Clotting Time (C T)
Clotting Time (CT)
Sample for Clotting Time
- Clotting Time is done on a fresh blood sample, and the patient needs to be in the lab.
Indications for clotting time
- Clotting Time is advised to find a bleeding disorder, most likely due to clotting factors deficiency.
- To Diagnose hemophilia.
- Because of other tests, it has lost its importance. Clotting time was done by the Lee-white method, but it was cumbersome, insensitive, and nonreproducible.
Definition of clotting time (CT)
Clotting time (CT) is the time that is required to form the clot. The most commonly used test of clotting time is activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) and prothrombin time (PT).
Precautions for clotting time (CT)
- It does not diagnose mild coagulation disorders.
- Blood should be taken in the least traumatic manner.
- Must avoid premature activation of the clotting process to ensure an accurate result.
- Avoid hemolysis of the sample.
- It is essential to get the history of the patient:
- Note physical appearance, site, the severity of the disease, and frequency of the bleeding episodes.
- Get an accurate history of the drugs.
- A detailed patient and family history is needed.
- Also, consider other contributing or underlying diseases.
Draw-backs of clotting time (CT):
- This is not a reliable test for the screening of bleeding condtions.
- It is insensitive to detect mild conditions of bleeding.
- It will detect only the severe bleeding condtions.
- Normal clotting time does not rule out coagulation abnormalities.
- There are many variables in performing the test.
- Routine preoperative clotting and bleeding times have little value for routine preoperative screening for bleeding, e.g., in the tonsillectomy.
Pathophysiology of Clotting Time (CT)
- Lee-White Clotting time was used to monitor the heparin therapy, but now it is replaced by the APTT.
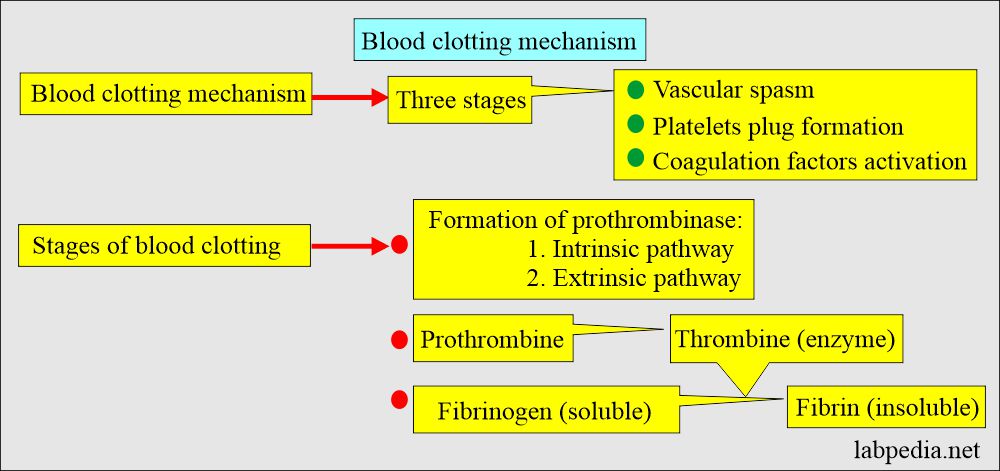
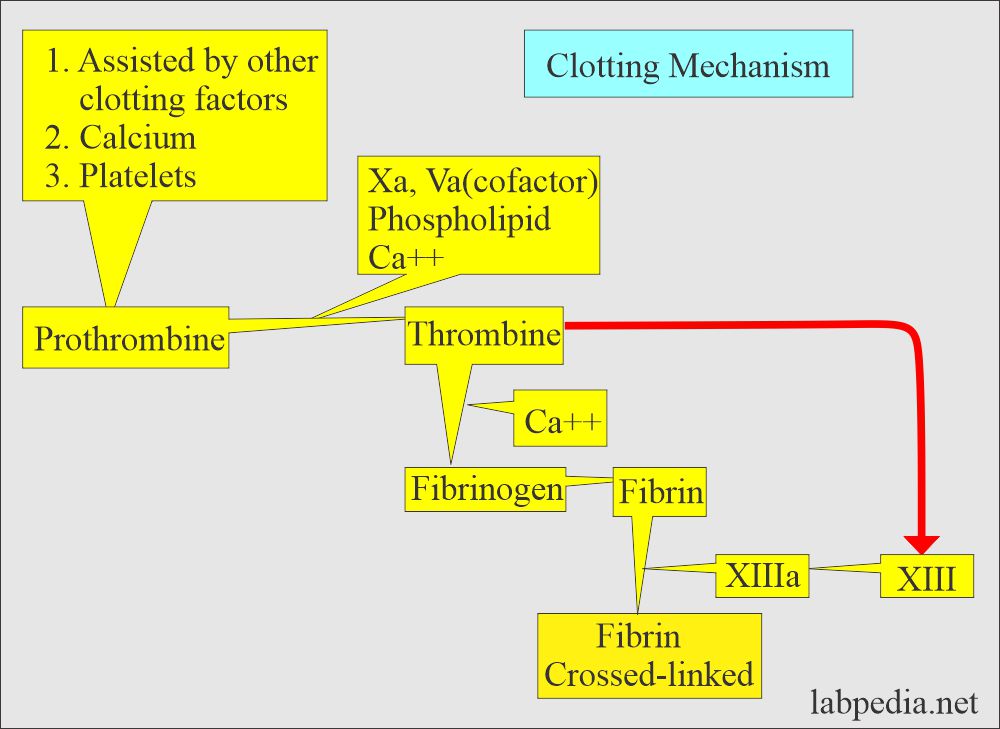
- For clot formation, prothrombin is converted into thrombin.
