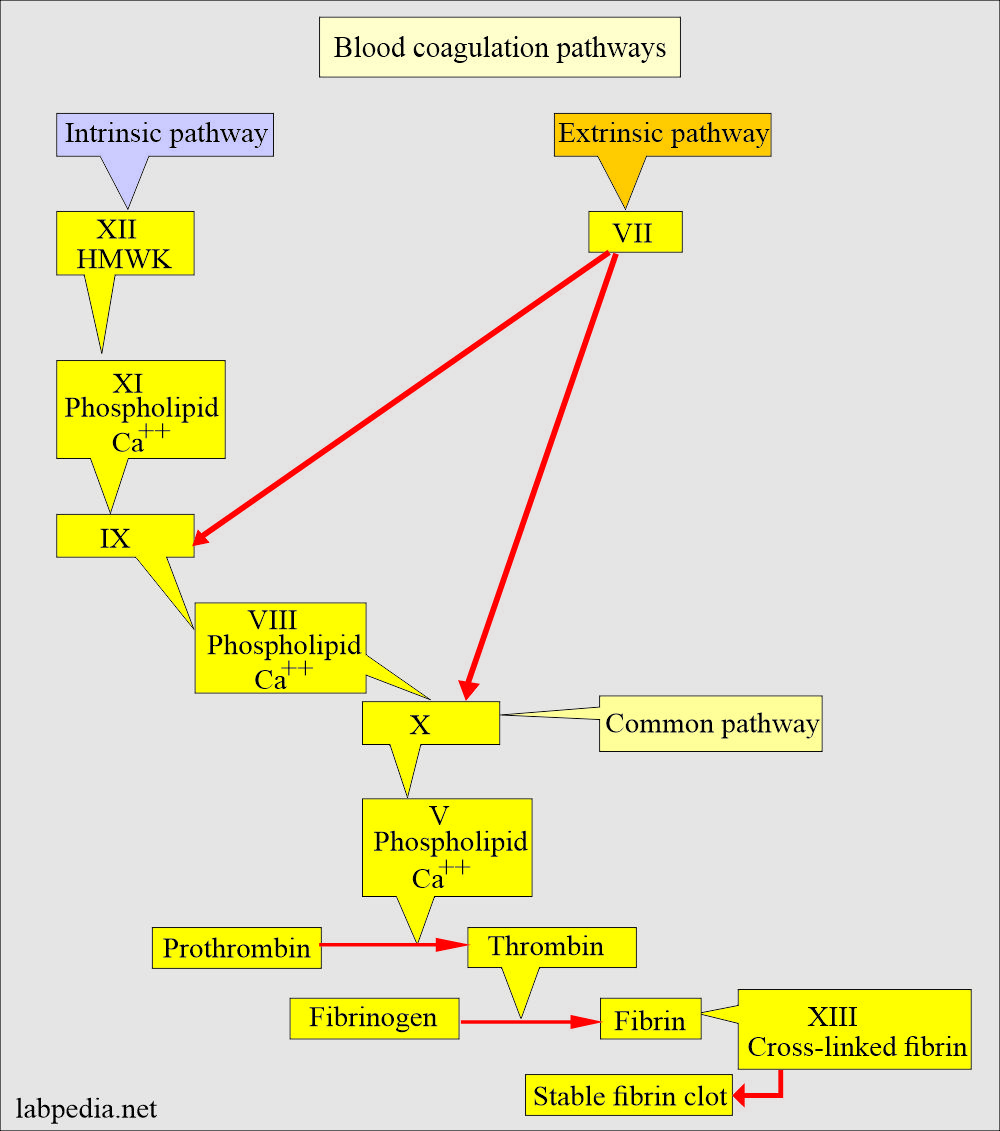
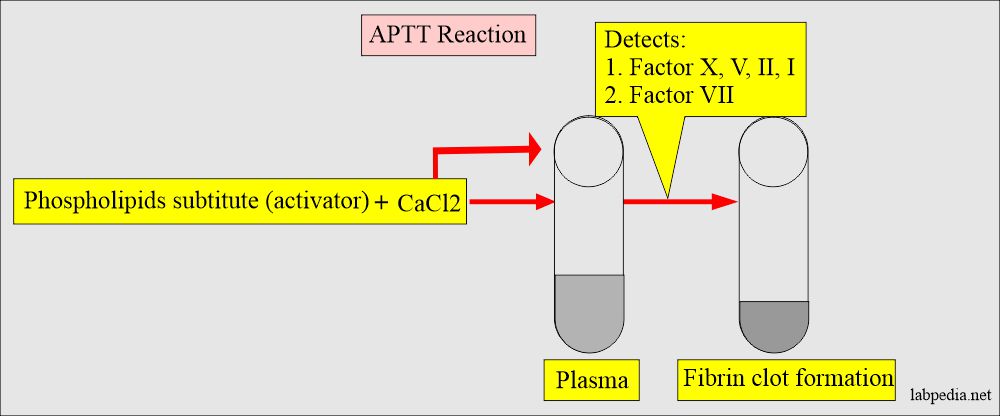
- APTT measures the intrinsic system and common pathways.
