Blood banking:- part 3 – Blood Donation Procedure, Blood Components and Their Indications
Blood Donation Procedure
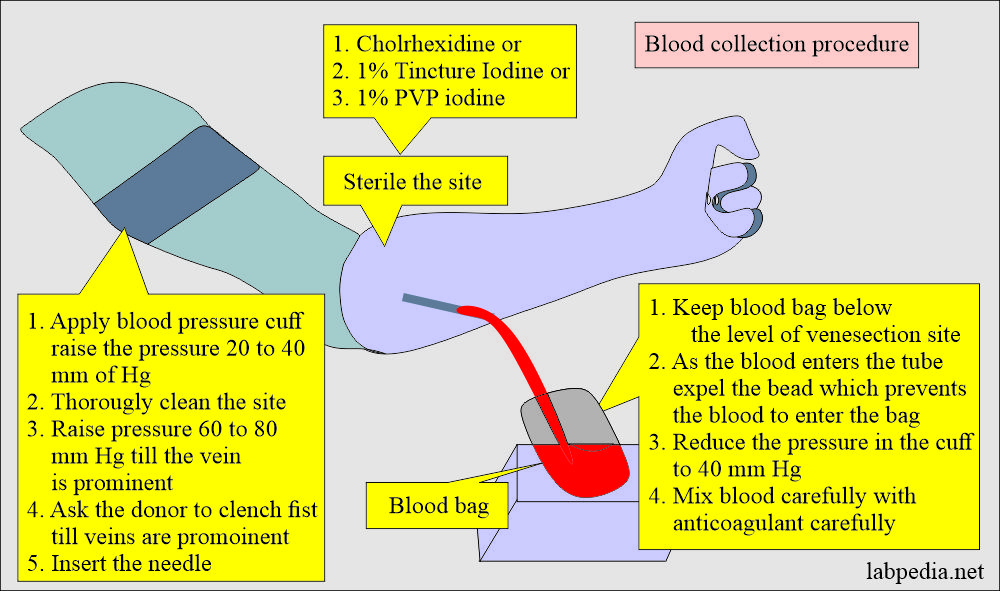
Procedure to collect blood from the donor.
Donor assurance:
- Make the donor comfortable and assure him about safety.
- Give some time to the donor to acclimatize to the atmosphere.
- Now apply the blood pressure cuff above the elbow and give a 20 to 40 mmHg pressure.
Cleaning the site:
- Now clean the site of venipuncture thoroughly.
- Can use chlorhexidine, 1% tincture iodine, or 1% PVP iodine.
Procedure for the collection of blood bag:
- Keep the blood pack below the level of the donor.
- Keep the pack in balance.
- Now increase the blood pressure to 60 to 80 mmHg till the vein is prominent. Ask him to clench their fist.
- Insert the needle into the vein; as blood comes out, remove the bead, preventing blood from entering the pack.
- Now reduce the pressure in the cuff.
- Carefully and slowly mix the blood with the anticoagulants.
- When blood donation is complete, reduce the pressure to 0 in the cuff.
- Clamp the blood pack (bag).
- Take out the needle and apply pressure on the venipuncture site.
Post-blood donation precautions:
- Please don’t allow the donor to sit immediately; ask him to lie down for at least 5 to 10 minutes.
- Sometimes the donor gets headaches, nausea, and dizziness.
- Donor blood pressure may become low.
- Label the pack and make at least 4 to 5 tubing segments for further testing.