- Thrombin converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin.
- For this process, clotting factors are needed, along with calcium.
- Also assisted by the factors produced by platelets and damaged tissue.
- So, clotting time is the time needed for the generation of thrombin from the complex clotting system.
- When there is any deficiency in these factors, it will lead to prolonged clotting time.
- It is rarely used because of the variation; the clotting factors assays are more accurate.
The procedure of clotting time (CT)
- Two methods can estimate clotting time:
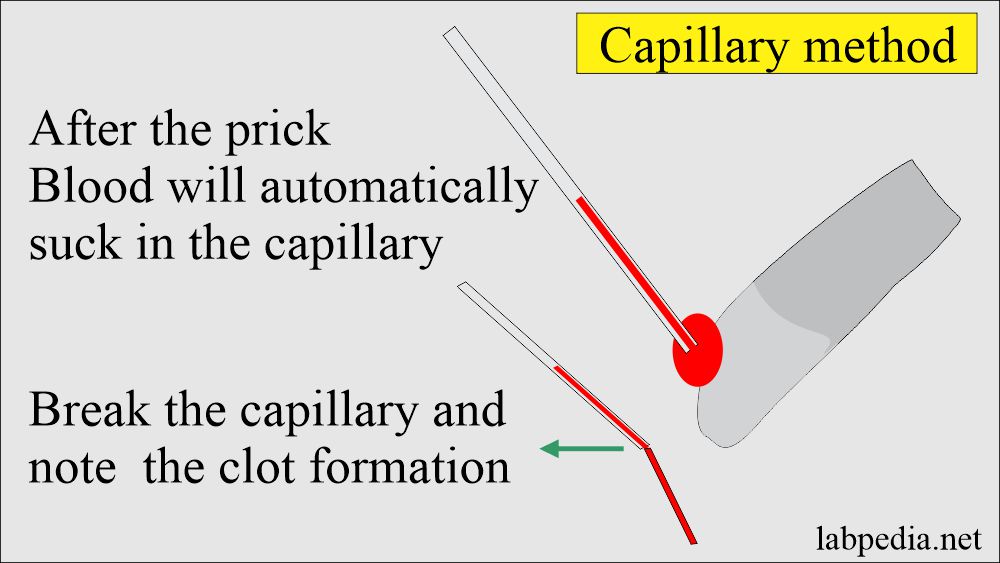
Capillary method of bleeding time.
- Prick the finger with the lancet.
- Hold the capillary over the blood, and the capillary will fill automatically.
- Now, after regular intervals, break the capillary.
- When a clot starts forming, that is the endpoint and clotting time.