- APTT detects the functioning of factors XII, XI, X, IX, VII, V, II, and I (12, 11, 10, 9, 7, 5, 2, 1).
- For the diagnosis of Hemophilia and Christmas disease.
- APTT evaluates all coagulation factors except factors VII and XIII.
- PT is advised to monitor the extrinsic pathway.
- PT is also advised to monitor the warfarin therapy.
- PT also advised detecting factor VII deficiency.
Definition of PTT and APTT:
The PTT is a one-stage clotting test.
- It screens for coagulation disorders.
- It can detect the deficiency of the intrinsic thromboplastin system.
- It also detects any deficiency of the extrinsic coagulation pathway.
Activated Partial Thromboplastin (APTT):
- APTT is PTT but with the addition of an activator, which decreases the time for the clot formation.
- APTT is more sensitive than PTT.
The Activated Partial Thromboplastin (APTT) detects:
- Deficiency of the intrinsic pathway.
- Incubating anticoagulants.
- Monitor heparin therapy.
- It is part of the coagulation panel.
Summary of the Coagulation process:
- To understand the basis of the PTT and APTT, we have to have the concept of the process of coagulation.
- In 1905 – 1906, P. Morowitz published the theory of blood coagulation. This was unchanged for 40 years. He divided coagulation into two phases.
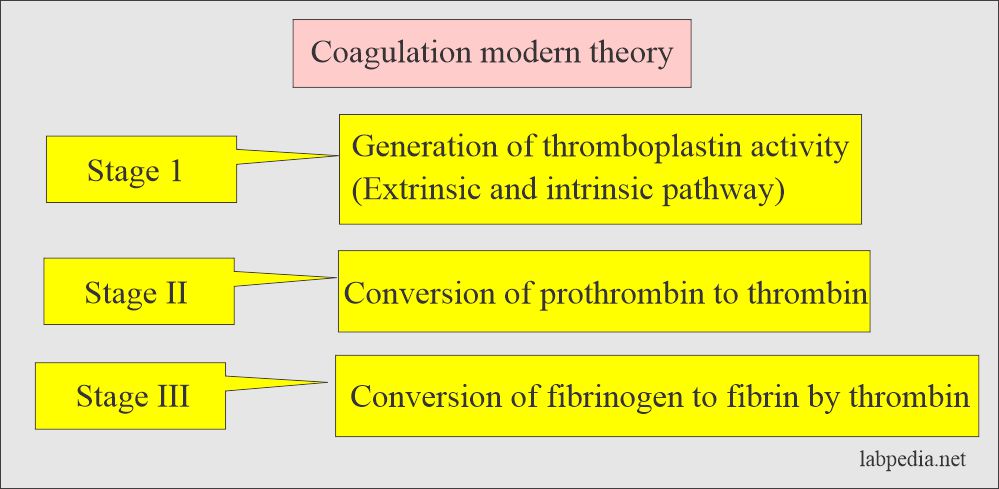
- Modern theory divided this process into three stages.