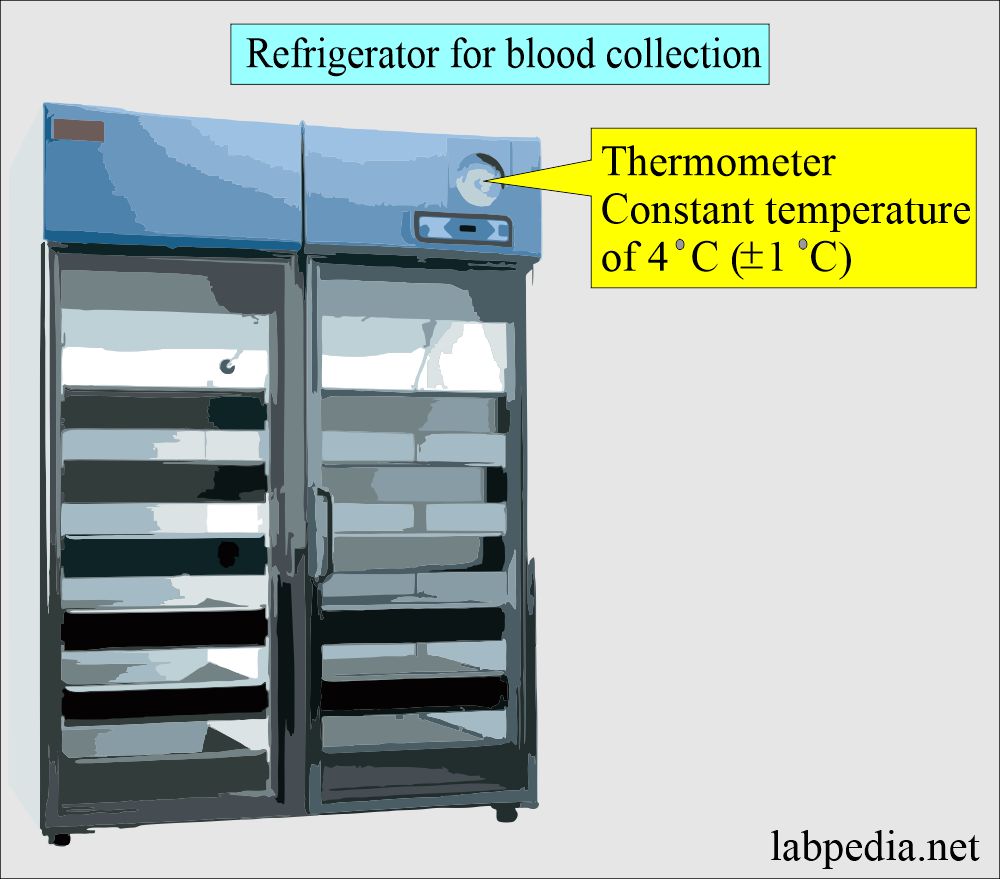
- Allow the blood to cool down before refrigeration is done. This period should not exceed more than one hour.
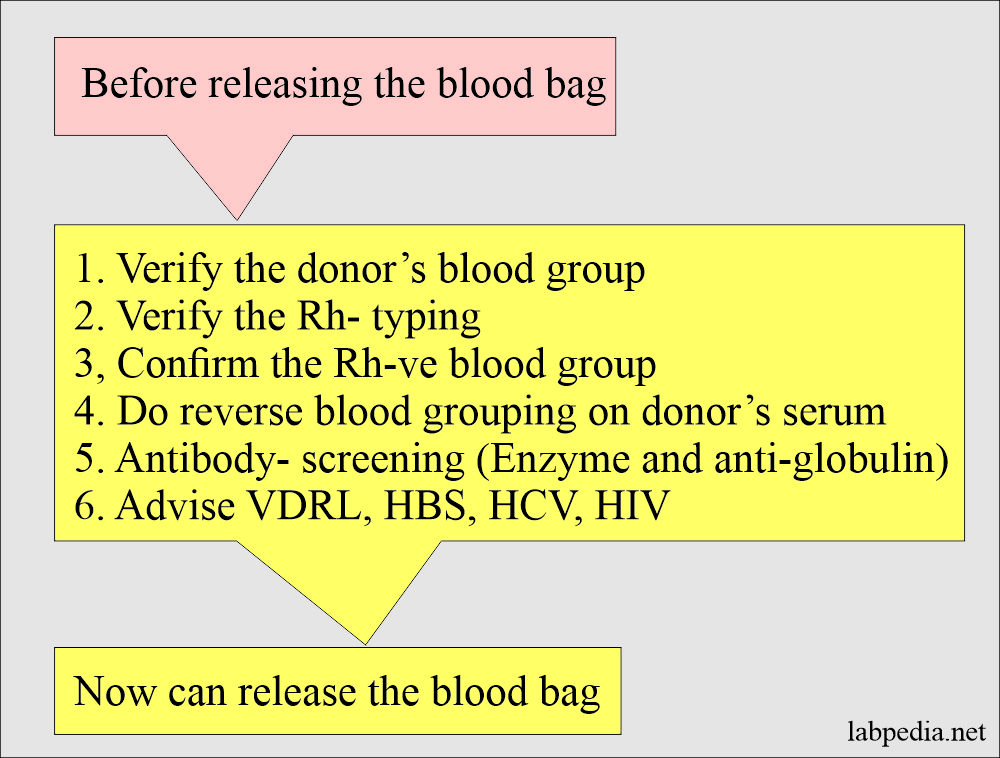
Before the donated blood is released, the following tests are mandatory:
- The following tests are done on the donor blood and the serum.