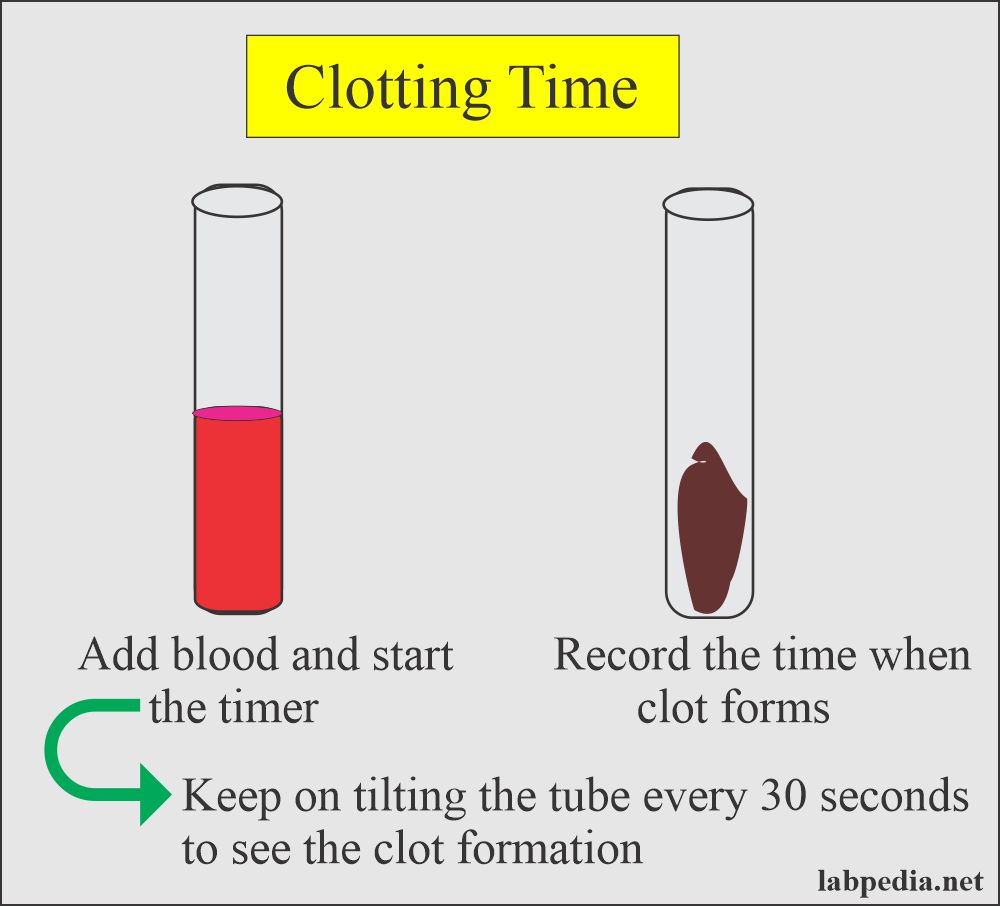
Test tube method of clotting time.
- Perform this test at 37 ° C.
- Take 4 ml of blood for the tube method and start the time.
- Note the time when there is the first appearance of the clot formation.
- This test can be done in multiple tubes to be more accurate.
Lee and White’s method of clotting time:
- Two siliconized tubes with a 10 cm external bore are taken.
- These tubes are prewarmed at 37 °C in a water bath.
- Take the blood sample, mostly taken from the antecubital vein.
- 2 to 2.5 mL of the blood is taken, and 1 mL of the blood is in each test tube.
- Start two stopwatches as you see the blood in the syringe.
- Keep the blood in the water bath and check for clotting by tilting each tube at 30 to 60 seconds intervals.
- Tilt the tube to greater than 90 degrees.
- Stop the stopwatch as you see the clot in the tube.
- Clotting time is expressed as the mean of the two stopwatches.
Disadvantages of clotting time:
- This test is insensitive, so it lost its value.
- There are many variables in the technique of performing the test.
- This fails to detect the moderate deficiency of coagulation factors.
- This test is only prolonged in severe deficiency.
- Normal clotting time is despite prolonged bleeding time seen in thrombocytopenia.
- This may be normal in patients taking anticoagulant therapy.
- This is usually normal when the intrinsic and common pathways are present in an amount not exceeding 1% of the normal plasma level.
- Because of all the above reasons, this test has lost its significance.
Normal clotting time (CT)
- The expected range is 4 to 10 minutes.
- The glass tube method clotting time is 5 to 15 minutes.
- The siliconized tube’s clotting time is 19 to 60 minutes (reference: Interpretation of diagnostic test by Jacques Wallach M.D.)
Causes of prolonged clotting time are:
- Coagulation factors deficiencies may be:
- Congenital.
- Acquired.
- Severe deficiency of any known plasma clotting factors except XIII (fibrin-stabilizing factor) and VII.
- Drugs like heparin and thrombin inhibitors.
- Marked hyperheparinemia.
- Afibrinogenemia.
Coagulation time normal seen in:
- Thrombocytopenia.
- Deficiency factor VII.
- Mild coagulation defects due to any reason.
- Von Willebrand syndrome.
Questions and answers:
Q1: Why is clotting time not advised nowadays to control heparin therapy?
Q2: What is the main drawback of clotting time(CT)?

Nice understanding,super,fabulous. Thank you sooo much😊
Thanks a lot.
Nice,clear cut explanation
Thanks.
information provided at one point, instead of searching at many places. highly appreciated.
Thanks.
Write three conditions when clotting time is not within normal range.
Coagulation time normal seen in:
Thrombocytopenia.
Deficiency factor VII.
Mild coagulation defects due to any reason.
Von Willebrand syndrome.