- The coagulation cascade is as follows:
Bleeding disorders have different presentations because of the etiology like:
- Platelet disorders give rise to:
- Petechiae.
- There is bleeding from the mucous membranes,
- Coagulation factors deficiency leads to:
- Deep hematomas.
- There is bleeding into the joints.
- There is hematuria.
- Bleeding disorders may be due to:
- Defects in the vascular system.
- Platelets disorders.
- Coagulation factors deficiency.
- Specific inhibitors.
- Fibrinolytic disorders.
Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT):
- APTT is very sensitive to coagulation factors deficiencies within the intrinsic pathway before the prothrombin to thrombin stage.
- Intrinsic pathway.
- Monitor heparin therapy.
APTT reagent contains:
- phospholipids substitute, activator.
- CaCl2 initiates fibrin clots.
- APTT test significance is:
- PTT is used to detect coagulation disorder, specifically detecting the deficiency of the intrinsic thromboplastin system and finding the defect in the extrinsic pathway.
- APTT detects the intrinsic pathway and common pathway deficiency (XII, XI, IX, VIII, X, II, and I).
- PT and APTT both abnormalities will tell us common pathways (X, V, II, and I).
- Advantages of APTT:
- APTT reproducibility is adequate where there is <10% variation.
- Its reaction is less (30 to 50 seconds).
- It is easy to perform.
- It can be used in automation.
- Disadvantages of APTT:
- Heparin above the required level causes APTT to be nonlinear and unreliable.
- Reagents from different companies produce different results, so it is not possible to compare the results.
- APTT is affected by warfarin.
Partial thromboplastin time (PTT):
- PTT was useful in detecting intrinsic factor abnormalities, but it was relatively insensitive to the effect of heparin.
- However, APTT was sensitive to the heparin effect.
- The APTT was very sensitive to coagulation factors deficiency within the intrinsic pathway before the prothrombin was converted to thrombin.
- Detect the Intrinsic thromboplastin system.
- Detects Common Pathway.
- Factor I (fibrinogen), Factor II (prothrombin), V, VIII, IX, X, XI, and XII.
- It is a one-stage clotting test.
- Detects extrinsic coagulation.
Prothrombin time (PT) is advised for:
- Prothrombin is a protein produced by the liver. Prothrombin production is dependent upon an adequate amount of vitamin K.
- It is one of the important screening tests for coagulation abnormality. It measures potential defects in stage II of coagulation, extrinsic pathway.
- To monitor anticoagulant therapy with Coumadin.
- It is advised for coagulation disorder.
- It may be part of liver functions.
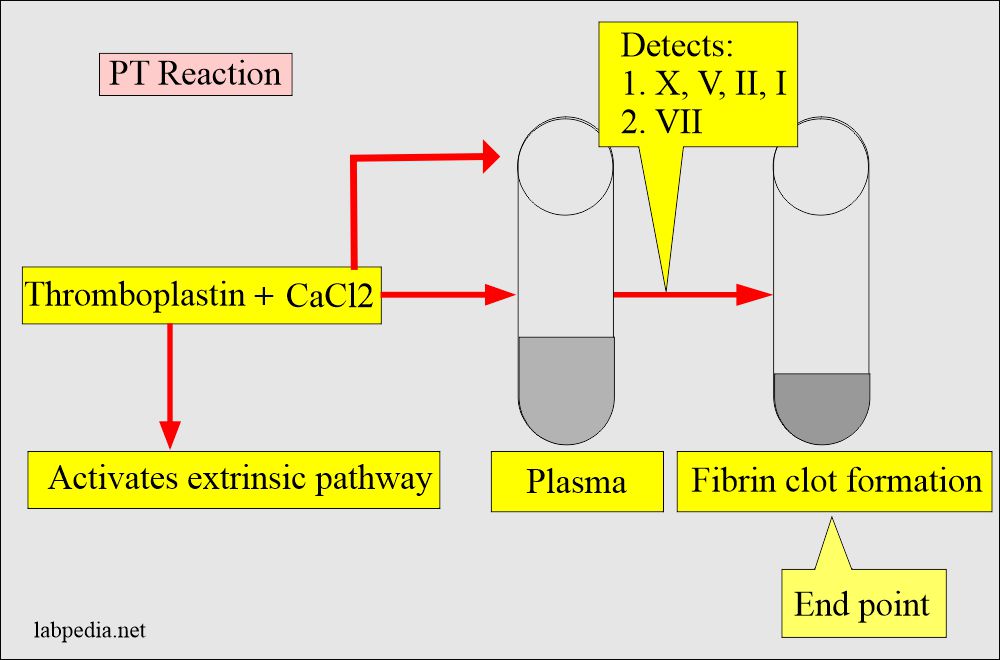
PT reagents contain:
- The plasma of the patient.