- The donor’s blood grouping ABO is verified.
- Verify the Rh typing. Rh-negative blood is reconfirmed.
- All Rh°(D) negative blood bags are confirmed.
- Now test for anti-CD and anti-DE.
- Perform Du tests on all r’ and r” blood bags.
- Reverse blood ABO grouping is done on the donor serum.
- Antibody screening is done by the enzyme and antiglobulin method.
- Perform the VDRL, HBS, HCV, and HIV.
- The donor’s blood grouping ABO is verified.
- After doing all these tests, you can now release the blood pack for donation to the patient.
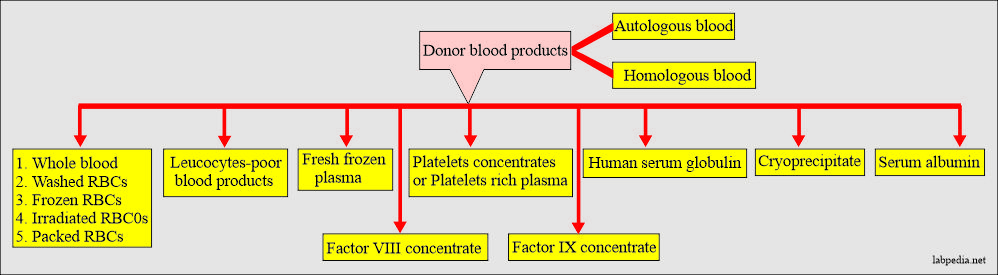
Blood components most common in use are:
- Whole blood.
- Fresh frozen plasma.
- Packed red blood cells.
- Frozen red blood cells.
- Human serum albumin.
- Human immune serum globulin.
- Antihemophilic factor concentrate (cryoprecipitate).
- Factor IX concentrate.
- Platelets concentrate or platelets-rich plasma.
- White blood cell poor blood (where the white cells are removed).
Blood donation criteria for the donor:
- Donors can donate their blood at intervals of 8 weeks.
- Healthy individuals can donate blood every 5 to 7 days for a limited period, around 1 to 2 months.
- In the above donor, an iron supplement is needed.
Autotransfusion (autologous transfusion):
- This is the blood collection and subsequent transfusion of the patient’s own blood.
- Can donate blood every 5 to 7 days before elective surgery.
- Advantages: This will prevent all transfusion reaction problems and transfusion-related infections and avoid religious beliefs.
Packed red blood cells:
- Packed RBCs consist of refrigerated stored RBCs without three-fourths plasma. The majority of plasma is removed.
- Advantages: This will avoid overloading and pulmonary edema.
-
- This is especially useful in patients with anemia where plasma is not needed.
- It is used in pure RBC deficiency.
- In case antibodies are present in the plasma of the donor.
- This also prevents other problems of the stored blood, like raised levels of potassium or ammonium level.
Washed red blood cells:
- These packed red blood cells were washed several times with saline, followed by centrifugation.
- This will remove >90% of the white blood cells and also removes platelets and plasma.
- 10% to 20% of RBCs are also lost in washing.
- Indications: There are very few indications for washed red blood cells.
- The cell washing will remove donor antibodies and is useful in IgA immune reactions.
- Washed RBCs are used for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
- Washed RBCs should be used within 24 hours after preparation (washing).
Fresh Frozen Plasma:
- Fresh frozen plasma is prepared from the fresh whole blood within 6 hours after collection.
- Fresh frozen plasma is separated from the RBCs after centrifugation at 4 °C temperature and frozen immediately.
- Before giving it to the patients, it must be thawed at 37 °C for at least 20 minutes or until the thawing is complete.
- Don’t delay after thawing to transfuse into the patient because factors V and VIII deteriorate quickly.
- An agitator machine and a specially designed microwave may accelerate the thawing process.
- Used for: Fresh frozen plasma is the choice treatment for coagulation factor deficiency such as factor VIII (Hemophilia A), von Willebrand’s disease, or fibrinogen.
Cryoprecipitate:
- Cryoprecipitate is prepared from fresh frozen plasma; the material does not become totally liquid when fresh frozen plasma is slowly thawed, and the major part has liquefied.
- Advantage: The major advantage over fresh frozen plasma is the reduced volume of transfused fluid.
- Each unit contains around 150 mg of fibrinogen.
- Cryoprecipitate is good for treating von Willebrand’s disease and Hemophilia A.
- Contents: Cryoprecipitate contains 50% of the factor around 50% factor VIII and von Willebrand factor activity.
- Fibrinogen and factor XIII are around 20% to 40%.
Albumin:
- 5% albumin instead of plasma can restore colloid oncotic pressure.
- In a normal person, 500 ml of blood contains 11 grams of albumin. 70% of the albumin is synthesized in the liver.
- Indications: To restore the colloid oncotic pressure.
- This is used in hypovolemic shock due to massive acute blood loss or extensive burns.
- It is not given in hypoalbuminemia due to chronic liver disease or loss through the kidneys or gastrointestinal tract.
Platelets:
- Platelets are supplied in units that contain platelets equivalent to one point of blood, roughly 5.5 x 1010.
- Can get multiple units from a single donor using platelet apheresis.
- Platelets are stored at room temperature.
- A single unit of the platelets will raise the platelet count to 7,000 to 11,000/cmm.
- Platelets should be transfused as soon as possible after collection to get the maximum functions of the platelets.
- Indications: Platelet transfusion may be prophylactic or therapeutic.
- Therapeutic transfusion occurs with severe thrombocytopenia <50,000/cmm and severe acute bleeding.
- When there is no bleeding but thrombocytopenia, we can give platelets transfusion prophylactically.
- Bleeding time may be the guide for the platelets transfusion.
- It is not indicated in idiopathic thrombocytopenia (ITP) unless the patient is actively bleeding.
- No use of platelets transfusion in case of drug-induced thrombocytopenia unless the drug is stopped.
Blood components and their indications:
| Components | Composition | Indications |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Granulocytes are collected by apheresis. |
|
|
platelets collected by apheresis, and volume is 200 to 300 mL |
|
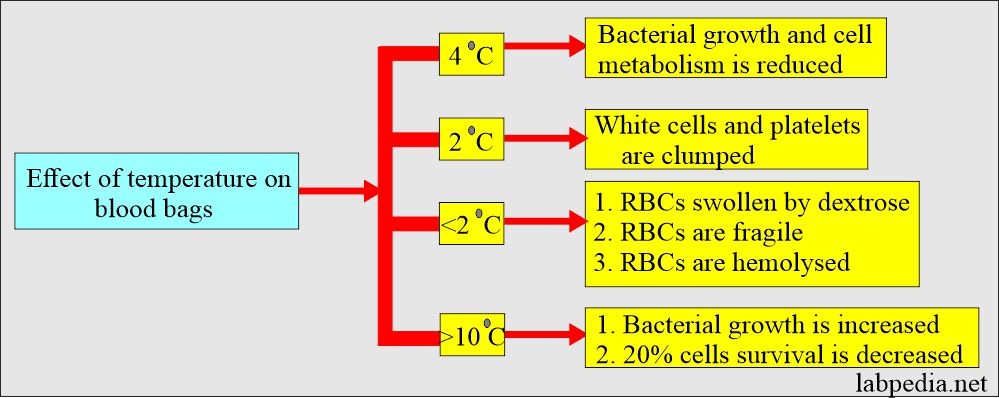
Effects of temperature on the storage of the blood:
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the purpose of albumin transfusion?
Question 2: How much cryoprecipitate one unit contains fibrinogen?