- Complete tissue thromboplastin (this will activate the extrinsic coagulation system).
- Phospholipids act as platelet substitutes.
- CaCl2.
PT test significance is:
- The PT test measures factors of extrinsic and common pathways (VII, X, V, II, and I).
- Factor VII is listed as the extrinsic system.
- Common pathways have the factors X, V, II, and I.
- PT test is ideal to detect early vitamin K deficiency.
- PT also monitors oral anticoagulant therapy.
- In case of severe fibrinogen deficiency, it produces an abnormal PT test.
- PT does not detect deficiency of factors XII, XI, IX, VIII, or XIII.
- In Hemophilia, PTT is prolonged.
- Coagulation factors are synthesized in the liver, so in liver diseases, they are decreased.
- PTT is prolonged in the abnormality of the deficiency of factors I, II, VII, XII, X, XI, and XII.
What is the normal value of PTT and APTT
Source 1
- Varies from lab to lab.
- Normal control is always run with the patient sample.
- In general, it is <35 seconds.
- PTT: 60 to 70 seconds.
- APTT: 30 to 40 seconds.
- If APTT is less than 50 seconds, then the therapeutic goal is not achieved, and the dose of Heparin may be increased.
- When APTT is greater than 100 seconds is risky for the patient, and there are chances of spontaneous bleeding.
- Panic value Usually, it is considered above 70 seconds.
- Heparin’s effect is immediate and short-lived as compared to warfarin.
Source 2
- APTT = 30 to 40 seconds
- PTT = 60 to 70 seconds
- PT = 11.0 to 13.0 seconds
- Possible critical values
- APTT = >70 seconds
- PTT = > 100 seconds
Abnormal High results of APTT are due to:
- All congenital deficiencies of Intrinsic system coagulation factors.
- Cirrhosis.
- Disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC ).
- Fibrin breakdown products.
- Factor XII deficiency.
- Hemophilia A and B.
- Hypofibrinogenemia.
- Malabsorption.
- Von Willebrand’s disease.
- Vit K deficiency.
- Fibrin breakdown products.
- Leukemia.
- Drugs.
- Heparin therapy.
- Warfarin therapy.
- In the case of streptokinase and urokinase.
- Circulating anticoagulant inhibitors. These may be specific for factor VIII.
- These are seen as anti-factor VIII and anti-factor IX in 5% to 10% of hemophilic patients.
- These are also in multiple plasma transfusions.
- Drug reactions.
- In the case of tuberculosis.
- In autoimmune diseases like SLE and rheumatoid arthritis.
Differential diagnoses of bleeding disorders (What is a normal PT aPTT level?):
| APTT | PT | Platelets count | Causes of bleeding disorders |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Test value for the layman:
- This test is advised in the case of patients with the treatment of Heparin or blood-thinning drugs.
- PTT and INR also have been done in patients with blood-thinning drugs (warfarin).
- Please, for more information, see PT and PTT.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What will be the coagulation profile in factor VII deficiency??
Question 2: What will be the coagulation profile in acute DIC?

[…] and APTT are prolonged in factor V […]